1. 属性选择器
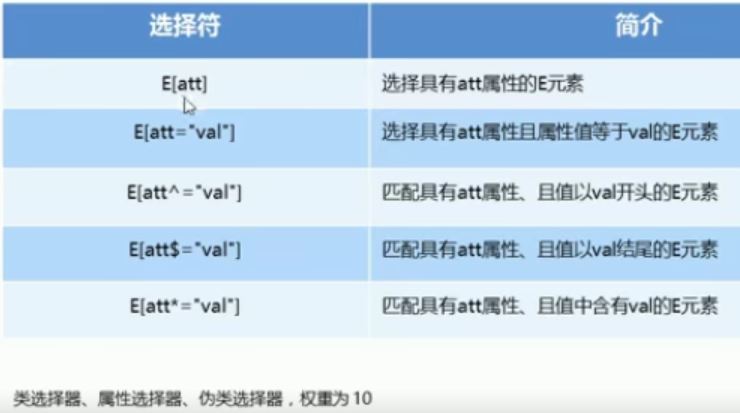
例1:直接写属性
<body>
<button>按钮</button>
<button>按钮</button>
<!-- 以下两个按钮禁用 -->
<button disabled="disabled">按钮</button>
<button disabled="disabled">按钮</button>
</body>
button {
cursor: pointer;
}
/* 属性选择器的使用方法 */
/* 这种方法不需要重新起类名 */
/* 选择的是既有button,又有disabled这个属性的元素 */
/* 类选择器、属性选择器、伪类选择器、权重为10 */
/*直接写属性*/
button[disabled] {
cursor: default;
}
例2:属性等于值的方法
<body>
<input type="text" value="文本框">
<input type="text" value="文本框">
<input type="text" value="文本框">
<input type="search" value="搜索框">
<input type="search" value="搜索框">
<input type="search" value="搜索框">
</body>
<style>
/*属性等于值的方法*/
input[type="search"] {
color: pink;
}
</style>
例3:
<body>
<div class="icon1">图标1</div>
<div class="icon2">图标2</div>
<div class="icon1">图标1</div>
<div class="icon1">图标1</div>
<div class="iicon4">图标4</div>
<div class="absiicon">图标5</div>
</body>
<style>
/* 以某个值开头的属性值 */
div[class^="icon"] {
color: red;
}
/* 以某个值结尾的属性值 */
div[class$="icon"] {
color: green;
}
/* 含有某个值的属性值 */
div[class*="icon"] {
color: blue;
}
</style>
2. 结构伪类选择器

对于nth-child(n):
- n可以是数字、关键字、和公式
- n如果是数字,就是选择第几个
- n常见的关键字有even(偶数)和odd(奇数)
- 常见的公式如下(如果n是公式,则从0开始计算)
- 但是第0个元素或者超出了元素的个数会被忽略
例1:
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
<li>7</li>
<li>8</li>
<li>9</li>
<li>10</li>
</ul>
</body>
<style>
ul li:first-child {
background-color: pink;
}
ul li:nth-child(8) {
background-color: lightpink;
}
ul li:last-child {
background-color: deeppink;
}
</style>
例2:
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
<li>7</li>
<li>8</li>
<li>9</li>
<li>10</li>
</ul>
</body>
<style>
/* n可以是关键词 */
ul li:nth-child(even) {
background-color: pink;
}
ul li:nth-child(odd) {
background-color: hotpink;
}
</style>
当n是公式的时候,常见的公式有:

<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
<li>7</li>
<li>8</li>
<li>9</li>
<li>10</li>
</ul>
</body>
<style>
/*n=0或n>元素个数,这些n会被忽略掉*/
/* n可以是公式 n从0开始计算 */
ul li:nth-child(n) {
/*0 1 2 3...*/
background-color: pink;
}
/*2n是偶数*/
ul li:nth-child(2n) {
/*0 2 4 6...*/
background-color: skyblue;
}
/*2n+1是奇数*/
ul li:nth-child(2n+1) {
/*1 3 5 ...*/
background-color: green;
}
/*5n选择的是0 5 10 */
ul li:nth-child(5n) {
background-color: #fff;
}
/* n+5从第5个后面开始 5 6 7...*/
ul li:nth-child(n+5) {
background-color: yellow;
}
/* -n+5选前5个:5 4 3 2 1 */
ul li:nth-child(-n+5) {
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
需要注意的地方:
<body>
<div>
<p>我是p标签</p>
<span>我是span</span>
<span>我是span</span>
<span>我是span</span>
<span>我是span</span>
</div>
</body>
<style>
/* 这样的选择方式,只是表示选择div的第几个孩子,而不管这个孩子是否属于同一个类型 */
/* 注意: div和nth-child(n)之间有空格 ,空格两边是父子级的关系,若没有空格表示的就是且*/
div :nth-child(1) {
background-color: pink;
}
div :nth-child(2) {
background-color: purple;
}
/* 以下一个都选不中,因为div :nth-child(1)表示选择div的第一个孩子(p),但是前面又加了一个span,这就是矛盾的,所以一个都选不中 */
div span:nth-child(1) {
background-color: yellow;
}
div span:nth-child(2) {/*选的是第一个span*/
background-color: orange;
}
/*再次说明,之前的 ul li:nth-child(2) 表示的是ul的第二个孩子,而且这个孩子必须是li
即空格两边是父子级的关系,若没有空格表示的就是且*/
</style>
解决办法:
<body>
<div>
<p>我是p标签</p>
<span>我是span</span>
<span>我是span</span>
<span>我是span</span>
<span>我是span</span>
</div>
</body>
<style>
/* of-type选择指定类型的元素 */
div span:first-of-type {
/*选中第一个span*/
background-color: purple;
}
div span:last-of-type {
/*选中最后一个span*/
background-color: skyblue;
}
div span:nth-of-type(2) {
/*选中第二个span*/
background-color: red;
}
</style>
3. 伪元素选择器
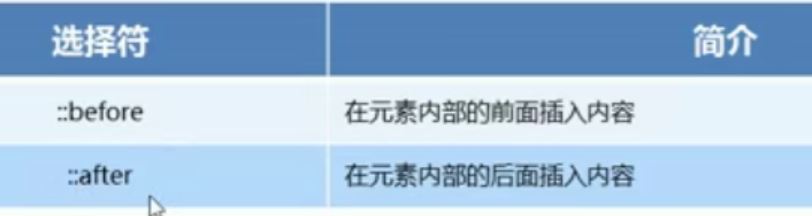
注意:
- before和after必须要有content属性
- before在内容的前面,after在内容的后面
- before和after创建一个元素,但是属于行内元素
- 因为在dom里看不见刚才创建的元素,所以我们称为伪元素
- 伪元素和标签选择器一样,权重为1
<body>
<div>是</div>
</body>
<style>
div {
300px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
div::before {
content: "我";
display: inline-block;
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
div::after {
content: "小猪佩奇";
display: inline-block;
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
案例:字体图标
<body>
<!-- 方法1 -->
<div>
<span></span>
</div>
<!-- 方法2 -->
<p></p>
<!-- 方法3 -->
<section></section>
</body>
<style>
/* 可以从网页中复制得到 */
@font-face {
font-family: 'icomoon';
src: url('fonts/icomoon.eot?9lb5m7');
src: url('fonts/icomoon.eot?9lb5m7#iefix') format('embedded-opentype'), url('fonts/icomoon.ttf?9lb5m7') format('truetype'), url('fonts/icomoon.woff?9lb5m7') format('woff'), url('fonts/icomoon.svg?9lb5m7#icomoon') format('svg');
font-weight: normal;
font-style: normal;
font-display: block;
}
div,
p,
section {
position: relative;
249px;
height: 35px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
/* 方法1 */
span {
position: absolute;
top: 10px;
right: 10px;
font-family: 'icomoon';
}
/* 方法2 */
p::after {
content: '';
font-family: 'icomoon';
position: absolute;
top: 10px;
right: 10px;
}
/* 方法3 */
section::after {
content: 'e902';
font-family: 'icomoon';
position: absolute;
top: 10px;
right: 10px;
}
</style>