1、基础概念
当两个或以上对共享内存操作的并发线程中,如果有一个改变数据,又没有同步机制的条件下,就会产生竞争条件,可能会导致执行无效代码、bug等异常行为。
竞争条件最简单的解决方法是使用锁。锁的操作非常简单,当一个线程需要访问部分共享内存时,它必须先获得锁才能访问。此线程对这部分共享资源使用完成之后,释放锁,然后其他线程才可再次获得锁并访问这部分资源。
然而,在实际使用中,这个方法经常导致死锁现象。当不同线程要求得到同一个锁时,死锁就会发生,此时程序不会继续执行,因为他们互相拿着对方需要的锁。
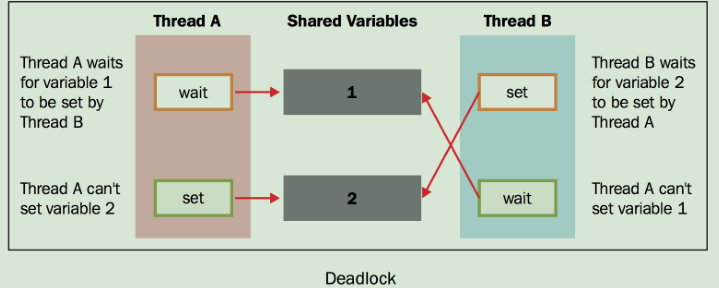
造成死锁的原因:线程A在使用资源2,线程B在使用资源1,如果在没有释放锁时,线程A又需要资源1,线程B又需要资源2,但是两个资源的锁都是被占用的,而且在对方的锁释放之前都处于等待且不释放锁的状态,此时就会造成死锁。
使用锁来解决同步问题是一个可行的方式,但是也存在潜在的问题。
2、使用Lock进行线程同步
示例:
# coding : utf-8 import threading shared_resource_with_lock = 0 shared_resource_with_no_lock = 0 count = 100000 shared_resource_lock = threading.Lock() # has lock def increment_with_lock(): global shared_resource_with_lock for i in range(count): shared_resource_lock.acquire() shared_resource_with_lock += 1 shared_resource_lock.release() def decrement_with_lock(): global shared_resource_with_lock for i in range(count): shared_resource_lock.acquire() shared_resource_with_lock -= 1 shared_resource_lock.release() # has no lock def increment_without_lock(): global shared_resource_with_no_lock for i in range(count): shared_resource_with_no_lock += 1 def decrement_without_lock(): global shared_resource_with_no_lock for i in range(count): shared_resource_with_no_lock -= 1 if __name__ == "__main__": t1 = threading.Thread(target=increment_with_lock) t2 = threading.Thread(target=decrement_with_lock) t3 = threading.Thread(target=increment_without_lock) t4 = threading.Thread(target=decrement_without_lock) t1.start() t2.start() t3.start() t4.start() t1.join() t2.join() t3.join() t4.join() print("the value of shared with lock is %s" %shared_resource_with_lock) print("the value of shared with no lock is %s" % shared_resource_with_no_lock)
执行结果:
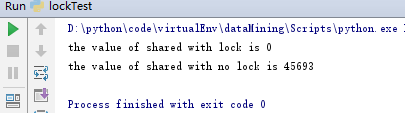
在有锁的情况下,我们会得到挣钱的结果,而没有锁的情况下,往往会出现错误的结果。
3、锁状态
锁有两种状态:locked(被某一线程拿到)和unlocked(可用状态)
操作锁的方式:acquire()和release()
如果状态是unlocked,可以调用acquire将状态改为locked
如果状态是locked,acquire会被block直到另一个线程调用release释放锁
如果状态是unlocked,调用release会导致RuntimError异常
如果状态是locked,可以调用release将状态改为unlocked