1.浏览RYU官网学习RYU控制器的安装和RYU开发入门教程,提交你对于教程代码的理解,包括但不限于
- 描述官方教程实现了一个什么样的交换机功能?
收到数据包就用泛洪的方式实现同一局域网内主机的互通
- 控制器设定交换机支持什么版本的OpenFlow?
OpenFlow 1.0,OpenFlow 1.1,OpenFlow 1.2,OpenFlow 1.3
- 控制器设定了交换机如何处理数据包?
from ryu.base import app_manager
from ryu.controller import ofp_event
from ryu.controller.handler import MAIN_DISPATCHER
from ryu.controller.handler import set_ev_cls
from ryu.ofproto import ofproto_v1_0
from ryu.lib.packet import packet
from ryu.lib.packet import ethernet
from ryu.lib.packet import ether_types
from ryu.lib.packet import ipv4
class SimpleSwitch(app_manager.RyuApp):
OFP_VERSIONS = [ofproto_v1_0.OFP_VERSION]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(SimpleSwitch, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
@set_ev_cls(ofp_event.EventOFPPacketIn, MAIN_DISPATCHER)
def _packet_in_handler(self, ev):
msg = ev.msg
datapath = msg.datapath
ofproto = datapath.ofproto
pkt = packet.Packet(msg.data)
eth = pkt.get_protocol(ethernet.ethernet)
if eth.ethertype == ether_types.ETH_TYPE_LLDP:
#ignore lldp packet
return
if eth.ethertype == ether_types.ETH_TYPE_IPV6:
#ignore ipv6 packet
return
print ("PACKET_IN:")
print (eth.ethertype)
print ("ethernet:")
print ("eth_src=",eth.src)
print ("eth_dst=",eth.dst)
if eth.ethertype == ether_types.ETH_TYPE_IP:
_ipv4 = pkt.get_protocol(ipv4.ipv4)
print ("ipv4:")
print ("ip_src=",_ipv4.src)
print ("ip_dst=",_ipv4.dst)
dpid = datapath.id
out_port = ofproto.OFPP_FLOOD
actions = [datapath.ofproto_parser.OFPActionOutput(out_port)]
data = None
out = datapath.ofproto_parser.OFPPacketOut(datapath=datapath, buffer_id=msg.buffer_id, in_port=msg.in_port, actions=actions, data=data)
datapath.send_msg(out)
print ("PACKET_OUT...")
print
示例代码可以分为3部分来看
+ 初始化(init)
+ 接收数据包并做判定,在这个部分中,我主要关心这几个数据结构
- msg,这个结构应该是一个完整的数据包的结构
- datapath,是一个数据路径,在本例中可以看出他包含ofproto
- ofproto,openflowprotocal,在本例中ofproto的作用是提供泛洪功能(不是很清楚怎么表述),见51行的ofproto.OFPP_FLOOD
- pkt和eth是函数返回的数据结构,eth包含由链路层协议类型
+ 下发流表,指导数据包的转发
- outport,出接口
- actions,执行动作
2.根据官方教程和提供的示例代码(SimpleSwitch.py),将具有自学习功能的交换机代码(SelfLearning.py)补充完整
from ryu.base import app_manager
from ryu.controller import ofp_event
from ryu.controller.handler import MAIN_DISPATCHER
from ryu.controller.handler import set_ev_cls
from ryu.ofproto import ofproto_v1_0
from ryu.lib.mac import haddr_to_bin
from ryu.lib.packet import packet
from ryu.lib.packet import ethernet
from ryu.lib.packet import ether_types
class SimpleSwitch(app_manager.RyuApp):
# TODO define OpenFlow 1.0 version for the switch
# add your code here
OFP_VERSIONS = [ofproto_v1_0.OFP_VERSION]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(SimpleSwitch, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.mac_to_port = {}
def add_flow(self, datapath, in_port, dst, src, actions):
ofproto = datapath.ofproto
match = datapath.ofproto_parser.OFPMatch(
in_port=in_port,
dl_dst=haddr_to_bin(dst), dl_src=haddr_to_bin(src))
mod = datapath.ofproto_parser.OFPFlowMod(
datapath=datapath, match=match, cookie=0,
command=ofproto.OFPFC_ADD, idle_timeout=0, hard_timeout=0,
priority=ofproto.OFP_DEFAULT_PRIORITY,
flags=ofproto.OFPFF_SEND_FLOW_REM, actions=actions)
# TODO send modified message out
# add your code here
datapath.send_msg(mod)
@set_ev_cls(ofp_event.EventOFPPacketIn, MAIN_DISPATCHER)
def _packet_in_handler(self, ev):
msg = ev.msg
datapath = msg.datapath
ofproto = datapath.ofproto
pkt = packet.Packet(msg.data)
eth = pkt.get_protocol(ethernet.ethernet)
if eth.ethertype == ether_types.ETH_TYPE_LLDP:
# ignore lldp packet
return
if eth.ethertype == ether_types.ETH_TYPE_IPV6:
# ignore ipv6 packet
return
dst = eth.dst
src = eth.src
dpid = datapath.id
self.mac_to_port.setdefault(dpid, {})
self.logger.info("packet in DPID:%s MAC_SRC:%s MAC_DST:%s IN_PORT:%s", dpid, src, dst, msg.in_port)
# learn a mac address to avoid FLOOD next time.
self.mac_to_port[dpid][src] = msg.in_port
if dst in self.mac_to_port[dpid]:
out_port = self.mac_to_port[dpid][dst]
else:
out_port = ofproto.OFPP_FLOOD
# TODO define the action for output
# add your code here
actions = [datapath.ofproto_parser.OFPActionOutput(out_port)]
# install a flow to avoid packet_in next time
if out_port != ofproto.OFPP_FLOOD:
self.logger.info("add flow s:DPID:%s Match:[ MAC_SRC:%s MAC_DST:%s IN_PORT:%s ], Action:[OUT_PUT:%s] ", dpid, src, dst, msg.in_port, out_port)
self.add_flow(datapath, msg.in_port, dst, src, actions)
data = None
if msg.buffer_id == ofproto.OFP_NO_BUFFER:
data = msg.data
# TODO define the OpenFlow Packet Out
# add your code here
out = datapath.ofproto_parser.OFPPacketOut(datapath=datapath, buffer_id=msg.buffer_id, in_port=msg.in_port, actions=actions, data=data)
datapath.send_msg(out)
print ("PACKET_OUT...")
3.在mininet创建一个最简拓扑,并连接RYU控制器

- 创建拓扑的python代码如下所示:
from mininet.topo import Topo
class MyTopo(Topo):
def __init__(self):
# initilaize topology
Topo.__init__(self)
# add hosts and switches
h1 = self.addHost('h1')
h2 = self.addHost('h2')
s1 = self.addSwitch('s1')
# add links
self.addLink(h1, s1, 1, 1)
self.addLink(h2, s1, 1, 2)
topos = {'mytopo': (lambda: MyTopo())}
- 执行代码的命令如下(注意选择OPENFLOW协议):
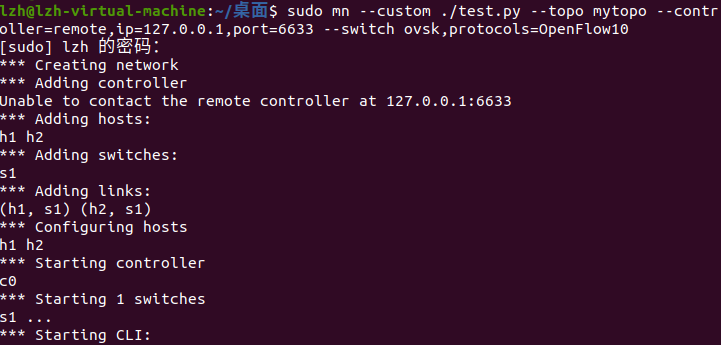
sudo mn --custom ./test.py --topo mytopo --controller=remote,ip=127.0.0.1,port=6633 --switch ovsk,protocols=OpenFlow10
-
运行mininet以后即创建网络拓
-
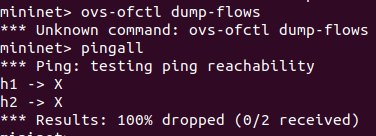
做联通测试,此时没有控制器指挥转发,h1和h2是无法实现双向连通的
-
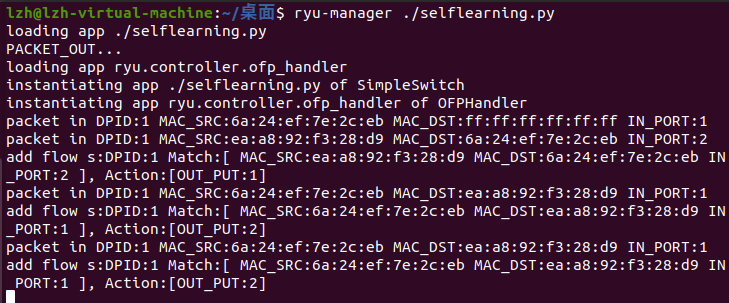
运行RYU控制器,指导交换机执行转发,可以看到控制器在执行h1 ping h2的时候下发流表指导转发
-
此时已经可以实现互通

-
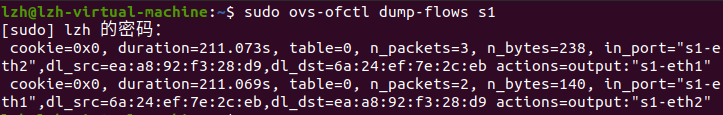
查看交换机S1的流表,看到相关的条目
5.写下你的实验体会
这次的实验其实也比较简单,最难的步骤应该是安装RYU。剩下的部分就是读懂代码,要自己补充的代码其实从示例代码中复制进去就好了。就是最近事情比较多,交的就比较晚了。