WF4B1 的Procedural Activity 之InvokeMethod , InvokeMethod<T> 使用
InvokeMethod 调用方法

类名: System.Activities.Statements.InvokeMethod
基类: CodeActivity
文件: System.Activities.dll
类型:sealed
说明:1. 可以使用类方式, 对象方式调用方法
2. 可以调用实例方法,静态方法
3. 支持参数数组
4. 支持方法泛型参数
5. 支持out参数,ref 参数
6. 支持等待异步方法调用完成
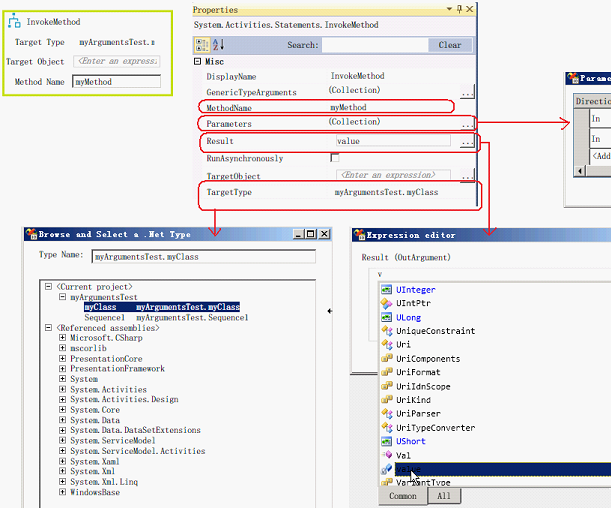
以类方式调用方法
这种方式,即使在同一个流程中,每调用一次,也会重新创建一次所要调用的类
|
|
例
1.定义[myClass]与[myMethod]方法,实现加法功能
2.定义In参数[inputV1,inputV2]与Out参数[value]
3.启动流程时传入[inputV1,inputV2]的值,
4.在流程中用[InvokeMethod]实现对[myClass.myMethod]的调用
5.用[WriteLine]的打印[value]值
调用方法类
namespace myArgumentsTest
{
public class myClass
{
public int myMethod(int v1, int v2)
{
return v1 + v2;
}
}
}
流程
<p:Activity mc:Ignorable=""
x:Class="myArgumentsTest.Sequence1"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/netfx/2009/xaml/activities/design"
xmlns:m="clr-namespace:myArgumentsTest;assembly=myArgumentsTest"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:p="http://schemas.microsoft.com/netfx/2009/xaml/activities"
xmlns:sad="clr-namespace:System.Activities.Debugger;assembly=System.Activities"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml">
<x:Members>
<x:Property Name="inputV1" Type="p:InArgument(x:Int32)" />
<x:Property Name="inputV2" Type="p:InArgument(x:Int32)" />
<x:Property Name="value" Type="p:OutArgument(x:Int32)" />
</x:Members>
<p:Sequence >
<p:InvokeMethod MethodName="myMethod" TargetType="m:myClass">
<p:InvokeMethod.Result>
<p:OutArgument x:TypeArguments="x:Int32">[value]</p:OutArgument>
</p:InvokeMethod.Result>
<p:InArgument x:TypeArguments="x:Int32">[inputV1]</p:InArgument>
<p:InArgument x:TypeArguments="x:Int32">[inputV2]</p:InArgument>
</p:InvokeMethod>
<p:WriteLine>[value.ToString()]</p:WriteLine>
</p:Sequence>
</p:Activity>
宿主
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Dictionary<string, object> inputCollection = new Dictionary<string, object>();
inputCollection.Add("inputV1", 123);
inputCollection.Add("inputV2", 456);
WorkflowInstance myInstance = new WorkflowInstance(new Sequence1(),inputCollection);
myInstance.Run();
System.Console.Read();
}
}
}
结果
以对象方式调用实例方法
这种方式,每次,都使用指定的对象调用,不会创建新对象
- TargetObject 属性 : 对象名,绑定到流程的参数上(浏览方式),不能与TargetType共存
- MethotName 属性 : 方法名 (字串方式)
- Parameters 属性 : 方法的参数,按方法参数顺序,可以绑定到流程的参数上
- Result 属性 : 方法的返回值,可以绑定到流程的参数上
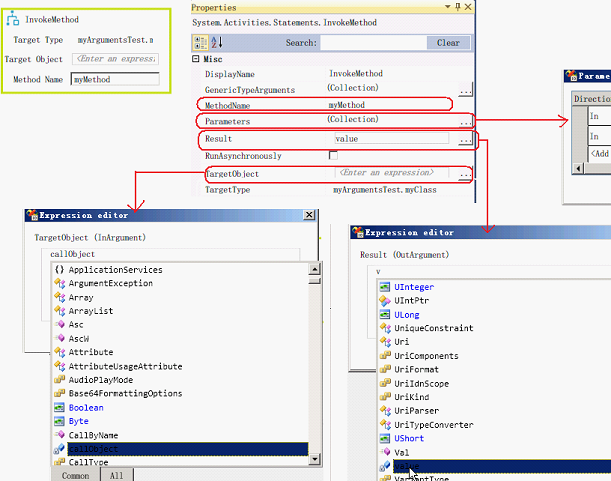
例
1.定义[myClass]与[myMethod]方法,实现加法功能
2.定义In参数[inputV1,inputV2]与Out参数[value]
3.定义In参数[callObject],类型为[myClass]
4.在外部实现一个[myClass]的子类[a],并[override myMethod]方法,本步只是为了测试是否兼容这种方式
5.启动流程时传入[inputV1,inputV2,callObject]的值,
6.在流程中用[InvokeMethod]实现对callObject]对象的[myMethod]调用
7.用[WriteLine]的打印[value]值
调用方法基类
namespace myArgumentsTest
{
public class myClass
{
public virtual int myMethod(int v1, int v2)
{
return v1 + v2;
}
}
}
流程
<p:Activity mc:Ignorable=""
x:Class="myArgumentsTest.Sequence1"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/netfx/2009/xaml/activities/design"
xmlns:m="clr-namespace:myArgumentsTest;assembly=myArgumentsTest"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:p="http://schemas.microsoft.com/netfx/2009/xaml/activities"
xmlns:sad="clr-namespace:System.Activities.Debugger;assembly=System.Activities"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml">
<x:Members>
<x:Property Name="inputV1" Type="p:InArgument(x:Int32)" />
<x:Property Name="inputV2" Type="p:InArgument(x:Int32)" />
<x:Property Name="value" Type="p:OutArgument(x:Int32)" />
<x:Property Name="callObject" Type="p:InArgument(m:myClass)" />
</x:Members>
<p:Sequence>
<p:InvokeMethod MethodName="myMethod">
<p:InvokeMethod.Result>
<p:OutArgument x:TypeArguments="x:Int32">[value]</p:OutArgument>
</p:InvokeMethod.Result>
<p:InvokeMethod.TargetObject>
<p:InArgument x:TypeArguments="m:myClass">[callObject]</p:InArgument>
</p:InvokeMethod.TargetObject>
<p:InArgument x:TypeArguments="x:Int32">[inputV1]</p:InArgument>
<p:InArgument x:TypeArguments="x:Int32">[inputV2]</p:InArgument>
</p:InvokeMethod>
<p:WriteLine>[value.ToString()]</p:WriteLine>
</p:Sequence>
</p:Activity>
宿主
public class a : myClass
{
public override int myMethod(int v1, int v2)
{
return (v1 + v2) * 10;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Dictionary<string, object> inputCollection = new Dictionary<string, object>();
inputCollection.Add("inputV1", 123);
inputCollection.Add("inputV2", 456);
inputCollection.Add("callObject", new a());
WorkflowInstance myInstance = new WorkflowInstance(new Sequence1(),inputCollection);
myInstance.Run();
System.Console.Read();
}
}
结果

调用静态方法
与[以类方式调用方法]的操作方式一样
- TargetType 属性 : 方法的类名(浏览方式),不能与TargetObject共存
- MethotName 属性 : 方法名 (字串方式)
- Parameters 属性 : 方法的参数,按方法参数顺序,可以绑定到流程的参数上
- Result 属性 : 方法的返回值,可以绑定到流程的参数上
例
调用方法
public class myClass
{
public myClass()
{
System.Console.WriteLine("new");
}
public static int add(int v1, int v2)
{
return v1 + v2;
}
}
流程

宿主
WorkflowInstance myInstance = new WorkflowInstance(new Sequence1());
myInstance.OnCompleted = delegate(WorkflowCompletedEventArgs e) { System.Console.WriteLine("Completed"); };
myInstance.Run();
System.Console.Read();
结果
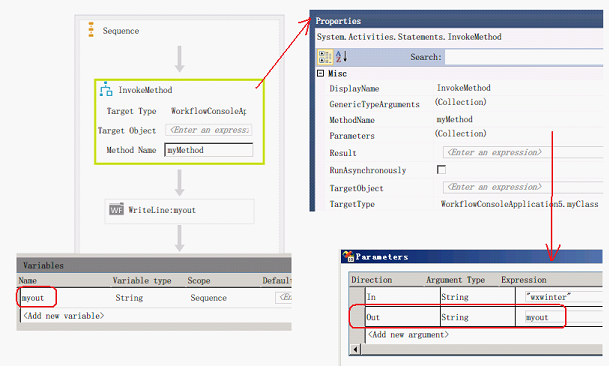
调用out参数方法
设置[Parameters] 集合,[Direction] 设为 [Out]
例
调用方法
public class myClass
{
public void myMethod(string v1,out string v2)
{
v2 = v1 + "wxd";
}
}
流程
宿主
WorkflowInstance myInstance = new WorkflowInstance(new Sequence1());
myInstance.OnCompleted = delegate(WorkflowCompletedEventArgs e) { System.Console.WriteLine("Completed"); };
myInstance.Run();
System.Console.Read();
结果
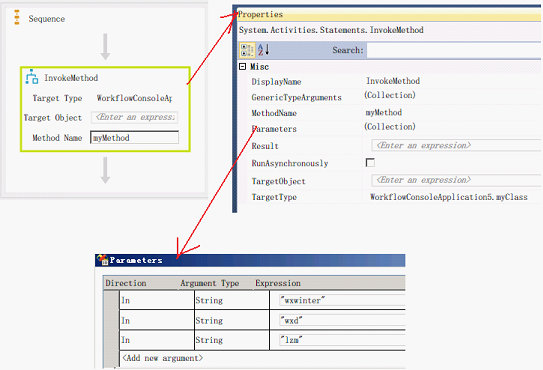
调用params参数方法
设置[Parameters] 集合,以指方法的参数
例
调用方法
public class myClass
{
public void myMethod(params string[] list)
{
for (int i = 0; i < list.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(list[i]);
}
}
}
流程
宿主
WorkflowInstance myInstance = new WorkflowInstance(new Sequence1());
myInstance.OnCompleted = delegate(WorkflowCompletedEventArgs e) { System.Console.WriteLine("Completed"); };
myInstance.Run();
System.Console.Read();
结果
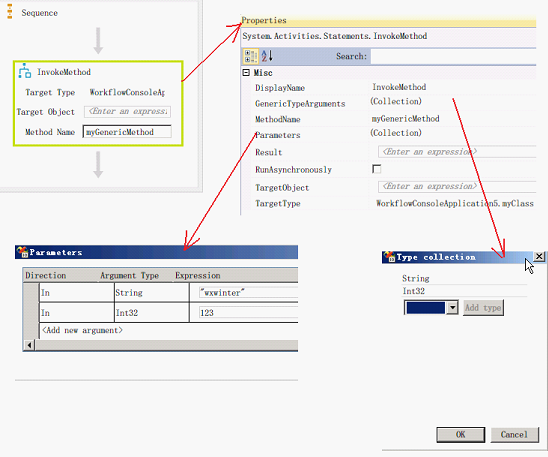
调用范型方法
[InvokeMethod ]可以调用范型方法,设置[GenericTypeArguments]集合,以指定范型方法的范型参数
设置[Parameters] 集合,以指方法的参数
例
调用方法
public class myClass
{
public void myGenericMethod<T1, T2>(T1 param1, T2 param2)
{
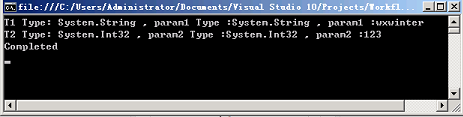
Console.WriteLine("T1 Type: {0} , param1 Type :{1} , param1 :{2}", typeof(T1), param1.GetType(), param1.ToString());
Console.WriteLine("T2 Type: {0} , param2 Type :{1} , param2 :{2}", typeof(T2), param2.GetType(), param2.ToString());
}
}
流程
宿主
WorkflowInstance myInstance = new WorkflowInstance(new Sequence1());
myInstance.OnCompleted = delegate(WorkflowCompletedEventArgs e) { System.Console.WriteLine("Completed"); };
myInstance.Run();
System.Console.Read();
结果
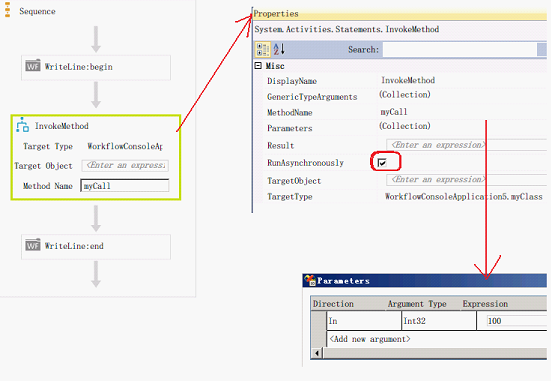
等待调用的方法中的线程
当[InvokeMethod]所调用的方法中的线程时,可以将[InvokeMethod]的[RunAsynchronously]属性设为[True]以实现等待调用的方法中的线程完成.
要使[RunAsynchronously]属性有效,需要用如下方式设计方法
1.为要实现该功能的方法添加如下两个方法
[IAsyncResult Begin[原使方法] ([原使方法参数], AsyncCallback callback, object asyncState)]
void End[原使方法] (IAsyncResult r)
2.当[RunAsynchronously]属性设为[False]时, [InvokeMethod]调用[原使方法]
3.当[RunAsynchronously]属性设为[True]时, [InvokeMethod]调用对应的[Begin]与[End]方法
4.如果没的提供与[调用方法]对应的[Begin]与[End]方法, [InvokeMethod]将忽略[RunAsynchronously]属性的值
例
调用方法
public class myClass
{
AsyncCallback callback;
IAsyncResult asyncResult;
int value;
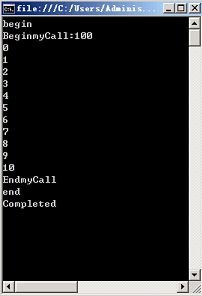
public void myCall(int value)
{
System.Console.WriteLine("myCall:{0}",value);
}
public IAsyncResult BeginmyCall(int value, AsyncCallback callback, object asyncState)
{
System.Console.WriteLine("BeginmyCall:{0}", value);
this.value = value;
this.callback = callback;
this.asyncResult = new myAsyncResult() { AsyncState = asyncState };
Thread thread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(myProcessThread));
thread.Start();
return this.asyncResult;
}
public void EndmyCall(IAsyncResult r)
{
Console.WriteLine("EndmyCall");
}
public void myProcessThread()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
{
System.Console.WriteLine(i);
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(500);
}
this.callback(this.asyncResult);
}
}
class myAsyncResult : IAsyncResult
{
public object AsyncState
{ get; set; }
public WaitHandle AsyncWaitHandle
{ get; set; }
public bool CompletedSynchronously
{ get { return true; } }
public bool IsCompleted
{ get { return true; } }
}
宿主
WorkflowInstance myInstance = new WorkflowInstance(new Sequence1());
myInstance.OnCompleted = delegate(WorkflowCompletedEventArgs e) { System.Console.WriteLine("Completed"); };
myInstance.Run();
System.Console.Read();
[RunAsynchronously]属性设为[False]
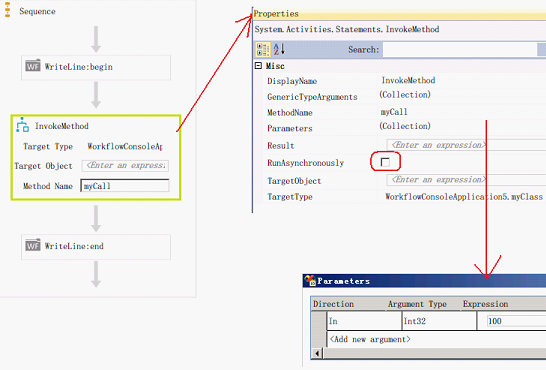

[RunAsynchronously]属性设为[True]
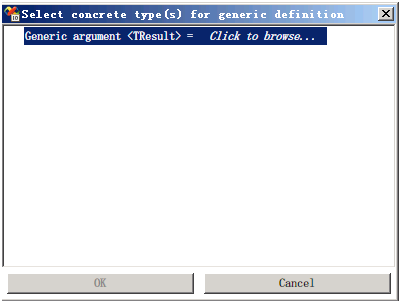
InvokeMethod<T> 调用方法

类名: System.Activities.Statements.InvokeMethod<TResult>
基类: CodeActivity<TResult>
文件: System.Activities.dll
类型:sealed
说明:1.使用方式与[InvokeMethod]想同
2.使用[InvokeMethod<T>]时,会要求指定方法的返回值类型