我们一起来了解Source、Channel和Sink的全链路过程。
一、Flume架构分析
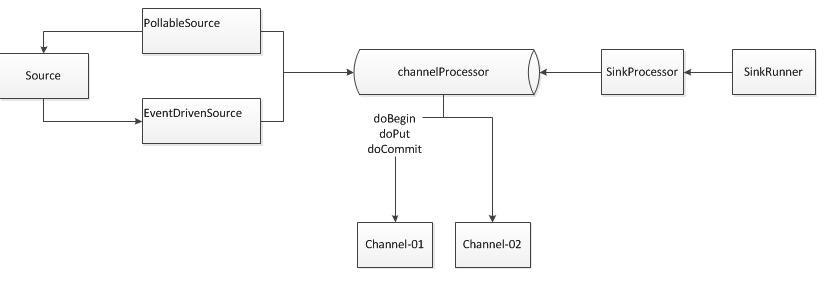
这个图中核心的组件是:
Source,ChannelProcessor,Channel,Sink。他们的关系结构如下:
Source {
ChannelProcessor {
Channel ch1
Channel ch2
…
}
}
Sink {
Channel ch;
}
SinkGroup {
Channel ch;
Sink s1;
Sink s2;
…
}
二、各组件详细介绍
1、Source组件
Source是数据源的总称,我们往往设定好源后,数据将源源不断的被抓取或者被推送。
常见的数据源有:ExecSource,KafkaSource,HttpSource,NetcatSource,JmsSource,AvroSource等等。
所有的数据源统一实现一个接口类如下:
@InterfaceAudience.Public
@InterfaceStability.Stable
public interface Source extends LifecycleAware, NamedComponent {
/**
* Specifies which channel processor will handle this source's events.
*
* @param channelProcessor
*/
public void setChannelProcessor(ChannelProcessor channelProcessor);
/**
* Returns the channel processor that will handle this source's events.
*/
public ChannelProcessor getChannelProcessor();
}
Source提供了两种机制: PollableSource(轮询拉取)和EventDrivenSource(事件驱动):
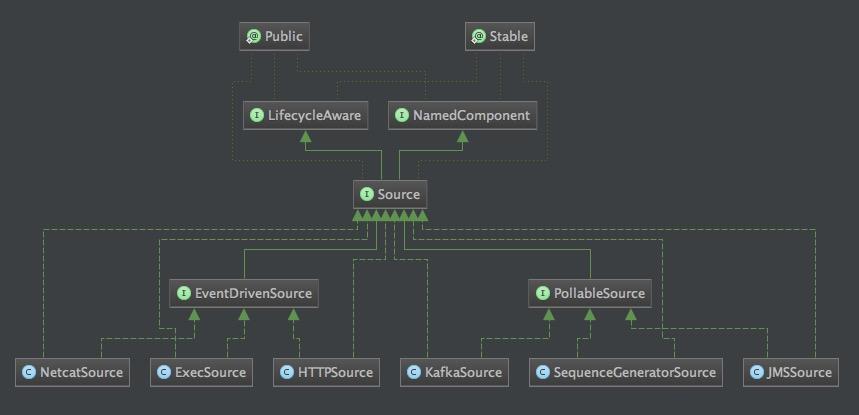
上图展示的Source继承关系类图。
通过类图我们可以看到NetcatSource,ExecSource和HttpSource属于事件驱动模型。KafkaSource,SequenceGeneratorSource和JmsSource属于轮询拉取模型。
Source接口继承了LifecycleAware接口,它的的所有逻辑的实现在接口的start和stop方法中进行。
下图是类关系方法图:
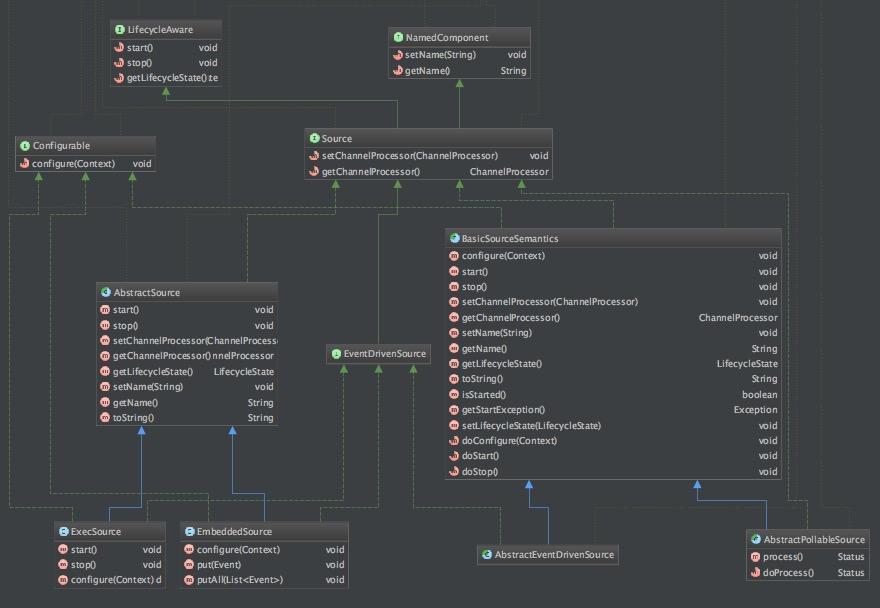
Source接口定义的是最终的实现过程,比如通过日志抓取日志,这个抓取的过程和实际操作就是在对应的Source实现中,比如:ExecSource。那么这些Source实现由谁来驱动的呢?现在我们将介绍SourceRunner类。看一下类继承结构图:
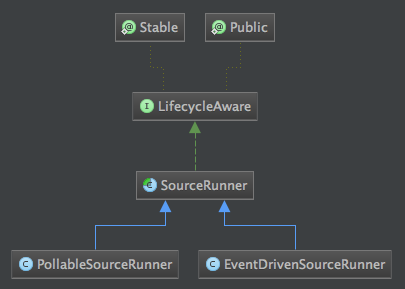
我们看一下PollableSourceRunner和EventDrivenSourceRunner的具体实现:
//PollableSourceRunner:
public void start() {
PollableSource source = (PollableSource) getSource();
ChannelProcessor cp = source.getChannelProcessor();
cp.initialize();
source.start();
runner = new PollingRunner();
runner.source = source; //Source实现类就在这里被赋与。
runner.counterGroup = counterGroup;
runner.shouldStop = shouldStop;
runnerThread = new Thread(runner);
runnerThread.setName(getClass().getSimpleName() + "-" +
source.getClass().getSimpleName() + "-" + source.getName());
runnerThread.start();
lifecycleState = LifecycleState.START;
}
//EventDrivenSourceRunner:
@Override
public void start() {
Source source = getSource();
ChannelProcessor cp = source.getChannelProcessor();
cp.initialize();
source.start();
lifecycleState = LifecycleState.START;
}
注:其实所有的Source实现类内部都维护着线程,执行source.start()其实就是启动了相应的线程。
刚才我们看代码,代码中一直都在展示channelProcessor这个类,同时最上面架构设计图里面也提到了这个类,那它到底是干什么呢,下面我们就对其分解。
2、Channel组件
Channel用于连接Source和Sink,Source将日志信息发送到Channel,Sink从Channel消费日志信息;Channel是中转日志信息的一个临时存储,保存有Source组件传递过来的日志信息。
先看代码如下:
ChannelSelectorConfiguration selectorConfig = config.getSelectorConfiguration();
ChannelSelector selector = ChannelSelectorFactory.create(sourceChannels, selectorConfig);
ChannelProcessor channelProcessor = new ChannelProcessor(selector);
Configurables.configure(channelProcessor, config);
source.setChannelProcessor(channelProcessor);
ChannelSelectorFactory.create方法实现如下:
public static ChannelSelector create(List<Channel> channels,
ChannelSelectorConfiguration conf) {
String type = ChannelSelectorType.REPLICATING.toString();
if (conf != null){
type = conf.getType();
}
ChannelSelector selector = getSelectorForType(type);
selector.setChannels(channels);
Configurables.configure(selector, conf);
return selector;
}
其中我们看一下ChannelSelectorType这个枚举类,包括了几种类型:
public enum ChannelSelectorType {
/**
* Place holder for custom channel selectors not part of this enumeration.
*/
OTHER(null),
/**
* 复用通道选择器
*/
REPLICATING("org.apache.flume.channel.ReplicatingChannelSelector"),
/**
* 多路通道选择器
*/
MULTIPLEXING("org.apache.flume.channel.MultiplexingChannelSelector");
}
ChannelSelector的类结构图如下所示:
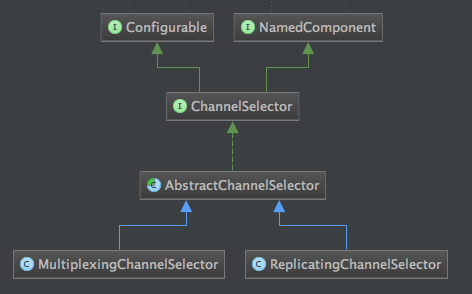
注:RelicatingChannelSelector和MultiplexingChannelSelector是二个通道选择器,第一个是复用型通道选择器,也就是的默认的方式,会把接收到的消息发送给其他每个channel。第二个是多路通道选择器,这个会根据消息header中的参数进行通道选择。
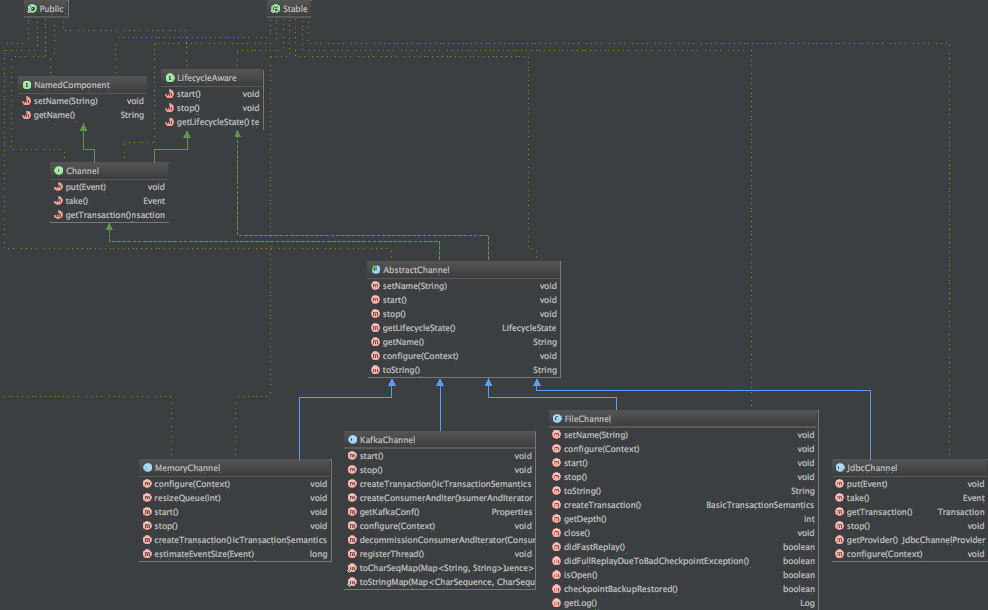
说完通道选择器,正式来解释Channel是什么,先看一个接口类:
public interface Channel extends LifecycleAware, NamedComponent {
public void put(Event event) throws ChannelException;
public Event take() throws ChannelException;
public Transaction getTransaction();
}
注:put方法是用来发送消息,take方法是获取消息,transaction是用于事务操作。
类结构图如下:
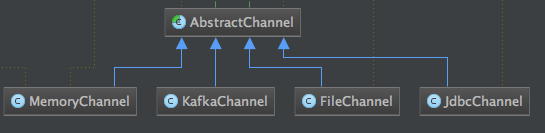
3、Sink组件
Sink负责取出Channel中的消息数据,进行相应的存储文件系统,数据库,或者提交到远程服务器。
Sink在设置存储数据时,可以向文件系统中,数据库中,hadoop中储数据,在日志数据较少时,可以将数据存储在文件系中,并且设定一定的时间间隔保存数据。在日志数据较多时,可以将相应的日志数据存储到Hadoop中,便于日后进行相应的数据分析。
Sink接口类内容如下:
public interface Sink extends LifecycleAware, NamedComponent {
public void setChannel(Channel channel);
public Channel getChannel();
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException;
public static enum Status {
READY, BACKOFF
}
}
Sink是通过如下代码进行的创建:
Sink sink = sinkFactory.create(comp.getComponentName(), comp.getType());
DefaultSinkFactory.create方法如下:
public Sink create(String name, String type) throws FlumeException {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(name, "name");
Preconditions.checkNotNull(type, "type");
logger.info("Creating instance of sink: {}, type: {}", name, type);
Class<? extends Sink> sinkClass = getClass(type);
try {
Sink sink = sinkClass.newInstance();
sink.setName(name);
return sink;
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println(ex);
throw new FlumeException("Unable to create sink: " + name
+ ", type: " + type + ", class: " + sinkClass.getName(), ex);
}
}
注:Sink是通过SinkFactory工厂来创建,提供了DefaultSinkFactory默认工厂,程序会查找org.apache.flume.conf.sink.SinkType这个枚举类找到相应的Sink处理类,比如:org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink,如果没找到对应的处理类,直接通过Class.forName(className)进行直接查找实例化实现类。
Sink的类结构图如下:
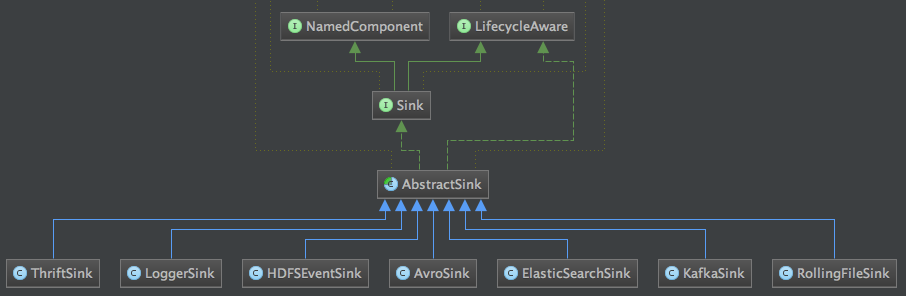
与ChannelProcessor处理类对应的是SinkProcessor,由SinkProcessorFactory工厂类负责创建,SinkProcessor的类型由一个枚举类提供,看下面代码:
public enum SinkProcessorType {
/**
* Place holder for custom sinks not part of this enumeration.
*/
OTHER(null),
/**
* 故障转移 processor
*
* @see org.apache.flume.sink.FailoverSinkProcessor
*/
FAILOVER("org.apache.flume.sink.FailoverSinkProcessor"),
/**
* 默认processor
*
* @see org.apache.flume.sink.DefaultSinkProcessor
*/
DEFAULT("org.apache.flume.sink.DefaultSinkProcessor"),
/**
* 负载processor
*
* @see org.apache.flume.sink.LoadBalancingSinkProcessor
*/
LOAD_BALANCE("org.apache.flume.sink.LoadBalancingSinkProcessor");
private final String processorClassName;
private SinkProcessorType(String processorClassName) {
this.processorClassName = processorClassName;
}
public String getSinkProcessorClassName() {
return processorClassName;
}
}
SinkProcessor的类结构图如下:
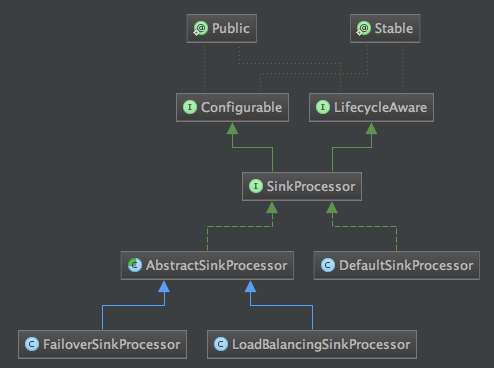
说明:
1、FailoverSinkProcessor是故障转移处理器,当sink从通道拿数据信息时出错进行的相关处理,代码如下:
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
// 经过了冷却时间,再次发起重试
Long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
while(!failedSinks.isEmpty() && failedSinks.peek().getRefresh() < now) {
//从失败队列中获取sink节点
FailedSink cur = failedSinks.poll();
Status s;
try {
//调用相应sink进行处理,比如将channel的数据读取存放到文件中,
//这个存放文件的动作就在process中进行。
s = cur.getSink().process();
if (s == Status.READY) {
//如果处理成功,则放到存活队列中
liveSinks.put(cur.getPriority(), cur.getSink());
activeSink = liveSinks.get(liveSinks.lastKey());
logger.debug("Sink {} was recovered from the fail list",
cur.getSink().getName());
} else {
// if it's a backoff it needn't be penalized.
//如果处理失败,则继续放到失败队列中
failedSinks.add(cur);
}
return s;
} catch (Exception e) {
cur.incFails();
failedSinks.add(cur);
}
}
Status ret = null;
while(activeSink != null) {
try {
ret = activeSink.process();
return ret;
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Sink {} failed and has been sent to failover list",
activeSink.getName(), e);
activeSink = moveActiveToDeadAndGetNext();
}
}
2、LoadBalancingSinkProcessor是负载Sink处理器
首先我们和ChannelProcessor一样,我们也要重点说明一下SinkSelector这个选择器。
先看一下SinkSelector.configure方法的部分代码:
if (selectorTypeName.equalsIgnoreCase(SELECTOR_NAME_ROUND_ROBIN)) {
selector = new RoundRobinSinkSelector(shouldBackOff);
} else if (selectorTypeName.equalsIgnoreCase(SELECTOR_NAME_RANDOM)) {
selector = new RandomOrderSinkSelector(shouldBackOff);
} else {
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<? extends SinkSelector> klass = (Class<? extends SinkSelector>)
Class.forName(selectorTypeName);
selector = klass.newInstance();
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new FlumeException("Unable to instantiate sink selector: "
+ selectorTypeName, ex);
}
}
结合上面的代码,再看类结构图如下:
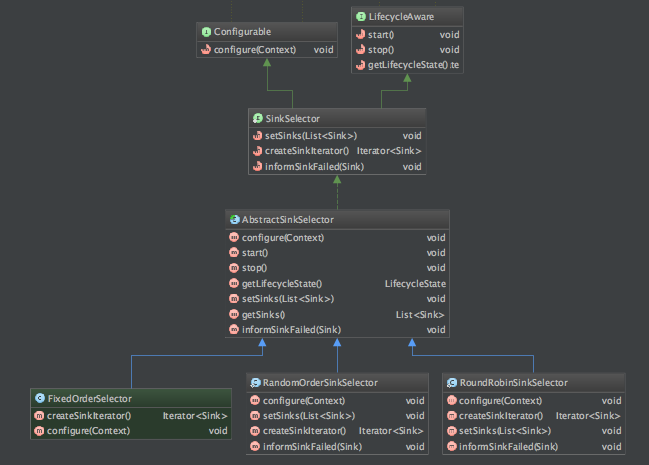
注:RoundRobinSinkSelector是轮询选择器,RandomOrderSinkSelector是随机分配选择器。
最后我们以KafkaSink为例看一下Sink里面的具体实现:
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
Status result = Status.READY;
Channel channel = getChannel();
Transaction transaction = null;
Event event = null;
String eventTopic = null;
String eventKey = null;
try {
long processedEvents = 0;
transaction = channel.getTransaction();
transaction.begin();
messageList.clear();
for (; processedEvents < batchSize; processedEvents += 1) {
event = channel.take();
if (event == null) {
// no events available in channel
break;
}
byte[] eventBody = event.getBody();
Map<String, String> headers = event.getHeaders();
if ((eventTopic = headers.get(TOPIC_HDR)) == null) {
eventTopic = topic;
}
eventKey = headers.get(KEY_HDR);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("{Event} " + eventTopic + " : " + eventKey + " : "
+ new String(eventBody, "UTF-8"));
logger.debug("event #{}", processedEvents);
}
// create a message and add to buffer
KeyedMessage<String, byte[]> data = new KeyedMessage<String, byte[]>
(eventTopic, eventKey, eventBody);
messageList.add(data);
}
// publish batch and commit.
if (processedEvents > 0) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
producer.send(messageList);
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
counter.addToKafkaEventSendTimer((endTime-startTime)/(1000*1000));
counter.