首先,我们从这个属性的名称中,可以很直观的看出它的作用,这个属性就是来设置窗口软键盘的交互模式的。
android:windowSoftInputMode属性一共有10个取值,分别是:
stateUnspecified,stateUnchanged,stateHidden,stateAlwaysHidden,stateVisible,stateAlwaysVisible,adjustUnspecified,adjustResize,adjustPan、adjustNothing。
我们设置属性的时候,可以在这10个值里面选择一个,也可以用"state...|adjust"的形式进行设置。那么,这些取值到底是怎么影响到软键盘与窗口之间的交互的呢?下面,我们就一个个的测试这10个取值,到底是如何影响软键盘的显示的。
1.stateUnspecified
中文意思是未指定状态,当我们没有设置android:windowSoftInputMode属性的时候,软件默认采用的就是这种交互方式,系统会根据界面采取相应的软键盘的显示模式,比如,当界面上只有文本和按钮的时候,软键盘就不会自动弹出,因为没有输入的必要。那么,当界面上出现了获取了焦点的输入框的时候,软键盘会不会自动的弹出呢?这个还真不一定!比如,在下面的这个界面布局中,软键盘并不会自动弹出。

就是说,默认的,在这种界面情况下,系统并不确定用户是否需要软键盘,因此不会自动弹出。但是,为什么说不一定呢?这是因为,如果我们在这个布局的外面,包裹上一个
ScrollView,软键盘就会自动的弹出来了!
如下,在这种布局文件下,软键盘会自动的弹出
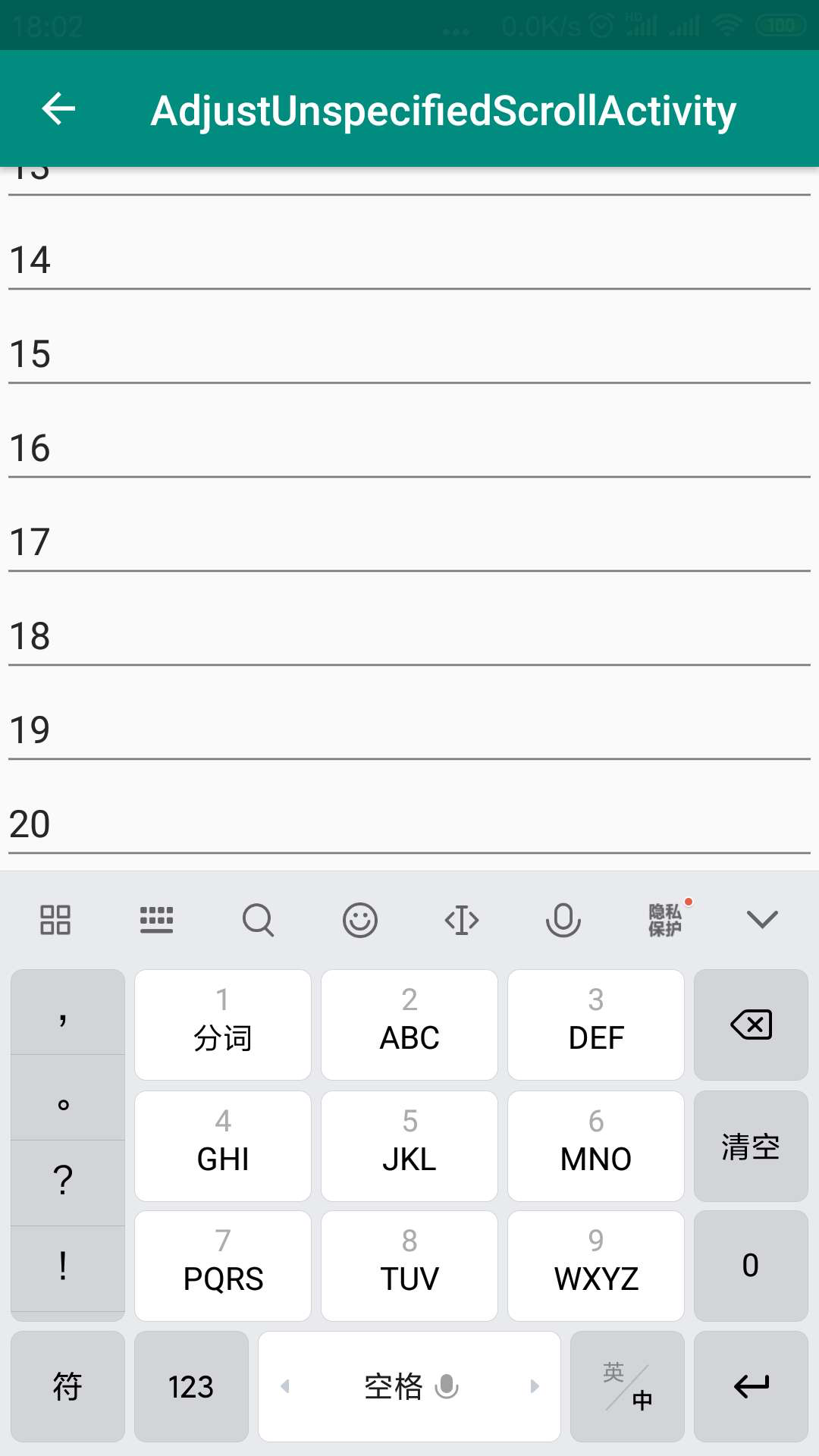
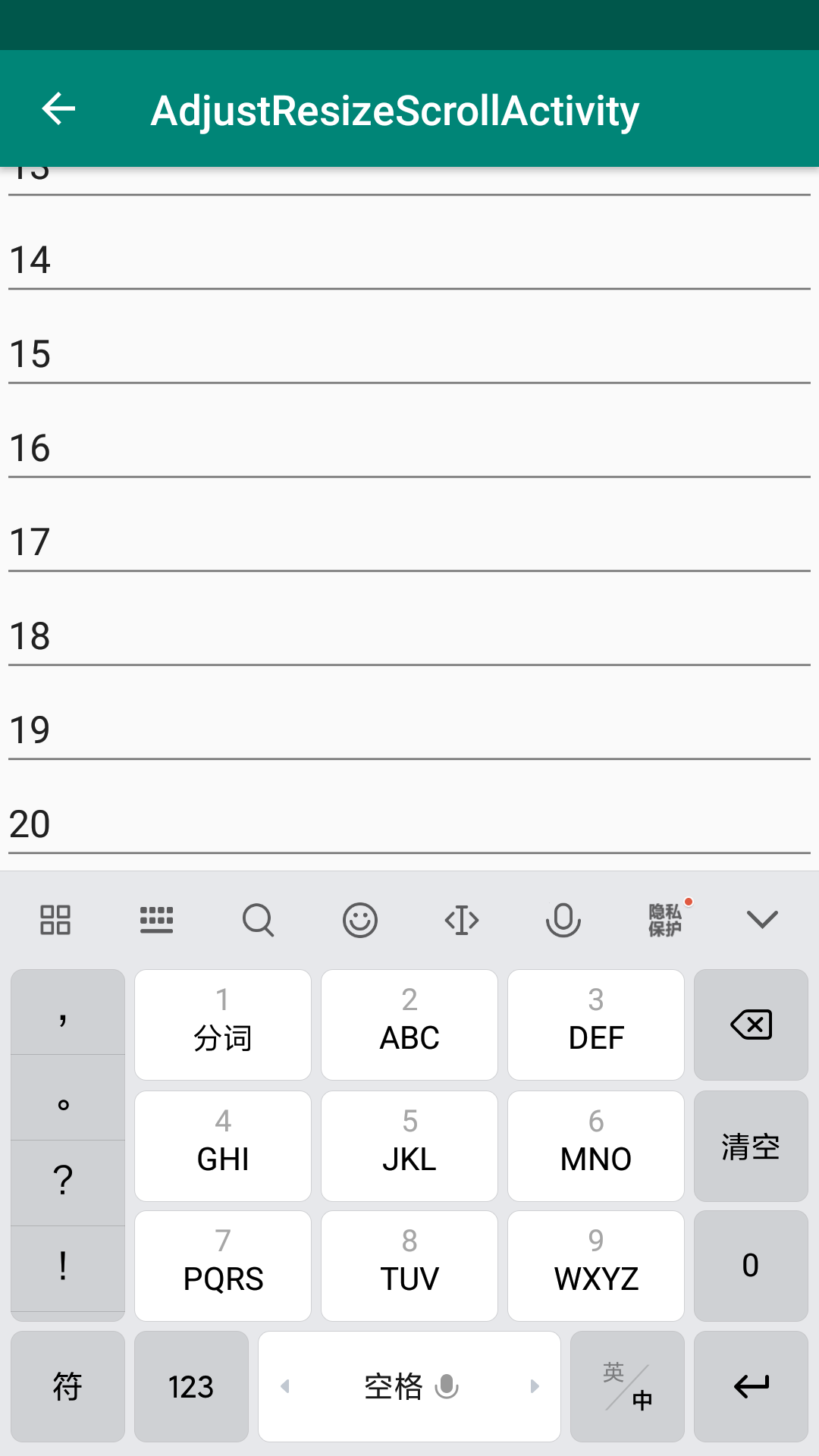
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <ScrollView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".stateunspecified.StateUnspecifiedScrollActivity"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical"> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatButton android:id="@+id/btn_state_unchanged_scroll" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="stateUnchanged_ScrollView" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatButton android:id="@+id/btn_state_hidden_scroll" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="stateHidden_ScrollView" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatButton android:id="@+id/btn_state_always_hidden_scroll" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="stateAlwaysHidden_ScrollView" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatButton android:id="@+id/btn_state_visible_scroll" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="stateVisible_ScrollView" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatButton android:id="@+id/btn_state_always_visible_scroll" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="stateAlwaysVisible_ScrollView" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="1" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="2" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="3" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="4" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="5" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="6" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="7" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="8" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="9" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="10" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="11" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="12" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="13" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="14" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="15" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="16" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="17" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="18" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="19" /> <androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatEditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="20" /> </LinearLayout> </ScrollView>
这确实是一个很奇怪的判断方式。因此,我们可以得出结论,当设置属性为stateUnspecified的时候,系统是默认不弹出软键盘的,但是当有获得焦点的输入框的界面有滚动的需求的时候,会自动弹出软键盘。至于为什么非要强调要获取焦点的输入框,这是因为,如果不是输入框获取焦点,软键盘也是不会自动弹出的,让界面不自动弹出软键盘的其中一个解决方案,就是在xml文件中,设置一个非输入框控件获取焦点,从而阻止键盘弹出。
android:focusable="true"
android:focusableInTouchMode="true"
2.stateUnchanged
中文的意思就是状态不改变的意思,我们应该怎么理解这句话呢?其实很好理解,就是说,当前界面的软键盘状态,取决于上一个界面的软键盘状态。举个例子,假如当前界面键盘是隐藏的,那么跳转之后的界面,软键盘也是隐藏的;如果当前界面是显示的,那么跳转之后的界面,软键盘也是显示状态。
3.stateHidden
顾名思义,如果我们设置了这个属性,那么键盘状态一定是隐藏的,不管上个界面什么状态,也不管当前界面有没有输入的需求,反正就是不显示。有个例外情况(如果从一个显示软键盘的界面返回,那么就会显示软键盘)。因此,我们可以设置这个属性,来控制软键盘不自动的弹出。
4.stateAlwaysHidden
这个属性也可以让软键盘隐藏,和stateHidden的区别是,从显示软键盘的页面返回的时候也会隐藏软键盘,而stateHidden则会显示软键盘。
5.stateVisible
设置为这个属性,可以将软键盘召唤出来,即使在界面上没有输入框的情况下也可以强制召唤出来。有个例外情况(如果从一个隐藏软键盘的界面返回,那么就会隐藏软键盘)。
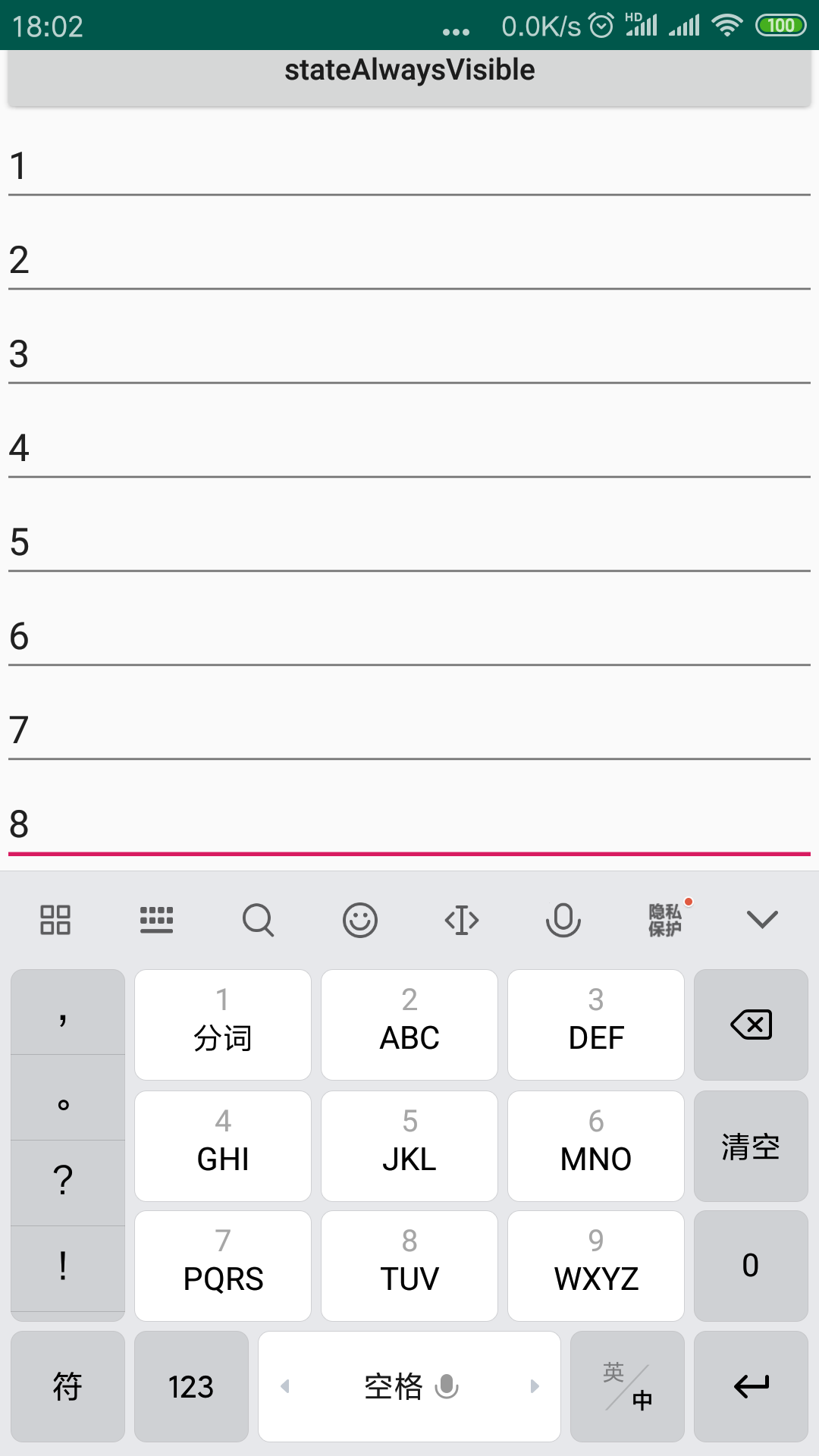
6.stateAlwaysVisible
这个属性也是可以将键盘召唤出来,但是与stateVisible属性有小小的不同之处。举个例子,当我们设置为stateVisible属性,如果当前的界面键盘是显示的,当我们点击按钮跳转到下个界面的时候,软键盘会因为输入框失去焦点而隐藏起来,当我们再次回到当前界面的时候,键盘这个时候是隐藏的。但是如果我们设置为stateAlwaysVisible,我们跳转到下个界面,软键盘还是隐藏的,但是当我们再次回来的时候,软键盘是会显示出来的。所以,这个Always就解释了这个区别,不管什么情况到达当前界面(正常跳转或者是上一个界面被用户返回),软键盘都是显示状态。
7.adjustUnspecified
从这个属性开始,就不是设置软键盘的显示与隐藏模式了,而是设置软键盘与软件的显示内容之间的显示关系。当我们没有设置这个值的时候,这个选项也是默认的设置模式。在这种情况下,系统会根据界面选择不同的模式。如果界面里面有可以滚动的控件(和adjustResize带有滚动控件的效果一样),比如ScrollView,系统会减小可以滚动的界面的大小,从而保证即使软键盘显示出来了,也能够看到所有的内容。如果布局里面没有滚动的控件(和adjustPan没有滚动控件的效果一样),那么软键盘可能就会盖住一些内容,我们从下面的图中可以看出差别。
没有滚动控件,软键盘下面的布局都被遮挡住了,若想修改,只能隐藏软键盘,然后选择。而且,重点注意一下上面的布局,当我们选择的输入框偏下的时候,上面的标题栏和布局被软键盘顶上去了。
布局里面有滑动控件,系统会自动的缩小整个界面的大小,因此,我们可以软键盘上面的小区域中显示所有的输入框。
这就是两中显示模式之间的差别。
8.adjustResize
这个属性表示Activity的主窗口总是会被调整大小,从而保证软键盘显示空间。
我们先看显示效果。
注意观察这个上面的标题栏和按钮,设置为adjustResize属性之后,对于没有滑动控件的布局,虽然还是不能选择所有的输入框,但是,窗口的显示方式发生了变化,默认属性时,整个布局是被顶上去了,但是设置为adjustResize属性,布局的位置并没有发生什么变化,这就是最大的区别。
而对于有滑动控件的布局来说,显示效果和默认是一样的。
9.adjustPan
如果设置为这个属性,那么Activity的屏幕大小并不会调整来保证软键盘的空间,而是采取了另外一种策略,系统会通过布局的移动,来保证用户要进行输入的输入框肯定在用户的视野范围里面,从而让用户可以看到自己输入的内容。对于没有滚动控件的布局来说,这个其实就是默认的设置,如果我们选择的位置偏下,上面的标题栏和部分控件会被顶上去。但是对于有滚动控件的布局来说,则不太一样,我们看下面的效果图。
首先,这是软键盘没有弹出的时候,有滚动控件的显示范围,最下面显示的是8.

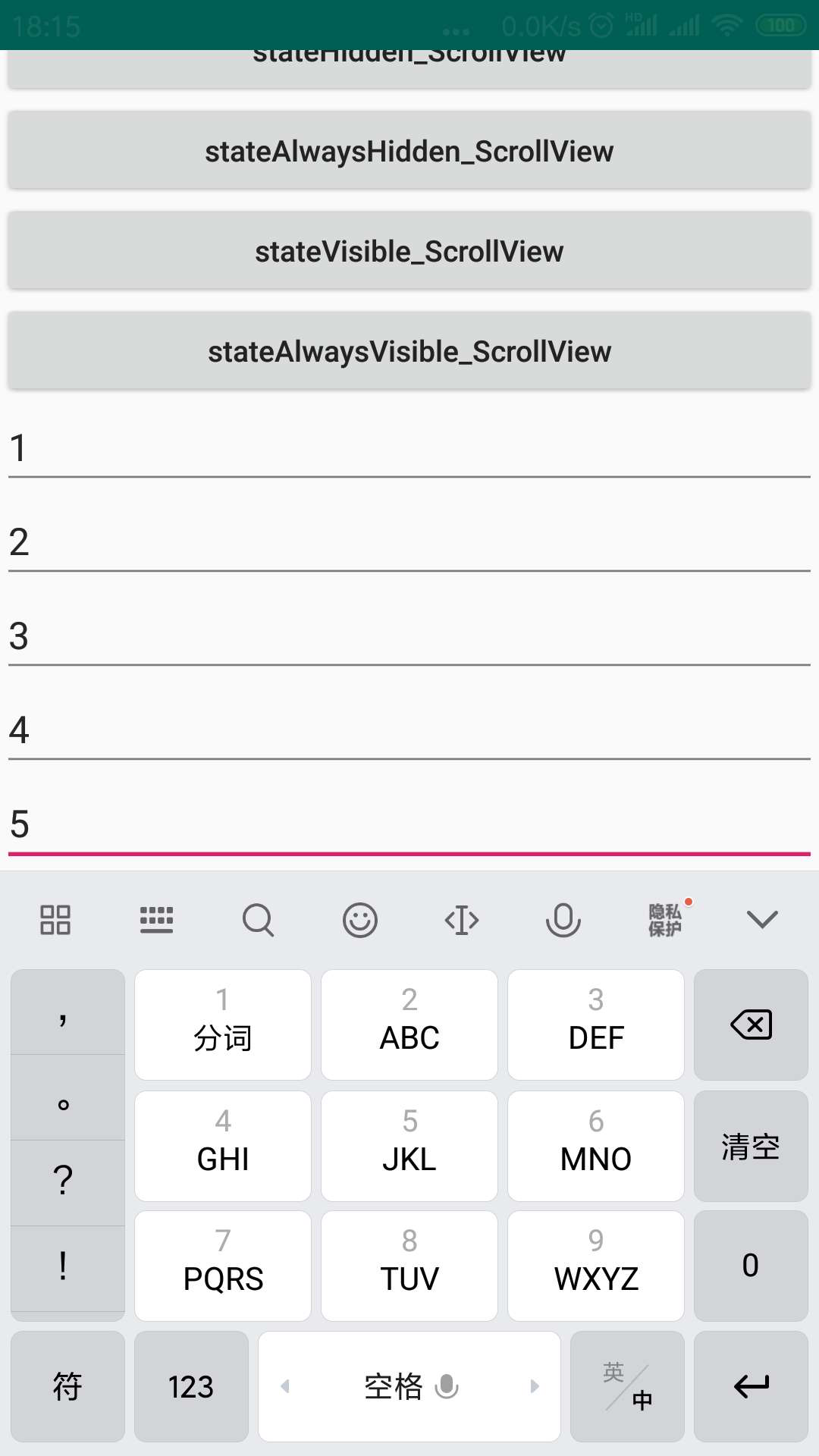
当我们点击5这个输入框,我们会发现下面的现象。
最上面只能够显示到按钮,标题栏已经不能看到了。
如果点击的输入框本身就可见,那么被顶上去的内容不能向下滑动显示;
而如果点击的输入框是通过向上滑动才可见,那么被顶上去的内容部分可以向下滑动。
而最下面也只能滑动到17,下面的内容也不能够滑动了。
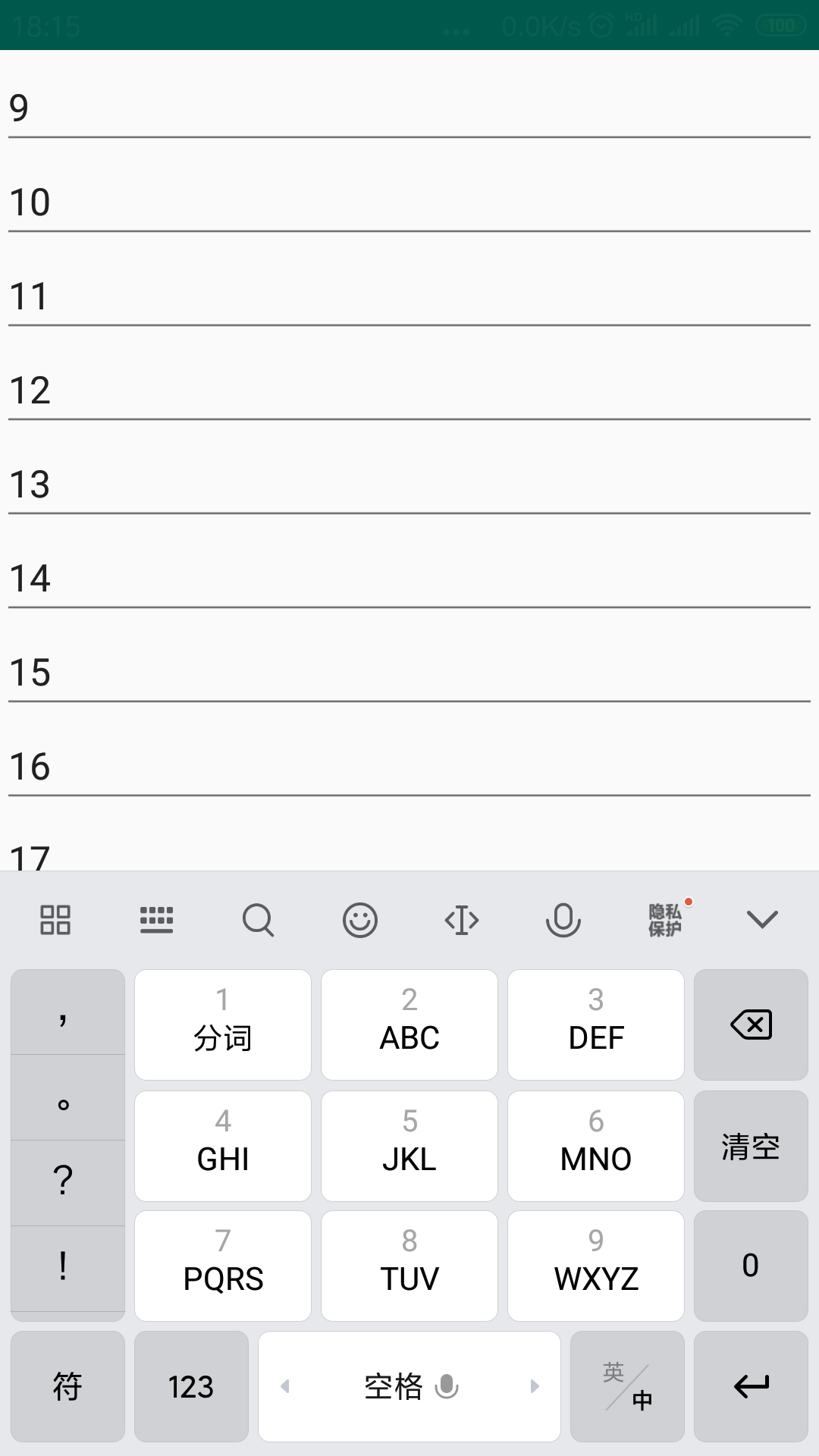
因此,我们就能够理解这个属性的作用了。
10、adjustNothing
如果设置为这个属性,那么Activity的屏幕大小并不会调整来保证软键盘的空间,系统也不会通过布局的移动,来保证用户要进行输入的输入框能在用户的视野范围之内。对于没有滚动控件的布局来说,这个其实是和adjustResize的没有滚动控件的布局效果是一样的。
对于有滚动控件的布局来说,布局中的输入框获取焦点弹出软键盘,不管这个输入框在弹出的软键盘之上或者被弹出的软键盘遮挡,布局都不会移动,但是手动滑动布局的时候页面可以部分滑动,滑动的距离比软键盘的高度略高。这个其实是和adjustPan的有滚动控件的布局当点击本身就在弹出的软键盘之上的输入框时的效果是一样的。如果点击的位置会被弹出的软键盘遮挡,那么效果就不一样了,这时向下滑动能够显示页面的顶部,而adjustPan被顶上去的页面是不能向下滑动显示的或者只能部分滑动(详见adjustPan);并且向上滑动时底部会锚在屏幕的底部,底部的内容会被软键盘遮挡,而adjustPan模式会被顶上去显示在软键盘之上。
通过以上的实验,我们可以得出结论,如果我们不设置"adjust..."的属性,对于没有滚动控件的布局来说,采用的是adjustPan方式,而对于有滚动控件的布局,则是采用的adjustResize方式。
了解了上面的这些知识之后,我们就可以根据自己的需求设置不同的方式了。而且,关于如何使得界面加载的时候不显示软键盘,我们也有了一个很清楚的认识。