| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/2018SE |
| ---- | ---- | ---- |
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/2018SE/homework/11406 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 寻找数组中第K大是哪个数 二叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历 |
| 学号 | 20189611 |
| 其他参考文献 | https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1os41117Fs?p=47|
题目名称:寻找数组中第K大是数 考察算法:排序算法
解题思路:先进行判断是否是满足条件小于10的六次方,然后建立数组存储输入的序列内容,进行循环输入l,r,k,循环次数为输入的m,
然后在建立一个数组存储截取到的第k个数进行判断k<=(r-l+1)调用数组的方法截取l到r的数值,存入新数组,然后调用数组sort
方法将其排序,新建一个答案数组存入,遍历数组输出。
解题代码:
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
int n=0;
do {
System.out.print("请输入小于10的六次方的序列长度:");
n =input.nextInt();
} while (n>Math.pow(10, 6)&&n<1);`
//定义队列数组
int [] line = new int[n];`
System.out.print("请输入序列值:");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
line[i]=input.nextInt();
}
System.out.print("请输入询问次数:");
int m =input.nextInt();
int l,r,k;
//定义数组存储答案
int []answer =new int[m];`
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
System.out.print("请输入l r k:");
l =input.nextInt();
r=input.nextInt();
k=input.nextInt();
if(k<=(r-l+1)){
//Arrays.copyOfRange截取数组中下标l到r的数值,不包括r
int[] newline =Arrays.copyOfRange(line, l-1, r);
//for (int i = 0; i < newline.length-1; i++) {
//for (int o = 0; o < newline.length-1-i; o++) {
//if (newline[o]>newline[o+1]) {
//int temp =newline[o];
//newline[o]=newline[o+1];
//newline[o+1]=temp;
//}
//}
// } }
//数组排序方法
Arrays.sort(newline);
answer[j]=newline[newline.length-k];
}else {
j--;
}
}
System.out.println("输出:");
for (int i : answer) {
System.out.println(i);
}
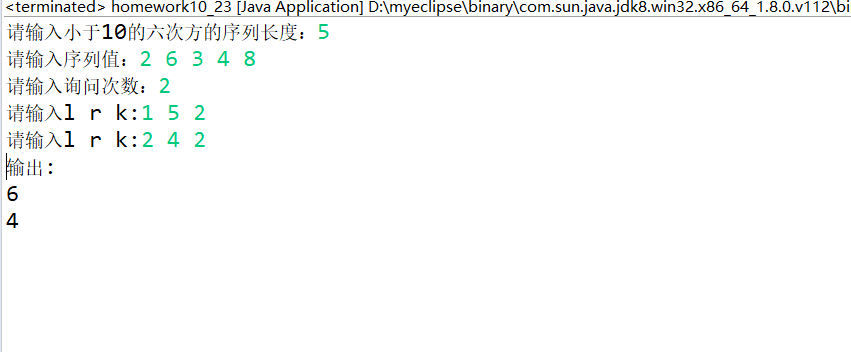
题目名称 二叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历 考察算法
解题思路 前序遍历:先访问根节点然后遍历左子树,在前序遍历右子树 在题中是先打印根结点A也就是data数据,然后去调用前序遍历
方法只输入左孩子参数输出tdnb,然后调用前序遍历方法只输入右孩子参数输出49156
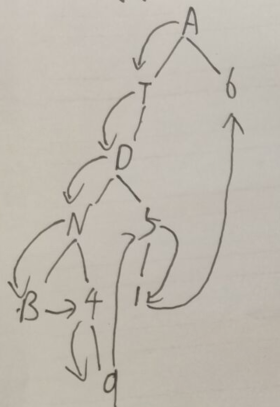
中序遍历 :从最末端左子树开始,访问它的根结点,然后中序遍历右子树,一层层往上直至全部访问完成,所以先是调用左孩
子,然后是根结点,然后是右子树所以bn49然后一层层往上
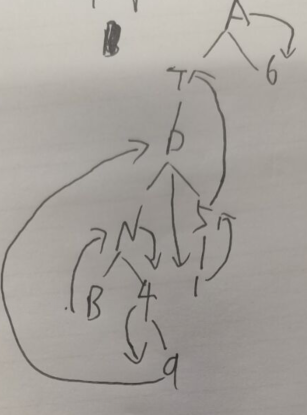
后序遍历:从左到右叶子优先,然后访问结点的方式所以是b94n 15d t6a
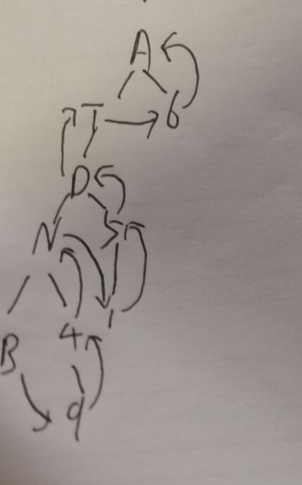
层级遍历就是从上往下从左到右,存入链表,先进后出
public class homewor1023_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
作业要求:叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历
自己实现四个方法,main方法中调用,将结果打印到控制台
*/
/* 二叉树的结构
A
/
T 6
/
D
/
N 5
/ /
B 4 1
9
*/
Node root = into();
// 先序遍历
System.out.print("先序遍历:");
A(root);
System.out.println();
// 中序遍历
System.out.print("中序遍历:");
B(root);
System.out.println();
// 后续遍历
System.out.print("后续遍历:");
C(root);
System.out.println();
// 层级遍历
System.out.print("层级遍历:");
D(root);
System.out.println();
}
private static void A(Node node) {
// TODO 先序遍历
if (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
A(node.l);
A(node.r);
}
}
private static void B(Node node) {
// TODO 中序遍历
if (node != null) {
B(node.l);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
B(node.r);
}
}
private static void C(Node node) {
// TODO 后续遍历
if (node != null) {
C(node.l);
C(node.r);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
}
private static void D(Node node) {
// TODO 层级遍历
if (node != null) {
LinkedList<Node> List = new LinkedList<Node>();
//先把根节点放到list
List.add(node);
Node newnode = null;
while (!List.isEmpty()) {
//移除列表中的一个元素(默认最后一个元素),并且返回该元素的值
newnode = (Node) List.pop();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
if (newnode.l != null) {
List.add(newnode.l);
}
if (newnode.r != null) {
List.add(newnode.r);
}
}}
}
// 构建一颗树,返回根节点
private static Node into(){
Node root = new Node("A");
Node node1 = new Node("T");
Node node2 = new Node("D");
Node node3 = new Node("N");
Node node4 = new Node("B");
Node node5 = new Node("6");
Node node6 = new Node("5");
Node node7 = new Node("4");
Node node8 = new Node("9");
Node node9 = new Node("1");
root.l = node1;
node1.l = node2;
node2.l = node3;
node2.r = node6;
node3.r = node7;
node7.r = node8;
node6.l = node9;
node3.l = node4;
root.r = node5;
return root;
}
// 节点
static class Node{
// 数据
Object data;
// 左孩子
Node l;
// 右孩子
Node r;
public Node(){}
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
this.l = null;
this.r = null;
}
public Node(Object data, Node l, Node r) {
this.data = data;
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
}
}
