OGNL是Object Graphic Navigation Language(对象图导航语言)的缩写,它是一个开源项目。 Struts2框架使用OGNL作为默认的表达式语言。
OGNL表达式
1、#号的用法
#用法1:访问OGNL上下文和Action上下文,#相当ActionContext.getContext()
a) 如果访问其他Context中的对象,由于他们不是根对象,所以在访问时,需要添加#前缀。
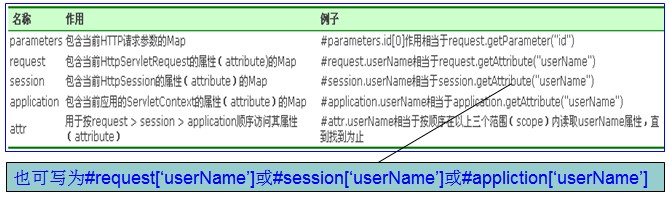
1 Action中代码: 2 ServletActionContext.getRequest().setAttribute("username", "username_request"); 3 ServletActionContext.getServletContext().setAttribute("username", "username_application"); 4 ServletActionContext.getContext().getSession().put("username", "username_session"); 5 ValueStack valueStack=ServletActionContext.getContext().getValueStack(); 6 valueStack.set("username", "username_valueStack"); 7 8 Jsp页面: 9 使用ognl表达式取值*****************************<br> 10 request:<s:property value="#request.username"/><br> 11 session:<s:property value="#session.username"/><br> 12 application:<s:property value="#application.username"/><br> 13 attr:<s:property value="#attr.username"/><br> 14 valueStack:<s:property value="username"/><br> 15 parameters:<s:property value="#parameters.cid[0]"/><br>
b) OGNL会设定一个根对象(root对象),在Struts2中根对象就是ValueStack(值栈)。如果要访问根对象(即ValueStack)中对象的属性,则可以省略 #命名对象,直接访问该对象的属性即可。
1 Action中代码: 2 ValueStack valueStack=ServletActionContext.getContext().getValueStack(); 3 valueStack.set("msg", "msg_xxx"); 4 Jsp页面: 5 valueStack:<s:property value="msg"/><br>
c) 深入理解值栈中的 ObjectStack
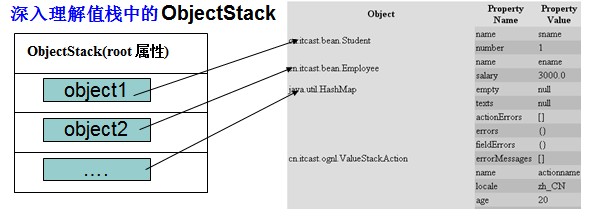
在OgnlValueStack类里有一个List类型的root变量,他存放了一组对象
处于第一位的对象叫栈顶对象。(list集合的 索引为0为栈顶)
通常我们在OGNL表达式里直接写上属性的名称即可访问root变量里对象的属性,
搜索顺序是从栈顶对象开始寻找,如果栈顶对象不存在该属性,就会从第二个对象寻找,如果没有找到就从第三个对象寻找,依次往下访问,直到找到为止。
1 Action中代码: 2 ValueStack valueStack=ServletActionContext.getContext().getValueStack(); 3 4 //set方法放置对象到map中,map再放入到栈(List集合)上 5 valueStack.set("student", new Student()); 6 valueStack.set("employee", new Employee()); 7 8 //直接放置对象到栈(List集合)上 9 valueStack.getRoot().add(0,new Student()); 10 valueStack.getRoot().add(1,new Employee()); 11 12 Jsp页面: 13 name:<s:property value="name"/><br> 14 age::<s:property value="age"/><br> 15 number::<s:property value="number"/><br> 16 salary:<s:property value="salary"/><br>
#用法2:集合的投影(过滤)
a) 集合的投影(只输出部分属性)collectionName.{ expression }
1 <s:iterator value="#request.persons.{name}" var="person"> 2 <s:property value="#person"/><br> 3 </s:iterator>
b) 集合的过滤
1) 集合的过滤有以下三种方式:
a.“?#”:过滤所有符合条件的集合,如:users.{?#this.age > 19};
b.“^#”:过滤第一个符合条件的元素,如:users.{^#this.age > 19};
c.“$#”:过滤最后一个符合条件的元素,如:users.{$#this.age > 19} 。
2) this 表示集合中的元素;
1 <s:iterator value="#request.persons.{?#this.age>24}" var="person"> 2 <s:property value="#person"/><br> 3 </s:iterator>
c) 集合的投影和过滤
投影(过滤)操作返回的是一个集合,可以使用索引取得集合中指定的元素,如:users.{?#this.age > 19}[0]
1 <s:iterator value="#request.persons.{?#this.age>24}.{name}" var="person"> 2 <s:property value="#person"/><br> 3 </s:iterator>
#用法3:构造Map,如#{‘foo1’:‘bar1’, ‘foo2’:‘bar2’}
这种方式常用在给radio或select、checkbox等标签赋值上
1 jsp页面: 2 <s:radio list=“#{‘male’:‘男’,‘female’:‘女’}” name=“sex” label=“性别” /> 3 运行结果是 4 <input type="radio" name="sex" id="sexmale" value="male"/>男 5 <input type="radio" name="sex" id="sexfemale" value="female"/>女
1 Action中的代码: 2 Map map=new HashMap(); 3 map.put("male", "男"); 4 map.put("female", "女"); 5 ServletActionContext.getRequest().setAttribute("map", map); 6 jsp页面: 7 <s:radio list="#request.map" name="sex" label="性别" /> 8 运行结果是 9 <input type="radio" name="sex" id="sexfemale" value="female"/>女 10 <input type=“radio” name=“sex” id=“sexmale” value=“male”>男
2、%用法
“%”符号的用途是在标签的属性值被理解为字符串类型时,告诉执行环境%{}里的是OGNL表达式。
1 形式一: { }中ognl表达式 2 Action中的代码: 3 ServletActionContext.getRequest().setAttribute("username", "username_request"); 4 jsp页面: 5 <s:textfield name="name" label="%{#request.username} "/> 6 运行结果是 7 username_request : <input type="text" name="name" value="" id="name"/> 8 形式二: { }中值用 ’ ’引起来,这是不再是ogle表达式,而是普通的字符串 9 jsp页面: 10 <s:textfield name="name" label="%{'foo'}"/> 11 运行结果是 12 foo : <input type="text" name="name" value="" id="name"/>
3、$用法
“$”有两个主要的用途
* 用于在国际化资源文件中,引用OGNL表达式
* 在Struts 2配置文件中,引用OGNL表达式
1 * 用于在国际化资源文件中,引用OGNL表达式<br> 2 <s:text name="ognl" /><br><br>
resources.properties
1 ognl=${error} ognl_base
1 在struts2配置文件中引用ognl表达式 ,引用request等作用域中的值 2 Action中的代码: 3 ServletActionContext.getRequest().setAttribute("msgxx", "msg_request"); 4 struts.xml文件中 5 <package name="ognl" namespace="/ognl" extends="struts-default" > 6 <action name="ognlAction_*" class="cn.itcast.ognl.OgnlAction" method="{1}"> 7 <result name="ognl">/ognl/ongl.jsp?msg=${#request.msgxx}</result> 8 </action> 9 </package> 10 jsp页面: 11 parameters Msg:<s:property value="#parameters.msg[0]"/> 12 运行结果是 13 msg_request
代码:
1、java
1 import java.util.Map; 2 3 import javax.servlet.ServletContext; 4 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 5 6 import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; 7 8 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext; 9 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; 10 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack; 11 12 @SuppressWarnings("serial") 13 public class OgnlAction extends ActionSupport { 14 15 private String name = "oname"; 16 17 private String sex = "male"; 18 19 public String getName() { 20 return name; 21 } 22 23 public void setName(String name) { 24 this.name = name; 25 } 26 27 public String getSex() { 28 return sex; 29 } 30 31 public void setSex(String sex) { 32 this.sex = sex; 33 } 34 35 public String test(){ 36 System.out.println("OgnlAction ************ test()"); 37 38 HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest(); 39 request.setAttribute("username", "username_request"); 40 request.setAttribute("password", "password_request"); 41 42 Map sessionMap = ServletActionContext.getContext().getSession(); 43 sessionMap.put("username", "username_session"); 44 sessionMap.put("password", "password_session"); 45 46 ServletContext sc = ServletActionContext.getServletContext(); 47 sc.setAttribute("username", "username_application"); 48 sc.setAttribute("password", "password_application"); 49 50 //方法一:获取ValueStack对象 51 ValueStack valueStack1 = (ValueStack)request.getAttribute("struts.valueStack"); 52 System.out.println("valueStack = "+valueStack1); 53 54 /* 55 * 插入的内容,实际上是先放置在一个map集合中,又把这个map集合放置在对象栈里 56 */ 57 valueStack1.set("error", "error_valueStack"); 58 valueStack1.set("msg", "msg_valueStack"); 59 60 valueStack1.getRoot().add(0, new Person()); 61 valueStack1.getRoot().add(0,new Employee()); 62 63 //方法二:获取ValueStack对象 64 /*ValueStack valueStack2 = ServletActionContext.getContext().getValueStack(); 65 System.out.println("valueStack = "+valueStack2);*/ 66 67 return "ognl"; 68 } 69 70 }
2、jsp
1 <%@ page language="java" pageEncoding="utf-8"%> 2 <%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%> 3 <html> 4 <head> 5 <title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title> 6 <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> 7 </head> 8 <body> 9 <:ognl.jsp<br> 10 使用EL表达式取值-----------------------------------------<br> 11 ${requestScope.username}<br> 12 ${sessionScope.username}<br> 13 ${applicationScope.username}<br><br><br><br> 14 使用Ognl表达式取值-----------------------------------------<br> 15 1 # 如果访问其他Context中的对象,由于他们不是根对象,所以在访问时,需要添加#前缀。<br> 16 <s:property value="#request.username"/><br> 17 <s:property value="#session.username"/><br> 18 <s:property value="#application.username"/><br><br> 19 <s:property value="#request['username']"/><br> 20 <s:property value="#parameters.cid[0]"/><br> 21 <s:property value="#attr.username"/><br><br> 22 2 # 如果要访问根对象(即ValueStack)中对象的属性,则可以省略#命名对象,直接访问该对象的属性即可。<br> 23 <s:property value="msg"/><br><br> 24 深入理解值栈中的 ObjectStack<br> 25 <s:property value="name"/><br> 26 <s:property value="sex"/><br> 27 <s:property value="age"/><br> 28 <s:property value="salary"/><br><br> 29 30 31 用法3:构造Map<br> 32 <s:radio list="#{'01':'男','02':'女'}"></s:radio><br><br><br><br> 33 %的用法:“%”符号的用途是在标签的属性值被理解为字符串类型时,告诉执行环境%{}里的是OGNL表达式。 <br> 34 <s:property value="#request.username"/><br> 35 <s:property value="%{#request.username}"/>%{}是万能用法,无论里面的表达式是不是ognl表达式,都会强制理解为ognl表达式<br><br> 36 37 “$”有两个主要的用途<br> 38 * 用于在国际化资源文件中,引用OGNL表达式<br> 39 <s:text name="ognl" /><br><br> 40 41 * 在Struts 2配置文件中,引用OGNL表达式<br> 42 <s:property value="#parameters.msgxx[0]"/><br><br> 43 44 <s:debug></s:debug> 45 </body> 46 </html>