原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yoainet/archive/2012/03/15/2398059.html
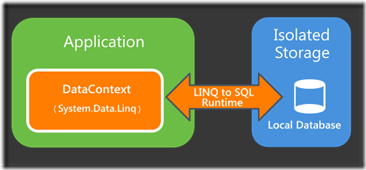
Windows Phone OS 7.1,可以将关系数据存储在驻留在应用程序独立存储容器的本地数据库中。Windows Phone 应用程序使用 LINQ to SQL 执行所有数据库操作;LINQ to SQL 用于定义数据库架构、选择数据,并将更改保存到驻留在独立存储中的基础数据库文件;提到LINQ to SQL,你会不会感到欣喜,It’s amazing在window phone里我们居然可以这样来持久化数据 :),本文将带领大家一同建立第一个windows phone本地数据库应用--联系人管理。
本系列包括以下:
1.数据库创建
2.从独立存储中找到数据库文件并copy到pc上
3.复用2中的数据库(其他程序使用2中的数据库文件或者使用2中初始的数据)
一、数据库实体表创建
1.简介:
windwo phone之前虽然不存在内置数据库的支持功能,但是可以使用一些开源项目,它们模仿传统的数据库行为将数据持久保存到独立存储中;
| Windows Phone7 DataBase http://winphone7db.codeplex.com | 项目实现了一个基于独立存储的window phone7数据库。该数据库由表组成,每一个表都支持任意数量的列 |
| Wp7 sqliteClient Preview http://sqlitewindowsphone.codeplex.com | 这是sqlite数据库引擎的window phone7实现 |
| Perst http://www.mcobject.com/perst | Perst是来自mcobject公司的一个商业的面向对象数据库系统,它可以再window phone或silverlight应用程序中搞笑的存储和检索数据 |
现在我们来介绍mango支持的独立存储中的本地数据库,而且使用linq to sql来管理和操作数据集
Linq to sql主要是通过数据上下文(DataContext)来映射我们的Model和DB table的结构,在运行时负责桥接对象(Model)和数据(Table)部分之间;数据上下文其实是数据库对象的一种代理,在C#中我们可以简单的通过创建一个Linq to sql数据上下文后,从服务器资源管理器中直接将DB(MS SQL)里的Table、View、Stroreed Procedure、Function直接拖到设计窗口里,当然vs会自动帮我们产生后台Model直接的关系;但是这些操作在mango 里是不支持的,因为数据库物理文件目前微软并没有提供手动创建的方法;
2.数据库创建:
linq to sql中对象关系功能是根据linq to sql中的实体映射详细信息来创建映射到对应数据上下文,所以我们需要先创建数据上下文和实体;
要创建数据上下文和数据库实体关系,需要添加对程序集System.Data.Linq的应用,我们实体model的特性如Table、Column都来自这个程序集
2.0创建数据上下文
首先新建一个类ContactorDataContext,然后让这个类派生自System.Data.Linq.DataContext,并重写构造函数
/// <summary>
/// 数据库上下文
/// </summary>
public class ContactorDataContext : DataContext
{
public ContactorDataContext(string connectionString)
: base(connectionString)
{ }
}
1 | <br><br> |
2.1创建实体model
一个实体model最终会映射为一个数据库表(必须有Table特性),实体的属性最终会映射为对应的列(必须有对应的Column)特性;
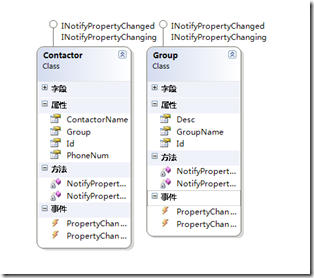
实体类图如下:
代码:
 View Code
View Code [Table]
public class Contactor : INotifyPropertyChanged, INotifyPropertyChanging
{
/// <summary>
/// Id自动增长
/// </summary>
private int _id;
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true, IsDbGenerated = true, DbType = "INT NOT NULL Identity", CanBeNull = false, AutoSync = AutoSync.OnInsert)]
public int Id
{
get
{
return _id;
}
set
{
if (_id != value)
{
NotifyPropertyChanging("Id");
_id = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged("Id");
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 联系人
/// </summary>
private string _contactorName;
[Column]
public string ContactorName
{
get
{
return _contactorName;
}
set
{
if (_contactorName != value)
{
NotifyPropertyChanging("ContactorName");
_contactorName = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged("ContactorName");
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 联系电话
/// </summary>
private string _phoneNum;
[Column]
public string PhoneNum
{
get
{
return _phoneNum;
}
set
{
if (_phoneNum != value)
{
NotifyPropertyChanging("PhoneNum");
_contactorName = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged("PhoneNum");
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 所属组
/// </summary>
[Column]
internal int _groupId;
private EntityRef<Group> _group;
[Association(Storage = "_group", ThisKey = "_groupId", OtherKey = "Id", IsForeignKey = true)]
public Group Group
{
get { return _group.Entity; }
set
{
NotifyPropertyChanging("Group");
_group.Entity = value;
if (value != null)
{
_groupId = value.Id;
}
NotifyPropertyChanging("Group");
}
}
#region INotifyPropertyChanged Members
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
// Used to notify the page that a data context property changed
private void NotifyPropertyChanged(string propertyName)
{
if (PropertyChanged != null)
{
PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
#endregion
#region INotifyPropertyChanging Members
public event PropertyChangingEventHandler PropertyChanging;
// Used to notify the data context that a data context property is about to change
private void NotifyPropertyChanging(string propertyName)
{
if (PropertyChanging != null)
{
PropertyChanging(this, new PropertyChangingEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
#endregion
}
[Table]
public class Group : INotifyPropertyChanged, INotifyPropertyChanging
{
/// <summary>
/// 编号,自动增长
/// </summary>
private int _id;
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true, IsDbGenerated = true, DbType = "INT NOT NULL Identity", CanBeNull = false, AutoSync = AutoSync.OnInsert)]
public int Id
{
get
{
return _id;
}
set
{
if (_id != value)
{
NotifyPropertyChanging("Id");
_id = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged("Id");
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 分组名称
/// </summary>
private string _groupName;
[Column]
public string GroupName
{
get
{
return _groupName;
}
set
{
if (_groupName != value)
{
NotifyPropertyChanging("GroupName");
_groupName = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged("GroupName");
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 分组描述
/// </summary>
private string _desc;
[Column]
public string Desc
{
get
{
return _desc;
}
set
{
if (_desc != value)
{
NotifyPropertyChanging("Desc");
_desc = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged("Desc");
}
}
}
#region INotifyPropertyChanged Members
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
// Used to notify the page that a data context property changed
private void NotifyPropertyChanged(string propertyName)
{
if (PropertyChanged != null)
{
PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
#endregion
#region INotifyPropertyChanging Members
public event PropertyChangingEventHandler PropertyChanging;
// Used to notify the data context that a data context property is about to change
private void NotifyPropertyChanging(string propertyName)
{
if (PropertyChanging != null)
{
PropertyChanging(this, new PropertyChangingEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
#endregion
}
2.2在DataContext中添加数据集
 View Code
View Code /// <summary>
/// 数据库上下文
/// </summary>
public class ContactorDataContext : DataContext
{
public ContactorDataContext(string connectionString)
: base(connectionString)
{ }
/// <summary>
/// 联系人表
/// </summary>
public Table<Contactor> Contactors;
/// <summary>
/// 分组表
/// </summary>
public Table<Group> Groups;
}
3.应用启动时初始化数据库
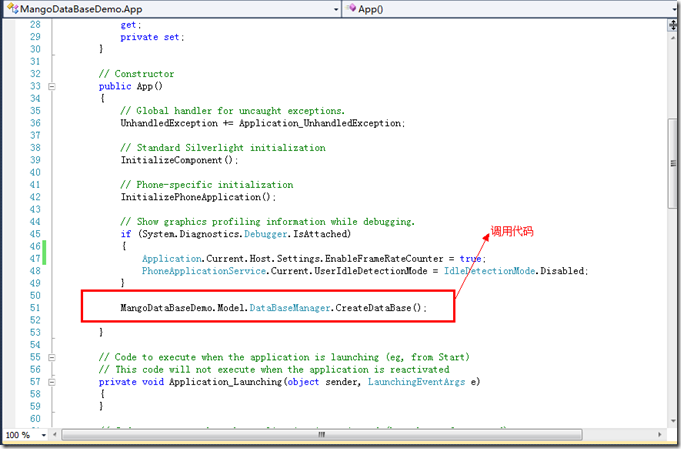
在app.xaml.cs的构造函数中创建数据库,初始化数据库只需要创建对应DataContext,并调用CreateDatabase()方法就可以了;
//创建数据库
using (ContactorDataContext db = new ContactorDataContext(DBConnectionString))
{
if (db.DatabaseExists() == false)
{
// 创建数据库
db.CreateDatabase();
//初始化数据
InitDefaultData();
}
}
为了方便管理数据库和数据库model的管理,我们创建对应的DBManager类,负责管理数据库的创建,默认数据的初始化
DataBaseManager代码:
 View Code
View Code public class DataBaseManager
{
public readonly static string DBConnectionString = "Data Source=isostore:/MyContactor.sdf";
/// <summary>
/// 创建数据库
/// </summary>
public static void CreateDataBase()
{
//创建数据库
using (ContactorDataContext db = new ContactorDataContext(DBConnectionString))
{
if (db.DatabaseExists() == false)
{
// 创建数据库
db.CreateDatabase();
//初始化数据
InitDefaultData();
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 初始化数据
/// </summary>
public static void InitDefaultData()
{
ContactorDataContext db = new ContactorDataContext(DBConnectionString);
//添加三个分组
db.Groups.InsertOnSubmit(new Group { GroupName = "好友" });
db.Groups.InsertOnSubmit(new Group { GroupName = "工作" });
db.Groups.InsertOnSubmit(new Group { GroupName = "家庭" });
db.SubmitChanges();
}
/// <summary>
/// 数据库上下文
/// </summary>
private static ContactorDataContext _contactorDataContext;
public static ContactorDataContext ContactorDataContext
{
get {
if(_contactorDataContext==null)
{
_contactorDataContext = new ContactorDataContext(DBConnectionString);
}
return _contactorDataContext;
}
}
}
好了,那么我们在app.xaml.cs构造函数去调用下就ok了..
对于测试ui很简单,我使用了Pivot,两个PivotItem分别显示联系人和联系人分组,两个PivotItem用于添加分组和添加联系人,项目使用mvvm,关于mvvm使用可以看我之前的mvvm
介绍; 具体代码可以再demo里查看..
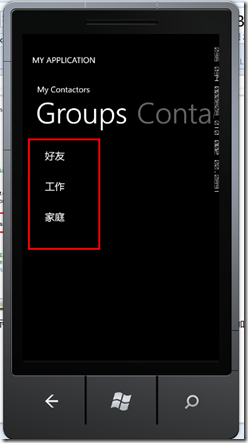
启动程序我们可以看到已经有了好友、工作、家庭三个分组了,这是因为在创建DataBase时,我们调用了InitDefaultData()方法,这个方法会向数据库里添加3个默认分组;
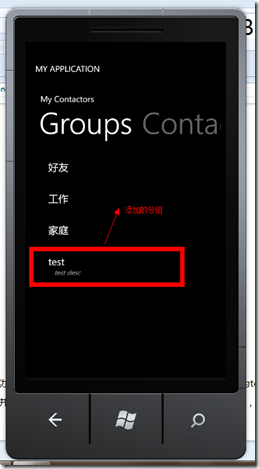
这就表明我们创建数据库和向数据库里添加数据成功;接着将pivot移到添加分组项,添加一个新的分组名称为test,描述为test desc,点击save后再回到分组列表
会看到我们添加的test 分组已经再列表里,当然这并不能说明我们确实保存成功了;谁知道是否真的持久化了,那我们退出该应用(一直按back就可以了)
然后再次打开应用,这时候看到分组列表:
我们的test在分组列表里,这才是说明之前的保存时真的持久化了;
到这里,我们已经完整的创建好了数据库,进行了读写操作(关于linq to sql的增、删、改、查方法,这里不做过多解释)
详情可以运行附件的demo。