码云地址:
https://gitee.com/YuRenDaZ/WordCount
个人PSP表格:
|
PSP2.1 |
PSP阶段 |
预估耗时 (分钟) |
实际耗时 (分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
180 |
120 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
180 |
120 |
|
Development |
开发 |
580 |
440 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
180 |
60 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
40 |
30 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
20 |
20 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
20 |
10 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
20 |
20 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
180 |
200 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
30 |
40 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
90 |
60 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
90 |
70 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
40 |
30 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
20 |
10 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
30 |
30 |
|
合计 |
850 |
630 |
一、功能需求分析
WordCount的需求可以概括为:对程序设计语言源文件统计字符数、单词数、行数,统计结果以指定格式输出到默认文件中,以及其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。可执行程序命名为:wc.exe,该程序处理用户需求的模式为:
wc.exe [parameter] [input_file_name]
存储统计结果的文件默认为result.txt,放在与wc.exe相同的目录下。
详细分析:
功能 -c :返回文件 file.c 的字符数
功能 -w :返回文件 file.c 的单词总数
功能 -l :返回文件 file.c 的总行数
功能 -o :将结果输出到指定文件outputFile.txt
要求 : 1. -o 功能后面必须有输出文件路径的参数。
2.在没有 -o 命令指定输出文件的时候默认将结果保存在exe同目录下的result.txt。
3.可以满足多个文件同时查询。
注意:
空格,水平制表符,换行符,均算字符。
由空格或逗号分割开的都视为单词,且不做单词的有效性校验,例如:thi#,that视为用逗号隔开的2个单词。
二、程序设计
A:大概设计
1):程序由工具类和主函数类构成。
2):程序使用main的入口参数。
B:详细设计
1):将每一个“-?”指令对应一个方法。
2):将功能方法写在一个类里,作为工具类。
3):使用条件判断语句来处理命令。
4):用集合存储需要查询的文件,以方便进行添加和遍历。
5):程序主要逻辑在main函数中进行。(逻辑并不非十分复杂)
三、程序编码(编码并不是最好的实现方法,希望各位同学能指出不足之处,我们大家一起进步!)
- 主函数逻辑主要是由循环语句和条件判断语句完成。代码如下:
1 import java.util.HashSet; 2 import java.util.Set; 3 4 public class WordCount { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 CountUtil countUtil = new CountUtil();//实例化工具类对象 8 Set<String> file_paths = new HashSet<String>() ; //创建用于存储输入文件的集合 9 String Output_file = "result.txt"; //存储输出文件名(默认为同目录下的result.txt文件) 10 String Result = ""; //存储查询结果 11 boolean isCharacters = false; //是否查询字符数 12 boolean isLines = false; //是否查询行数 13 boolean isWords = false; //是否查询单词数 14 for (int i = 0;i<args.length;i++) { //循环读取入口参数 15 if (args[i].startsWith("-")) { //判断是否是命令 16 switch (args[i]) { 17 case "-c": 18 isCharacters = true; //是-c指令,激活查询条件 19 break; 20 case "-l": 21 isLines = true; //是-l指令,激活查询条件 22 break; 23 case "-w": 24 isWords =true; //是-w指令,激活查询条件 25 break; 26 case "-o": 27 if(!args[i+1].startsWith("-")) //-o指令 判断后面是否有指定输出文件 28 { 29 Output_file = args[i+1]; //args[i+1]必须为输出文件 30 i++; 31 }else { 32 System.out.println("input error !"); //提示输入错误并终止程序 33 System.exit(0); 34 } 35 break; 36 default: 37 System.out.println("input error !"); 38 break; 39 } 40 } 41 else file_paths.add(args[i]); //将不属于命令的字符串存储在集合里面 42 } 43 44 if (isWords) { 45 Result+=countUtil.ReturnWords(file_paths)+" "; //调用查询单词方法,并做字符串拼接 46 } 47 if (isLines) { 48 Result+=countUtil.ReturnLines(file_paths)+" "; //调用查询行数方法,并做字符串拼接 49 } 50 if (isCharacters) { 51 Result+=countUtil.ReturnCharacters(file_paths)+" "; //调用查询字符数方法,并做字符串拼接 52 } 53 System.out.println(Result); 54 countUtil.OutputFile(Output_file, Result); //将结果输出到文件 55 } 56 }
- 在工具类中各方法的实现:(基本上都是基于IO流的操作)
ReturnCharacters方法,返回查询结果(String类型),参数为输入文件的集合。代码如下:

public String ReturnCharacters(Set<String> file_paths) { int Count = 0,bytes = 0; String result = "";//用于存储返回值 byte [] tem = new byte[20*1024];//用存储读取数据的定常字节数组 int len = tem.length;//得到tem的长度以避免循环时反复调用.length FileInputStream in = null;//声明一个文件输入流 try { for (String file_path : file_paths) { in = new FileInputStream(file_path);//得到字符输入流,string为文件绝对路径 while ((bytes = in.read(tem,0,len))!=-1) { Count+=bytes;//统计累计读取的字符数 } result += file_path+",字符数:"+Count+" ";//结果字符串拼接 Count = 0; } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("有文件输入错误,请核对!(如果不会使用相对路径,请使用绝对路径)"); //检查到文件不存在,提示错误 System.exit(0); //结束程序 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { in.close();//关闭输入流 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return result; }
ReturnWords方法,返回查询结果(String类型),参数为输入文件的集合。代码如下:

1 public String ReturnWords(Set<String> file_paths){ 2 int Count = 0; //存储单词数 3 String result = "";//存储返回值 4 StringBuffer saveString = new StringBuffer();//因为string具有不可变性,用StringBuffer来进行读取的添加 5 String tmp = ""; //缓存字符串 6 FileInputStream in = null;//声明文件字符输入流 7 InputStreamReader isr = null;//声明字节输入流 8 BufferedReader bis = null;//声明缓存输入流 9 try { 10 for (String file_path : file_paths) { //foreach循环遍历数组 11 in = new FileInputStream(file_path);//实例化文件输入流对象 12 isr = new InputStreamReader(in);//实例化字节输入流对象 13 bis = new BufferedReader(isr);//实例化缓存输入流对象 14 while ((tmp=bis.readLine())!=null) { //readLine()返回读取的字节,若没有了就返回null 15 saveString.append(tmp); //将新读出来的数据接在已保存的后面 16 } 17 tmp = saveString.toString(); //用字符串存储,以用split方法区分单词 18 String [] total = tmp.split("[\s+,\. ]");//用正则表达式将字符串按单词格式分开 19 Count = total.length; //字符串数组长度就是单词个数 20 result += file_path+",单词数:"+Count+" "; //结果字符串拼接 21 Count = 0; 22 } 23 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 24 System.out.println("有文件输入错误,请核对!(如果不会使用相对路径,请使用绝对路径)"); //检查到文件不存在,提示错误 25 System.exit(0); //结束程序 26 } catch (IOException e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 }finally { 29 try { 30 in.close();//关闭文件字符输入流 31 isr.close();//关闭字节输入流 32 bis.close();//关闭缓存输入流 33 } catch (IOException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 37 } 38 return result; 39 }
ReturnLines方法,返回查询结果(String类型),参数为输入文件的集合。代码如下:

1 public String ReturnLines(Set<String> file_paths) { 2 int Count = 0; 3 String result = ""; 4 FileInputStream in = null;//声明文件字符输入流 5 InputStreamReader isr = null;//声明字节输入流 6 BufferedReader bis = null;//声明缓存输入流 7 try { 8 for (String file_path : file_paths) { //foreach循环遍历数组 9 in = new FileInputStream(file_path);//实例化文件输入流对象 10 isr = new InputStreamReader(in);//实例化字节输入流对象 11 bis = new BufferedReader(isr);//实例化缓存输入流对象 12 while (bis.readLine()!=null) { 13 Count++; 14 } 15 result += file_path+",行数:"+Count+" "; //结果字符串拼接 16 Count = 0; 17 } 18 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 19 System.out.println("有文件输入错误,请核对!(如果不会使用相对路径,请使用绝对路径)"); //检查到文件不存在,提示错误 20 System.exit(0); //结束程序 21 } catch (IOException e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 }finally { 24 try { 25 in.close();//关闭文件字符输入流 26 isr.close();//关闭字节输入流 27 bis.close();//关闭缓存输入流 28 } catch (IOException e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 32 } 33 return result; 34 }
OutputFile方法,将结果保存在文件中,返回boolean型,参数为文件路径和内容。代码如下:

1 public boolean OutputFile(String File_path,String Context){ 2 File OutputFile = new File(File_path); //创建File对象 3 FileOutputStream os = null; //声明 文件输出流 4 byte [] a = null; //用于存储Context转化的byte字节数组 5 try { 6 if(!OutputFile.exists()) { //判断文件是否存在 7 OutputFile.createNewFile(); //不存在,创建一个文件 8 } 9 os = new FileOutputStream(OutputFile); //获得输出流对象 10 a = Context.getBytes(); //将Context转化为Byte数组,以便写入文件 11 os.write(a); //将byte数组写入文件 12 } catch (IOException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 }finally { 15 try { 16 os.close(); //关闭输出流 17 } catch (IOException e) { 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } 20 } 21 return true; 22 } 23 }
四、代码测试
代码调试方法参照 https://www.cnblogs.com/xy-hong/p/7197725.html
由于是使用的main函数的入口参数,所以之前并未接触过这类方式的程序编写。在经过查阅后在改文章上找到了调试方式。具体操作再次不予详述,请参照以上链接。
因为要求不能用已有得测试框架进行测试,所以就自己设计了一个测试类。在类中,分为单独针对每一个需要测试得方法都设计一个测试方法,然后再主函数中调用达到一次性全部测试得效果。
import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; public class ProTest { public static void main(String[] args) { testOutputFile(); testReturnCharacters(); testReturnLines(); testReturnWords(); } public static void testReturnCharacters() { Set<String> file_paths = new HashSet<String>(); String file1 = "F://test.c"; String file2 = "F://test.java"; file_paths.add(file2); file_paths.add(file1); System.out.println("testReturnCharacters():"); System.out.println(new CountUtil().ReturnCharacters(file_paths)); } public static void testReturnWords() { Set<String> file_paths = new HashSet<String>(); String file1 = "F://test.c"; String file2 = "F://test.java"; file_paths.add(file2); file_paths.add(file1); System.out.println("testReturnWords():"); System.out.println(new CountUtil().ReturnWords(file_paths)); } public static void testReturnLines() { Set<String> file_paths = new HashSet<String>(); String file1 = "F://test.c"; String file2 = "F://test.java"; file_paths.add(file2); file_paths.add(file1); System.out.println("testReturnLines():"); System.out.println(new CountUtil().ReturnLines(file_paths)); } public static void testOutputFile() { String file_path = "result.txt"; String context = "OutPutFile test !"; if(new CountUtil().OutputFile(file_path, context)) { System.out.println("File output success !"); }else { System.out.println("error !"); } } }
直接运行测试类,得到结果:
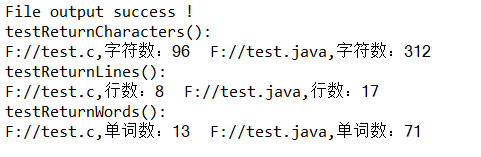
用例测试:
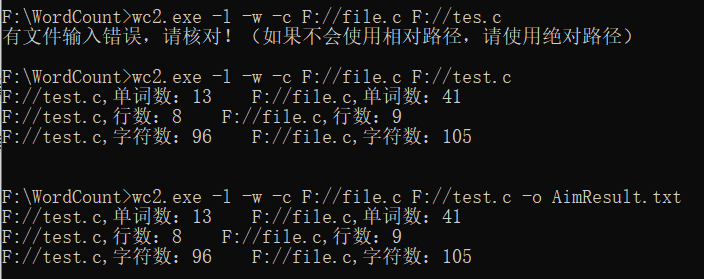
文件中的结果:
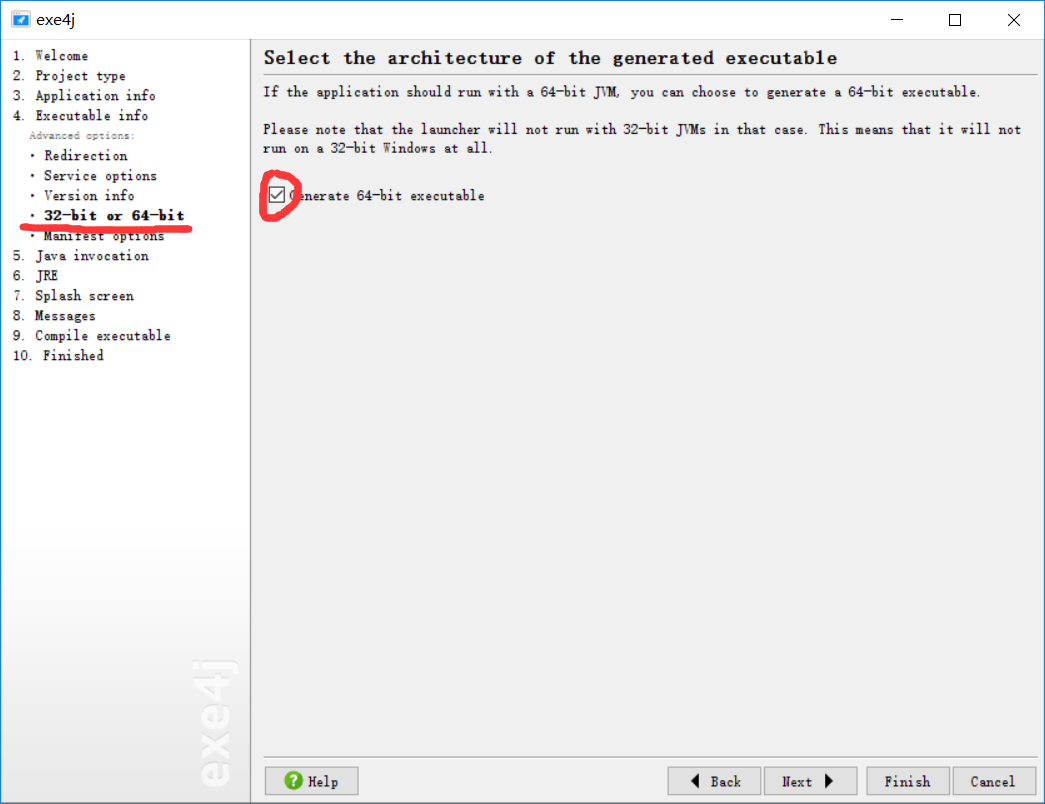
五、将项目导出为exe可执行文件
依赖工具:exe4j
参考方法:手把手教你如何把java代码,打包成jar文件以及转换为exe可执行文件(注意:改博客中没有指出32位和64位系统的差别,具体如下)
六、项目与远程库同步过程(码云)
有关git和码云项目的远程连接以及工作提交等相关操作参考Git和Github简单教程(该教程非常的详细,值得推荐。)
本项目一共有三次项目提交,分别是初始代码、复审代码、测试后修改的最终代码。
七、个人总结
第一次撰写博客有很多迷茫之处,但是在撰写博客的过程中我发现这其实是对整个项目过程的一次回顾与反思。在以前的作业中,通常都是写完代码测试完后就不再关注,也不会反在完成项目的途中犯过什么样的错误。每当下次遇到同样的问题还是会被困扰住,所以我觉得写博客是真的有必要的。虽然写出来的博客没人看,没人会在意,但是这并不是开始学习的我们的目的。我们的目的就在于回顾过程,反思过程中的错误,让项目的过程在我们脑海里留下更深的印象。最后,这次的作业的量还是算比较大的,但是却真的能感觉到有很多的收获。很多东西都是词不达意的,真的用心体会过就能明白。
感谢以上引用的各链接的作者们,希望你们的文章能帮助更多的人。
