摘要:在数据库查询中,往往会需要查询多个表的数据,比如查询会员信息同时查询关于这个会员的订单信息,如果分语句查询的话,效率会很低,就需要用到join关键字来连表查询了。
Join并行
Join并行1. 多表join介绍2. 多表Join的方式不使用Join buffer使用Join buffer3. Join执行流程(老执行器)
1. 多表join介绍
JOIN子句用于根据两个或多个表之间的相关列来组合它们。 例如:
Orders:

Customers:

SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderDate
FROM Orders
INNER JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID=Customers.CustomerID;

2. 多表Join的方式
Hash join使用新执行器实现,在这里不做讨论
MySQL支持的都是Nested-Loop Join,以及它的变种。
不使用Join buffer
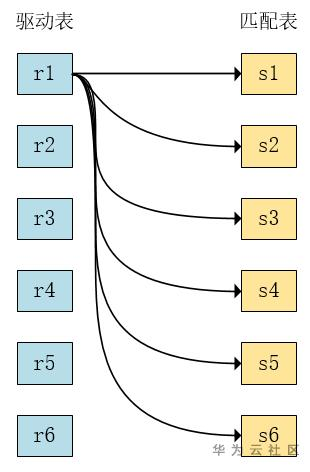
a) Simple Nested-Loop
对r表的每一行,完整扫描s表,根据r[i]-s[i]组成的行去判断是否满足条件,并返回满足条件的结果给客户端。
mysql> show create table t1; +-------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Table | Create Table | +-------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | t1 | CREATE TABLE `t1` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci | +-------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> show create table t3; +-------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Table | Create Table | +-------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | t3 | CREATE TABLE `t3` ( `id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci | +-------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select /*+ NO_BNL() */ * from t1, t3 where t1.id = t3.id; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100.00 | NULL | | 1 | SIMPLE | t3 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 50.00 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ 2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
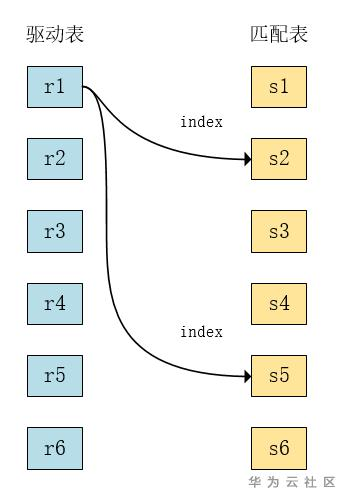
b) Index Nested-Loop
对r表的每一行,先根据连接条件去查询s表索引,然后回表查到匹配的数据,并返回满足条件的结果给客户端。
mysql> show create table t2; +-------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Table | Create Table | +-------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | t2 | CREATE TABLE `t2` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, KEY `index1` (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci | +-------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from t1, t2 where t1.id = t2.id; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100.00 | NULL | | 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | ref | index1 | index1 | 4 | test.t1.id | 1 | 100.00 | Using index | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+ 2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
使用Join buffer
a) Block Nested Loop
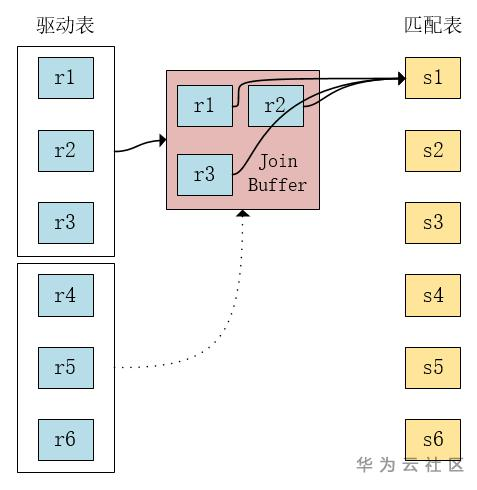
从r表读取一部分数据到join cache中,当r表数据读完或者join cache满后,做join操作。
JOIN_CACHE_BNL::join_matching_records(){ do { //读取s表的每一行 qep_tab->table()->file->position(qep_tab->table()->record[0]); //针对s的每一行,遍历join buffer for(each record in join buffer) { get_record(); rc = generate_full_extensions(get_curr_rec()); //如果不符合条件,直接返回 if (rc != NESTED_LOOP_OK) return rc; } } while(!(error = iterator->Read())) }
mysql> explain select * from t1, t3 where t1.id = t3.id; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100.00 | NULL | | 1 | SIMPLE | t3 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 50.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+ 2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
b) Batched Key Access
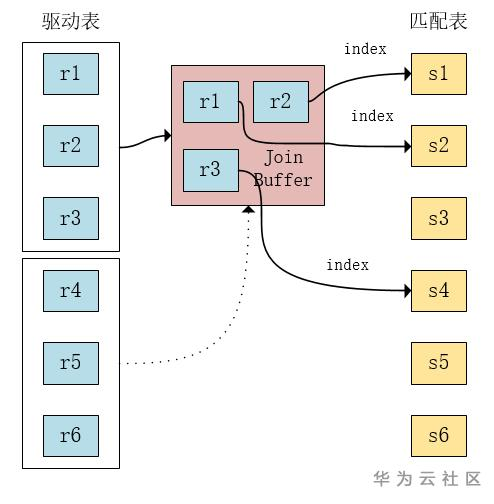
从r表读取一部分数据到join cache中,s表中记录r表被连接的列的值作为索引,查询所有符合条件的索引,然后将这些符合条件的索引排序,然后统一回表查询记录。
其中,对于每一个cached record,都会有一个key,通过这个key去s表扫描所需的数据。
dsmrr_fill_buffer(){ while((rowids_buf_cur < rowids_buf_end) && !(res = h2->handler::multi_range_read_next(&range_info))){ //下压的index条件 if (h2->mrr_funcs.skip_index_tuple && h2->mrr_funcs.skip_index_tuple(h2->mrr_iter, curr_range->ptr)) continue; memcpy(rowids_buf_cur, h2->ref, h2->ref_length); } varlen_sort( rowids_buf, rowids_buf_cur, elem_size, [this](const uchar *a, const uchar *b) { return h->cmp_ref(a, b) < 0; }); } dsmrr_next(){ do{ if (rowids_buf_cur == rowids_buf_last) { dsmrr_fill_buffer(); } // first match if (h2->mrr_funcs.skip_record && h2->mrr_funcs.skip_record(h2->mrr_iter, (char *)cur_range_info, rowid)) continue; res = h->ha_rnd_pos(table->record[0], rowid); break; } while(true); } JOIN_CACHE_BKA::join_matching_records(){ while (!(error = file->ha_multi_range_read_next((char **)&rec_ptr))) { get_record_by_pos(rec_ptr); rc = generate_full_extensions(rec_ptr); if (rc != NESTED_LOOP_OK) return rc; } }
mysql> show create table t1; +-------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Table | Create Table | +-------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | t1 | CREATE TABLE `t1` ( `f1` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `f2` int(11) DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci | +-------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> show create table t2; +-------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Table | Create Table | +-------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | t2 | CREATE TABLE `t2` ( `f1` int(11) NOT NULL, `f2` int(11) NOT NULL, `f3` char(200) DEFAULT NULL, KEY `f1` (`f1`,`f2`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci | +-------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain SELECT /*+ BKA() */ t2.f1, t2.f2, t2.f3 FROM t1,t2 WHERE t1.f1=t2.f1 AND t2.f2 BETWEEN t1.f1 and t1.f2 and t2.f2 + 1 >= t1.f1 + 1; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+-------------+------+----------+---------------------------------------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+-------------+------+----------+---------------------------------------------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | Using where | | 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | ref | f1 | f1 | 4 | test1.t1.f1 | 7 | 11.11 | Using index condition; Using join buffer (Batched Key Access) | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+-------------+------+----------+---------------------------------------------------------------+ 2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
c) Batched Key Access(unique)
与Batched Key Access不同的是,r中的列是s的唯一索引,在r记录写入join cache的时候,会记录一个key的hash table,仅针对不同的key去s表中查询。(疑问,为什么只有unique的时候才能用这种方式?不是unique的话,s表中可能会扫描出多条数据,也可以用这种方式去处理,减少s表的重复扫描)。 JOIN_CACHE_BKA_UNIQUE::join_matching_records(){ while (!(error = file->ha_multi_range_read_next((char **)&key_chain_ptr))) { do(each record in chain){ get_record_by_pos(rec_ptr); rc = generate_full_extensions(rec_ptr); if (rc != NESTED_LOOP_OK) return rc; } } }
与Batched Key Access不同的是,r中的列是s的唯一索引,在r记录写入join cache的时候,会记录一个key的hash table,仅针对不同的key去s表中查询。(疑问,为什么只有unique的时候才能用这种方式?不是unique的话,s表中可能会扫描出多条数据,也可以用这种方式去处理,减少s表的重复扫描)。 JOIN_CACHE_BKA_UNIQUE::join_matching_records(){ while (!(error = file->ha_multi_range_read_next((char **)&key_chain_ptr))) { do(each record in chain){ get_record_by_pos(rec_ptr); rc = generate_full_extensions(rec_ptr); if (rc != NESTED_LOOP_OK) return rc; } } }
3. Join执行流程(老执行器)
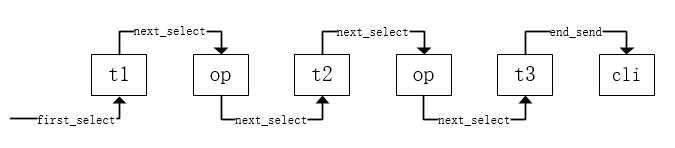
sub_select <--------------------------------------------+ | -> iterator::read() // 读一行数据 | | -> evaluate_join_record() //检查这行数据是否符合条件 | | -> next_select() ---+ | | | sub_select_op <--------+ | | -> op->put_record() // 前表数据写入join cache | | -> put_record_in_cache() | | -> join->record() | | -> join_matching_records() | | -> (qep_tab->next_select)(join, qep_tab + 1, 0) // 继续调用next_select | -> end_send()