考虑如果两点在一个环中,那么这两点一定可以构出双联通分量.
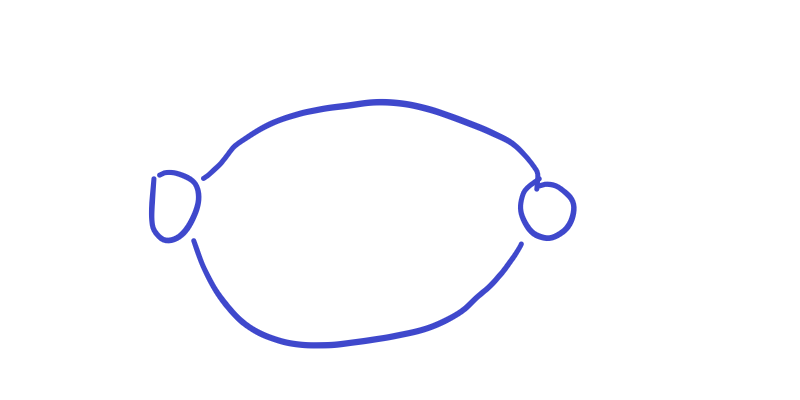
考虑环和环镶嵌,那么两个环中的点一定都互为双联通分量.
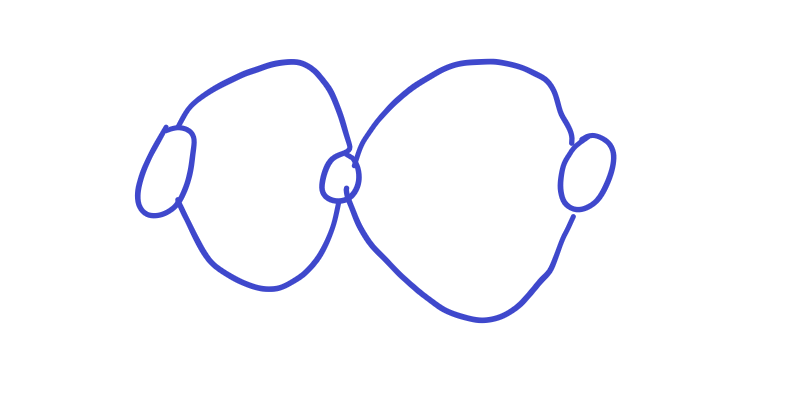
由此,我们想到一个算法:
将删边转为反向加边,用LCT维护图.
当我们连接两个点时,分两种两种情况.
1.不连通 : 没啥说的,直接连上
2.连通 : 那么说明要被连接的两点在一个换中,如下图:
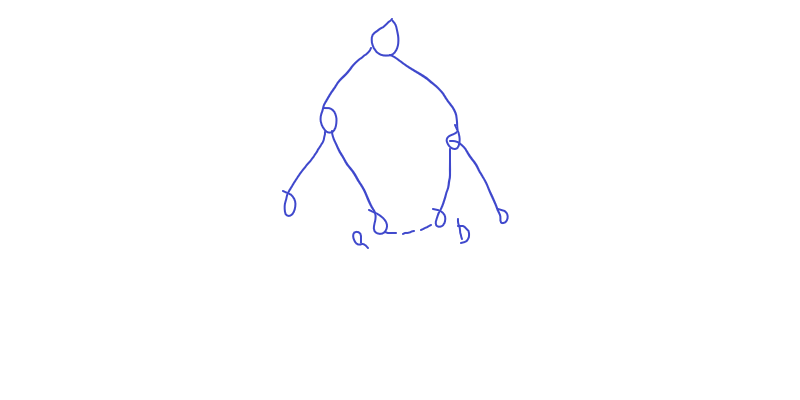
显然,整条路径上的所有点都互为双连通.
不过,与其维护点,我们维护边,将两点间所有边都设成 1.
在查询两个点是否为双联通时看看边权和是否等于边数即可(想一想,为什么 ? )
因为两点间的边都被赋值,有两种情况:
1. 两点为环,被统一赋值,显然正确.
2. 这条链被多个段落所覆盖,段落与段落之间至少有一个公共点,符合上述第二个结论,显然正确.
Code:
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <set>
#include <string>
#define setIO(s) freopen(s".in","r",stdin) ,freopen(s".out","w",stdout)
#define inf 1000000000
#define maxn 300007
#define pr pair<int,int>
using namespace std;
set <pr> b;
struct Union{
int p[maxn];
void init(){ for(int i=0;i<maxn;++i) p[i]=i; }
int find(int x){ return p[x]==x ? x : p[x]=find(p[x]);}
int merge(int a,int b){
int x=find(a),y=find(b);
if(x==y) return 1;
p[x]=y;
return 0;
}
}tree;
int tot;
int ans[maxn];
int ch[maxn][2],f[maxn],val[maxn];
int sta[maxn],tag[maxn],sumv1[maxn],addv[maxn],sumv2[maxn];
int lson(int x){ return ch[x][0]; }
int rson(int x){ return ch[x][1]; }
int get(int x){ return ch[f[x]][1]==x; }
int isRoot(int x){ return !(ch[f[x]][0]==x||ch[f[x]][1]==x); }
void mark(int x){ if(x) swap(ch[x][0],ch[x][1]),tag[x]^=1; }
void update(int x){ sumv1[x]=sumv2[x],addv[x]=1,val[x] = 1; }
void pushdown(int x){
if(tag[x]) mark(lson(x)), mark(rson(x)), tag[x]=0;
if(addv[x]) update(lson(x)),update(rson(x)),addv[x]=0;
}
void pushup(int x){
sumv1[x]=sumv1[lson(x)]+sumv1[rson(x)] + val[x];
sumv2[x]=sumv2[lson(x)]+sumv2[rson(x)] + 1;
}
void rotate(int x) {
int old=f[x],oldf=f[old],which=get(x);
if(!isRoot(old)) ch[oldf][ch[oldf][1]==old]=x;
ch[old][which]=ch[x][which^1],f[ch[old][which]]=old;
ch[x][which^1]=old,f[old]=x,f[x]=oldf;
pushup(old),pushup(x);
}
void splay(int x){
int v=0,u=x;
sta[++v]=u;
while(!isRoot(u)) sta[++v]=f[u],u=f[u];
while(v) pushdown(sta[v--]);
u=f[u];
for(int fa;(fa=f[x])!=u;rotate(x))
if(f[fa]!=u) rotate(get(fa)==get(x)?fa:x);
}
void Access(int x){ for(int y=0;x;y=x,x=f[x]) splay(x),ch[x][1]=y,pushup(x); }
void makeRoot(int x){ Access(x),splay(x),mark(x); }
void split(int x,int y){ makeRoot(x),Access(y),splay(y); }
void link(int a,int b){
if(tree.merge(a,b) == 1) { makeRoot(a),Access(b),splay(b),update(b); }
else{
makeRoot(a);
f[f[a]=++tot]=b;
}
}
struct E{ int x,y; }err[maxn];
struct OPT{ int opt,x,y; }opt[maxn];
char chf[10];
int main(){
//setIO("input");
int n,m,q;
tot=100001;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q),tree.init();
for(int i=1;i<tot;++i) sumv1[i]=sumv2[i]=val[i]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i) {
scanf("%d%d",&err[i].x,&err[i].y);
if(err[i].y>err[i].x) swap(err[i].x,err[i].y);
}
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++) {
scanf("%s",chf);
scanf("%d%d",&opt[i].x,&opt[i].y);
if(opt[i].y>opt[i].x) swap(opt[i].x,opt[i].y);
if(chf[0]=='Z')
{
opt[i].opt=1;
b.insert(make_pair(opt[i].x,opt[i].y));
}
else opt[i].opt=0;
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
if(b.find(make_pair(err[i].x,err[i].y))==b.end())
{
link(err[i].x,err[i].y);
}
}
for(int i=q;i>=1;--i) {
if(opt[i].opt==1) { link(opt[i].x,opt[i].y); }
else {
int a=opt[i].x,b=opt[i].y;
if(tree.find(a)!=tree.find(b)) {ans[i]=0;continue; }
makeRoot(a),Access(b),splay(b);
if(sumv1[b]==sumv2[b]) ans[i]=1;
else ans[i]=0;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=q;++i)
if(opt[i].opt==0) {
if(ans[i]==1) printf("Yes
");
else printf("No
");
}
return 0;
}