一、查询缓存
查询缓存的使用,主要是为了提高查询访问速度。将用户对同一数据的重复查询过程简单化,不在每次均从数据库中查询获取结果数据,从而提高访问速度。
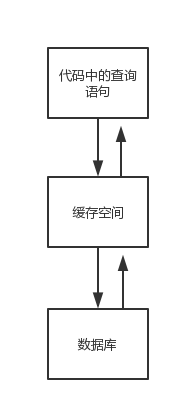
MyBatis的查询缓存机制,根据缓存区的作用域与生命周期,可划分为两种:一级缓存和二级缓存。
MyBatis查询缓存的作用域是根据映射文件mapper的namespace划分的,相同namespace的mapper查询数据存放在同一个缓存区域。不同的namespace下的数据互不干扰。无论是一级缓存还是二级缓存,都是按照namespace进行分别存放的。
但一、二级缓存的不同之处在于,SqlSession一旦关闭,则SQLSession中的数据将不存在,即一级缓存就不存在,而二级缓存的生命周期会与整个应用同步,与SQLSession是否关闭无关。
简单的说,一级缓存是在同一线程(同一SQLSession)间共享数据,而二级缓存是在不同线程间共享数据。
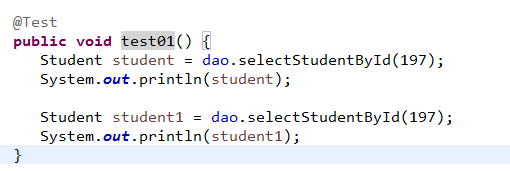
二、一级缓存的证明

三、从缓存中查找数据的依据

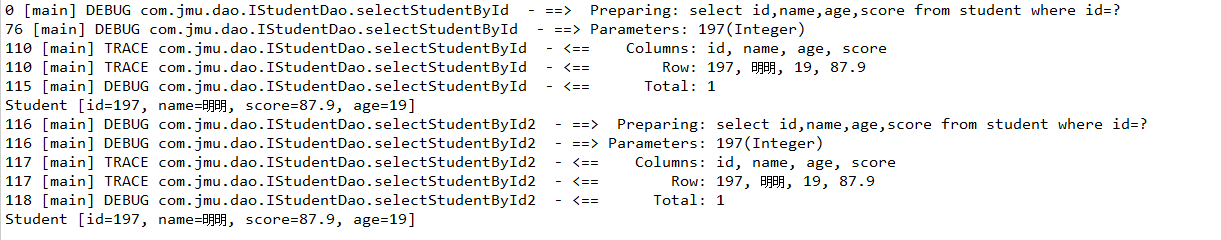
MyBatis的查询依据是:Sql的id+SQL语句。
Hibernate的查依据是:查询结果对象的id。
缓存的底层实现是一个Map,Map的value是查询结果。Map的key,即查询依据,使用的ORM架构不同,查询依据就不不同。
ORM:
ORM(Object Relational Mapping)框架采用元数据来描述对象一关系映射细节,元数据一般采用XML格式,并且存放在专门的对象一映射文件中。
只要提供了持久化类与表的映射关系,ORM框架在运行时就能参照映射文件的信息,把对象持久化到数据库中。
当前ORM框架主要有五种:Hibernate(Nhibernate),iBATIS,mybatis,EclipseLink,JFinal。
元数据:是描述其它数据的数据 (data about other data)
四、增删改对一级缓存的影响
1 @Test 2 public void test03() { 3 Student student = dao.selectStudentById(197); 4 System.out.println(student); 5 //增删改操作都会清空一级缓存 6 dao.insertStudent(new Student("阿古斯",26,96.5)); 7 Student student1 = dao.selectStudentById(197); 8 System.out.println(student1); 9 }
输出:
0 [main] DEBUG com.jmu.dao.IStudentDao.selectStudentById - ==> Preparing: select id,name,age,score from student where id=? 75 [main] DEBUG com.jmu.dao.IStudentDao.selectStudentById - ==> Parameters: 197(Integer) 116 [main] TRACE com.jmu.dao.IStudentDao.selectStudentById - <== Columns: id, name, age, score 116 [main] TRACE com.jmu.dao.IStudentDao.selectStudentById - <== Row: 197, 明明, 19, 87.9 120 [main] DEBUG com.jmu.dao.IStudentDao.selectStudentById - <== Total: 1 Student [id=197, name=明明, score=87.9, age=19] 121 [main] DEBUG com.jmu.dao.IStudentDao.insertStudent - ==> Preparing: insert into student(name,age,score) values(?,?,?) 122 [main] DEBUG com.jmu.dao.IStudentDao.insertStudent - ==> Parameters: 阿古斯(String), 26(Integer), 96.5(Double) 123 [main] DEBUG com.jmu.dao.IStudentDao.insertStudent - <== Updates: 1 124 [main] DEBUG com.jmu.dao.IStudentDao.selectStudentById - ==> Preparing: select id,name,age,score from student where id=? 124 [main] DEBUG com.jmu.dao.IStudentDao.selectStudentById - ==> Parameters: 197(Integer) 124 [main] TRACE com.jmu.dao.IStudentDao.selectStudentById - <== Columns: id, name, age, score 125 [main] TRACE com.jmu.dao.IStudentDao.selectStudentById - <== Row: 197, 明明, 19, 87.9 125 [main] DEBUG com.jmu.dao.IStudentDao.selectStudentById - <== Total: 1 Student [id=197, name=明明, score=87.9, age=19]
结论:增删改操作都会清空一级缓存,无论是否提交
五、内置二级缓存
(1)二级缓存的开启
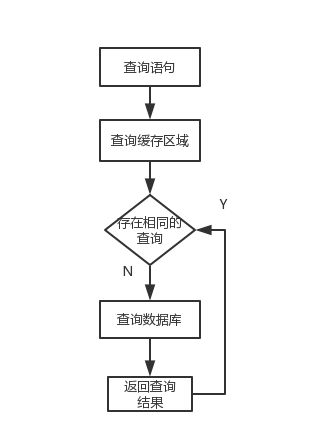
MyBatis的使用二级缓存的目的是为了防止同一查询(相同Sql id、相同的Sql语句)的反复执行。
Hibernate中的缓存就是为了在多个查询间共享查询结果(所有查询中只要查询结果中存在改对象的,就直接从缓存中读取)
MyBatis内置的二级缓存为org.apache.ibatis.cache.Impl.PerpetualCache.
首先,证明二级缓存的存在。
因为SqlSession一旦关闭,一级缓存就不存在,而二级缓存的生命周期会与整个应用同步,与SQLSession是否关闭无关。
sqlSession.close();
开启内置的二级缓存步骤:
- 对实体进行序列化

- 在映射文件中添加<cache/>标签;
缓存命中率:
【DEBUG】 Cache Hit Ratio:0.5
(2)增删改对二级缓存的影响
1 public void test01() { 2 sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); 3 dao = sqlSession.getMapper(IStudentDao.class); 4 Student student = dao.selectStudentById(197); 5 System.out.println(student); 6 7 sqlSession.close(); 8 9 sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); 10 dao = sqlSession.getMapper(IStudentDao.class); 11 12 dao.insertStudent(new Student("",0,0)); 13 14 Student student1 = dao.selectStudentById(197); 15 System.out.println(student1); 16 }
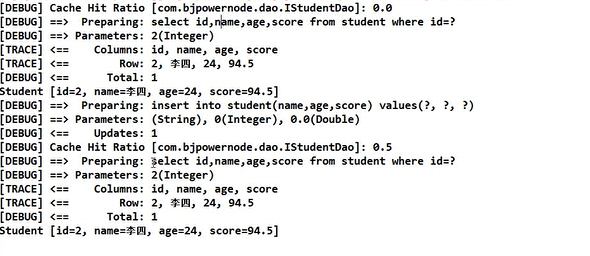
上面的例子说明:
- 增删改同样会清空二级缓存;
- 对于二级缓存的清空,实际上是对所查找key对应的value置为null,而非将<key,value>对,即Entry对象删除
- 从DB中重新进行select查询的条件是:A、缓存中根本不存在这个key;B、缓存中存在改key所对应的Entry对象,但其value为null
(3)二级缓存的配置
- size:二级缓存中可以存放的最多对象个数,默认为1024个。(实际上就是HashMap的长度,可以放多少Entry对象)
- eviction:逐出策略。当二级缓存中的对象达到最大值时,就需要通过逐出策略将缓存中的对象移出缓存。默认为LRU。常用的策略有:FIFO(First in First out)先进先出、LRU(Least Recently Used)未被使用时间最长的。
- flushInterval:刷新缓存的时间间隔,单位毫秒。这里的刷新缓存即清空缓存。一般不指定,即当执行增删改时刷新缓存。
- readOnly:设置缓存中数据是否只读。默认false。
(4)二级缓存的关闭
(1)全局关闭
<settings>
<!-- 关闭二级缓存 -->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="false" />
</settings>
(2)局部关闭

(5)二级缓存的使用原则
- 多个namespace不要操作同一张表
- 不要在关联关系表上执行增删改操作(一个namespace一般对同一个表,若表间存在关联关系,也就意味着同一个表可能会出现多个namespace。若其中一个namespace对表进行增删改操作而影响到了其关联表数据,而这个关联表的数据修改之后刷新当前namespace下的二级缓存,而对另一个namespace下的二级缓存数据没有影响)
- 查询多于修改时使用二级缓存