题目大意:有t组数据,每组数据给你n张海报(1<=n<=10000),下面n组数据分别给出每张海报的左右范围(1 <= l <= r <= 10000000),下一张海报会覆盖前一张海报,求最后可见(包括完全和不完全可见)的海报有几张。
例如:
1 5 1 4 2 6 8 10 3 4 7 10
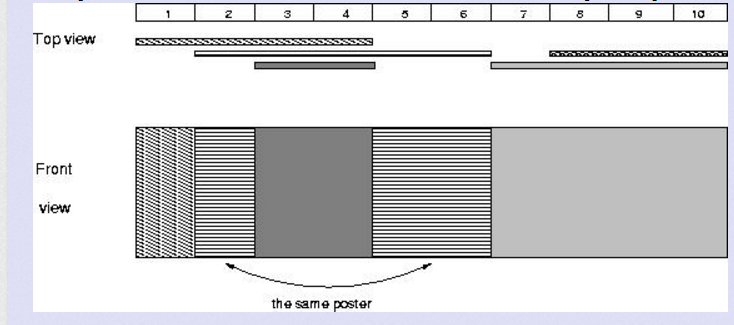
如上图所示,答案为4。
解题思路:其实这是一道区间染色问题,但是由于查找区间太大,显然直接建树会导致MLE,所以这里通过使用对区间的离散化来缩小查找范围。参考了一些大牛博客,简单说一下。
通俗点说,离散化就是压缩区间,使原有的长区间映射到新的短区间,但是区间压缩前后的覆盖关系不变。举个例子:
有一条1到10的数轴(长度为9),给定4个区间[2,4] [3,6] [8,10] [6,9]。现在我们抽取这4个区间的8个端点,2 4 3 6 8 10 6 9。删除相同点并对其升序排序,得2 3 4 6 8 9 10
然后建立映射
2 3 4 6 8 9 10
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
那么新的4个区间为 [1,3] [2,4] [5,7] [4,6],覆盖关系没有被改变。新数轴为1到7,即原数轴的长度从9压缩到6。
但是对于这道题目来说,这样简单的离散化是不行的,比如三张海报为:1~10、1~4、7~10,就有区间[1,10],[1,4],[7,10]。
按照上述方法离散化后的到区间[1,4],[1,2],[3,4]。答案为2,实际上答案为3。
因为上述做法忽略了区间[2,3]的存在,也就是原来的5~6这一块。
新的离散方法为:在相差大于1的数间加一个数(我选择加入两个数的中间值),这样的含义是用一个数字来表示其中间的那块区间,解决某块区间被忽略的问题。
例如在上面1 4 6 10中,
X[ 1 ] = 1, X[ 2 ]=2,X[ 3 ] = 4,X[ 4 ] = 5, X[ 5 ] = 7,X[ 6 ]=8, X[ 7 ] = 10
这样之后,第一次是1~7被染成1;第二次1~3被染成2;第三次5~7被染成3
最终,1~3为2,4为1,5~7为3,于是输出正确结果3。
代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #define LC(a) ((a<<1)) 5 #define RC(a) ((a<<1)+1) 6 #define MID(a,b) ((a+b)>>1) 7 using namespace std; 8 typedef long long ll; 9 const int N=5e4*4; 10 11 struct node{ 12 ll l,r; 13 ll color;//颜色为-1表示混合色 14 }tree[N]; 15 16 struct knode{ 17 ll l,r;//用来存储题目给定的区间 18 }tmp[N]; 19 20 ll ans[N];//记录颜色i是否存在 21 ll Hash[N];//存储坐标映射 22 ll point[N];//存储坐标序列 23 //下推 24 void pushdown(ll p){ 25 tree[RC(p)].color=tree[LC(p)].color=tree[p].color; 26 } 27 //上推 28 void pushup(ll p){ 29 tree[p].color=(tree[LC(p)].color==tree[RC(p)].color?tree[LC(p)].color:-1); 30 } 31 32 void build(ll p,ll l,ll r){ 33 tree[p].l=l; 34 tree[p].r=r; 35 tree[p].color=0; 36 if(l==r){ 37 return; 38 } 39 build(LC(p),l,MID(l,r)); 40 build(RC(p),MID(l,r)+1,r); 41 } 42 43 void update(ll p,ll l,ll r,ll color){ 44 if(r<tree[p].l||l>tree[p].r) 45 return; 46 if(l<=tree[p].l&&r>=tree[p].r){ 47 tree[p].color=color; 48 return; 49 } 50 //**释放lazy标记 51 if(tree[p].color!=-1){ 52 pushdown(p); 53 } 54 update(LC(p),l,r,color); 55 update(RC(p),l,r,color); 56 pushup(p); 57 } 58 59 void query(ll p,ll l,ll r){ 60 if(r<tree[p].l||l>tree[p].r) 61 return; 62 //纯色,不用再找下去 63 if(tree[p].color!=-1){ 64 ans[tree[p].color]=1; 65 return; 66 } 67 query(LC(p),l,r); 68 query(RC(p),l,r); 69 } 70 71 //二分查找 72 ll Bin_search(ll l,ll r,ll x){ 73 ll mid; 74 while(l<=r){ 75 mid=(l+r)/2; 76 if(x==Hash[mid]) return mid; 77 if(x<Hash[mid]) r=mid-1; 78 else if(x>Hash[mid]) l=mid+1; 79 } 80 return -1; 81 } 82 83 int main(){ 84 ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 85 ll t,n; 86 cin>>t; 87 while(t--){ 88 cin>>n; 89 //***对输入数据进行离散化 90 ll m1=0; 91 92 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 93 ll l,r; 94 cin>>tmp[i].l>>tmp[i].r; 95 point[++m1]=tmp[i].l; 96 point[++m1]=tmp[i].r; 97 } 98 sort(point+1,point+1+m1); 99 ll m2=0; 100 for(int i=1;i<=m1;i++){ 101 if(point[i]!=point[i-1]){ 102 if(point[i]-point[i-1]>1&&i!=1){ 103 Hash[++m2]=(point[i]+point[i-1])>>1; 104 Hash[++m2]=point[i]; 105 } 106 else 107 Hash[++m2]=point[i]; 108 } 109 } 110 //**建树 111 build(1,1,m2); 112 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 113 ll l=Bin_search(1,m2,tmp[i].l); 114 ll r=Bin_search(1,m2,tmp[i].r); 115 update(1,l,r,i); 116 } 117 memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans)); 118 query(1,1,m2); 119 ll cnt=0; 120 for(int i=1;i<=m2;i++){ 121 if(ans[i]){ 122 cnt++; 123 } 124 } 125 cout<<cnt<<endl; 126 } 127 }