代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理
代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-cookbook
数据:http://www.cs.cornell.edu/people/pabo/movie-review-data/rt-polaritydata.tar.gz
问题:加载和使用预训练的嵌套,并使用这些单词嵌套进行情感分析,通过训练线性逻辑回归模型来预测电影的好坏
步骤如下:
- 必要包
- 声明模型参数
- 读取并转换文本数据集,划分训练集和测试集
- 构建图
- 训练
step1:必要包
import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import random import os import pickle import string import requests import collections import io import tarfile import urllib.request import text_helpers from nltk.corpus import stopwords from tensorflow.python.framework import ops ops.reset_default_graph() os.chdir(os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))) # Start a graph session sess = tf.Session()
step2:声明模型参数
# Declare model parameters embedding_size = 200 vocabulary_size = 2000 batch_size = 100 max_words = 100 # Declare stop words stops = stopwords.words('english')
step3:读取并转换本文数据集,划分训练集和测试集
# Load Data print('Loading Data') data_folder_name = 'temp' texts, target = text_helpers.load_movie_data(data_folder_name) # Normalize text print('Normalizing Text Data') texts = text_helpers.normalize_text(texts, stops) # Texts must contain at least 3 words target = [target[ix] for ix, x in enumerate(texts) if len(x.split()) > 2] texts = [x for x in texts if len(x.split()) > 2] # Split up data set into train/test train_indices = np.random.choice(len(target), round(0.8*len(target)), replace=False) test_indices = np.array(list(set(range(len(target))) - set(train_indices))) texts_train = [x for ix, x in enumerate(texts) if ix in train_indices] texts_test = [x for ix, x in enumerate(texts) if ix in test_indices] target_train = np.array([x for ix, x in enumerate(target) if ix in train_indices]) target_test = np.array([x for ix, x in enumerate(target) if ix in test_indices]) # Load dictionary and embedding matrix加载CBOW嵌套中保存的单词字典 dict_file = os.path.join(data_folder_name, 'movie_vocab.pkl') word_dictionary = pickle.load(open(dict_file, 'rb')) # Convert texts to lists of indices根据单词字典将加载的句子转化为数值型numpy数组 text_data_train = np.array(text_helpers.text_to_numbers(texts_train, word_dictionary)) text_data_test = np.array(text_helpers.text_to_numbers(texts_test, word_dictionary)) # Pad/crop movie reviews to specific length电影影评长度不一,不满100维的用0凑满,超过100维的取前100维 text_data_train = np.array([x[0:max_words] for x in [y+[0]*max_words for y in text_data_train]]) text_data_test = np.array([x[0:max_words] for x in [y+[0]*max_words for y in text_data_test]])
step4:构建图
print('Creating Model') # Define Embeddings:创建嵌套变量,用于之后加载CBOW训练好的嵌套向量 embeddings = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([vocabulary_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0)) # Define model: # Create variables for logistic regression变量 A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[embedding_size,1])) b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1])) # Initialize placeholders数据占位符 x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, max_words], dtype=tf.int32) y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32) # Lookup embeddings vectors embed = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embeddings, x_data) # Take average of all word embeddings in documents计算句子中所有单词的平均嵌套 embed_avg = tf.reduce_mean(embed, 1) # Declare logistic model (sigmoid in loss function) model_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(embed_avg, A), b) # Declare loss function (Cross Entropy loss) loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(model_output, y_target)) # Actual Prediction prediction = tf.round(tf.sigmoid(model_output)) predictions_correct = tf.cast(tf.equal(prediction, y_target), tf.float32) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(predictions_correct) # Declare optimizer my_opt = tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(0.005) train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)
step5:训练
# Intitialize Variables init = tf.initialize_all_variables() sess.run(init) # Load model embeddings加载CBOW训练好的嵌套矩阵 model_checkpoint_path = os.path.join(data_folder_name,'cbow_movie_embeddings.ckpt') saver = tf.train.Saver({"embeddings": embeddings}) saver.restore(sess, model_checkpoint_path) # Start Logistic Regression print('Starting Model Training') train_loss = [] test_loss = [] train_acc = [] test_acc = [] i_data = [] for i in range(10000): rand_index = np.random.choice(text_data_train.shape[0], size=batch_size) rand_x = text_data_train[rand_index] rand_y = np.transpose([target_train[rand_index]]) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) # Only record loss and accuracy every 100 generations if (i+1)%100==0: i_data.append(i+1) train_loss_temp = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) train_loss.append(train_loss_temp) test_loss_temp = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: text_data_test, y_target: np.transpose([target_test])}) test_loss.append(test_loss_temp) train_acc_temp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) train_acc.append(train_acc_temp) test_acc_temp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: text_data_test, y_target: np.transpose([target_test])}) test_acc.append(test_acc_temp) if (i+1)%500==0: acc_and_loss = [i+1, train_loss_temp, test_loss_temp, train_acc_temp, test_acc_temp] acc_and_loss = [np.round(x,2) for x in acc_and_loss] print('Generation # {}. Train Loss (Test Loss): {:.2f} ({:.2f}). Train Acc (Test Acc): {:.2f} ({:.2f})'.format(*acc_and_loss))

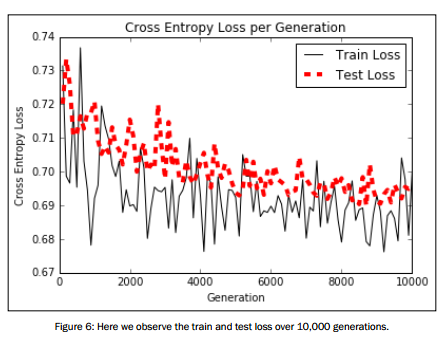
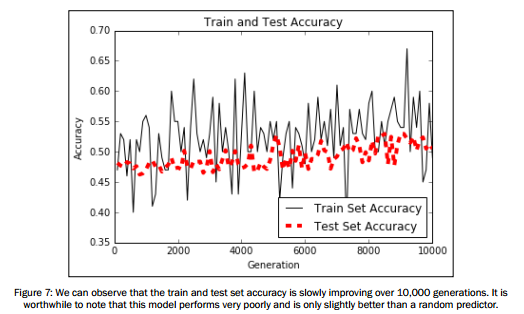
可视化结果展示:
# Plot loss over time plt.plot(i_data, train_loss, 'k-', label='Train Loss') plt.plot(i_data, test_loss, 'r--', label='Test Loss', linewidth=4) plt.title('Cross Entropy Loss per Generation') plt.xlabel('Generation') plt.ylabel('Cross Entropy Loss') plt.legend(loc='upper right') plt.show() # Plot train and test accuracy plt.plot(i_data, train_acc, 'k-', label='Train Set Accuracy') plt.plot(i_data, test_acc, 'r--', label='Test Set Accuracy', linewidth=4) plt.title('Train and Test Accuracy') plt.xlabel('Generation') plt.ylabel('Accuracy') plt.legend(loc='lower right') plt.show()