Thread的start()方法
public class ThreadTest extends Thread{ public void run(){ try { for(int i =0 ;i<5;i++) { Thread.sleep(1000); //Thread.currentThread().xxx() 表示执行当前代码的线程方法 //this.xxx 当前线程的方法 System.out.println("Thread = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args){ ThreadTest th = new ThreadTest(); th.start(); //main也相当于一个线程 for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("Thread = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
执行结果

意味着cpu执行线程的顺序是无序的,随机的
那么start()方法对于线程的执行顺序是否有影响呢?
public class ThreadTest extends Thread{ public void run(){ //Thread.currentThread().xxx() 表示执行当前代码的线程方法 System.out.println("Thread = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } public static void main(String[] args){ ThreadTest th = new ThreadTest(); ThreadTest th0 = new ThreadTest(); ThreadTest th1 = new ThreadTest(); ThreadTest th2 = new ThreadTest(); ThreadTest th3 = new ThreadTest(); th.start(); th0.start(); th1.start(); th2.start(); th3.start(); } }
结果
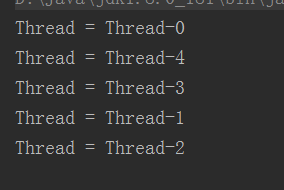
欧豁,start()方法的启动顺序和最终线程的执行顺序是不同的
看下源码public synchronized void start() { /** * This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"
* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added * to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM. * * A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW". */ if (threadStatus != 0) throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); /* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started * so that it can be added to the group's list of threads * and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */ group.add(this); boolean started = false; try {
start0(); started = true; } finally { try { if (!started) { group.threadStartFailed(this); } } catch (Throwable ignore) { /* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then it will be passed up the call stack */ } } }
有个start0()的本地方法,同时还有一个registerNatives()
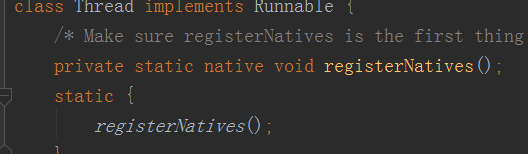
registerNatives()方法就是注册本地方法让Thread使用
有个Thread.c文件
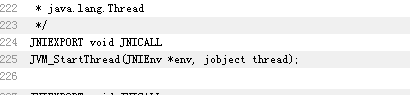
vmSymbols.hpp中发现

所以执行顺序是 start()-->start0()--->JVM_StratThread---->run()_method_name
run()
public class ThreadTest extends Thread{ public void run(){ for(int i=1;i<5;i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("Thread = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args){ ThreadTest th = new ThreadTest(); th.run(); for(int i=1; i<5;i++){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("Thread = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
结果总共执行了8次
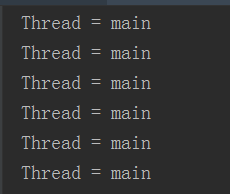
所以用run()启动没有多线程的效果
isAlive() 只有线程在启动的过程中,返回true
getId() 获得线程的id
getName() 获得线程名,上边的代码结果中的Thread-0就是默认的,也可以在new的时候指定线程的名字
getPriority()和setPriority(int newPriority) 获取/设置优先级,优先级越高越容易执行,默认优先级是5,优先级可以被继承
----------------------------------------------------------未完待续----------------------------------------------------------------------------