目录
A - Can't Wait for Holiday
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
typedef long long LL;
string s;
int main() {
cin >> s;
if (s == "SAT") cout << 1 << endl;
if (s == "FRI") cout << 2 << endl;
if (s == "THU") cout << 3 << endl;
if (s == "WED") cout << 4 << endl;
if (s == "TUE") cout << 5 << endl;
if (s == "MON") cout << 6 << endl;
if (s == "SUN") cout << 7 << endl;
return 0;
}
B - ROT N
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
typedef long long LL;
int n;
string s;
int main() {
cin >> n >> s;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
cout << char((s[i] - 'A' + n) % 26 + 'A');
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
C - Buy an Integer
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
typedef long long LL;
LL A, B, X;
int main() {
cin >> A >> B >> X;
int len = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
if (A * (LL)pow(10, i - 1) + B * (LL)i > X) {
len = i - 1;
break;
}
}
if (len == 0)
cout << 0 << endl;
else if (len >= 10 || len == -1) {
cout << 1000000000 << endl;
} else {
X -= B * len;
if (X / A > 1e9)
cout << 1000000000 << endl;
else
cout << min(X / A, (LL)pow(10, len ) - 1) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
D - Coloring Edges on Tree
给出一个n个节点的树,问需要多少颜色才能使得每个点连的边都是不同的颜色,并给出一种涂色方案
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
typedef long long LL;
int n, cnt;
struct node {
int u, v;
int color;
} E[N];
vector<pair<int,int>> mp[N];
void dfs(int now, int fa, int color) {
int last = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < mp[now].size(); i++) {
int ne = mp[now][i].first;
int id = mp[now][i].second;
if (ne == fa) continue;
int flag = 1;
for (int j = last+1; j <= cnt; j++) {
if (j == color) continue;
E[id].color = j;
flag = 0;
break;
}
if (flag) {
cnt++;
E[id].color = cnt;
}
last = E[id].color;
dfs(ne, now, E[id].color);
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &E[i].u, &E[i].v);
mp[E[i].u].push_back({E[i].v,i});
mp[E[i].v].push_back({E[i].u,i});
}
dfs(1, 0, 0);
printf("%d
", cnt);
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) {
printf("%d
", E[i].color);
}
return 0;
}
E - Rem of Sum is Num
给出一个数组,找出符合以下条件的子区间的个数:
这个子区间的和 % k ==(这个区间的数字个数)。
类似的题目都要想到处理前缀和,然后对前缀和取模
但是又不能枚举,考虑对式子进行转化:
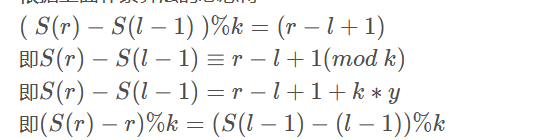
式子来自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43408238/article/details/103484868
所以转化为寻找如上式子的子区间个数,但是要注意取模不可能超过k,所以需要利用类似滑动窗口的东西,限制个数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
typedef long long LL;
LL f[N];
map<LL, LL> mp;
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%lld", &f[i]);
f[i] += f[i - 1];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
f[i] = (f[i] - i) % m;
}
m--;
m = min(m, n);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
mp[f[i]]++;
}
LL sum = 0;
for (int i = m; i <= n; ++i) {
mp[f[i]]++;
sum += mp[f[i - m]] - 1;
mp[f[i - m]]--;
}
for (int i = n - m + 1; i <= n; ++i) {
sum += mp[f[i]] - 1;
mp[f[i]]--;
}
cout << sum;
return 0;
}
F - Sugoroku
单调队列优化DP
给出一个长度为n+1的01字符串,0可以走,1不能走,现在从0号点走到n号点,每次可以跳最多m步,问最少跳几次可以到达n点,输出每次跳的步数
dp求解,类似lis的更新方法:
dp[i]=min(dp[j]+1,dp[i])
但是n为1e5,无法采用n2的算法,所以可以利用单调队列维护长度为m的区间内的dp值的最小值,然后直接转化即可
至于输出路径,利用pre数组维护即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
typedef long long LL;
int n, m;
int dp[N], q[N],pre[N];
string s;
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
cin >> s;
int hh = 0, tt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
if (s[i] == '0') dp[i] = 1, pre[i] = 0;
else dp[i] = 0x3f3f3f3f;
if (hh <= tt && i - m + 1 > q[hh]) hh++;
while (hh <= tt && dp[q[tt]] > dp[i]) tt--;
q[++tt] = i;
}
hh++;
for (int i = m+1; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = 0x3f3f3f3f;
if (s[i] == '0') dp[i] = min(dp[q[hh]] + 1,dp[i]),pre[i]=q[hh];
else dp[i] = 0x3f3f3f3f;
if (hh <= tt && i - m + 1 > q[hh]) hh++;
while (hh <= tt && dp[q[tt]] > dp[i]) tt--;
q[++tt] = i;
}
stack<int> st;
//for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) cout << pre[i] << ' ';
//cout << endl;
if (dp[n] != 0x3f3f3f3f) {
int now = n;
while (now!=0) {
st.push(now - pre[now]);
now = pre[now];
}
while (!st.empty()) {
cout << st.top() << ' ';
st.pop();
}
cout << endl;
} else
cout << -1 << endl;
return 0;
}