什么是反向代理?
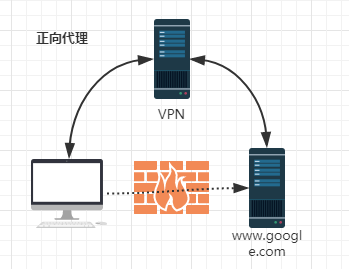
我们看图说话,我们用电脑访问谷歌,由于防火墙的存在,我们并不能直接访问。需要借助VPN来实现。这就是一个简单的正向代理的例子。这里你能够发现,正向代理“代理”的是客户端,而且客户端是知道目标的,而目标是不知道客户端是通过VPN访问的。

再来看反向代理,我们平时上百度查资料,基本都能得到我们想要的。所以我们就会说百度什么都知道。真的是百度什么都知道吗???
当然不是,百度只是去找知道的人告诉他答案,然后再来告诉我们的而已。他只是个传话的,也就是代理人。在这个过程中,那些知道答案的人(服务端)是不知道谁访问的,就知道是百度来问自己的。对于客户端来说,我们只问百度就行,由你百度想办法弄到答案告诉我就行。在这里,反向代理“代理”的是服务端。刚好与上文的正向代理相反。
应用
好了,我们知道了反向代理的概念,我们就要用啊。
准备一个tomcat启动项目。或者springboot项目运行起来。
这里我建议用springboot项目,因为啥呀?一个字,“快”啊!
启动后,保证能够通过输入地址:localhost:8084/index/能够得到结果。
我们要做的就是,我们在不知道这个地址的情况下,通过访问nginx也能得到结果,对不对?这样就实现了我们的反向代理了。
实现
我们的要求明确了,那怎么实现呢?
修改nginx/conf/nginx.conf文件
location / {proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8084;}
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8084; 表示把请求都交给http://127.0.0.1:8111来处理

1 #user nobody; 2 worker_processes 1; 3 4 #error_log logs/error.log; 5 #error_log logs/error.log notice; 6 #error_log logs/error.log info; 7 8 #pid logs/nginx.pid; 9 10 events { 11 worker_connections 1024; 12 } 13 14 http { 15 include mime.types; 16 default_type application/octet-stream; 17 18 #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' 19 # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' 20 # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; 21 22 #access_log logs/access.log main; 23 24 sendfile on; 25 #tcp_nopush on; 26 27 #keepalive_timeout 0; 28 keepalive_timeout 65; 29 30 #gzip on; 31 32 server { 33 listen 80; 34 server_name localhost; 35 36 #charset koi8-r; 37 38 #access_log logs/host.access.log main; 39 40 location / { 41 proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8084; 42 } 43 44 #error_page 404 /404.html; 45 46 # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html 47 # 48 error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; 49 location = /50x.html { 50 root html; 51 } 52 53 # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 54 # 55 #location ~ .php$ { 56 # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; 57 #} 58 59 # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 60 # 61 #location ~ .php$ { 62 # root html; 63 # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; 64 # fastcgi_index index.php; 65 # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; 66 # include fastcgi_params; 67 #} 68 69 # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root 70 # concurs with nginx's one 71 # 72 #location ~ /.ht { 73 # deny all; 74 #} 75 } 76 77 # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration 78 # 79 #server { 80 # listen 8000; 81 # listen somename:8080; 82 # server_name somename alias another.alias; 83 84 # location / { 85 # root html; 86 # index index.html index.htm; 87 # } 88 #} 89 90 # HTTPS server 91 # 92 #server { 93 # listen 443 ssl; 94 # server_name localhost; 95 96 # ssl_certificate cert.pem; 97 # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; 98 99 # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; 100 # ssl_session_timeout 5m; 101 102 # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; 103 # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; 104 105 # location / { 106 # root html; 107 # index index.html index.htm; 108 # } 109 #} 110 111 }
然后重新启动nginx
nginx -s reload
访问:127.0.0.1:80/context
注意:如果你改过了nginx的端口,比如前文说的9090,那也要将80改为9090,后面的context是访问接口的路由,该是什么就是什么。
这样就可以得到想要的结果了。
意义何在
既然可以通过127.0.0.1:8084/context访问,为啥要通过访问127.0.0.1:9090/context来代理呢?
这里就涉及到下面的内容了,静待文件的处理和负载均衡。
