1144. 递减元素使数组呈锯齿状
给你一个整数数组 nums,每次 操作 会从中选择一个元素并 将该元素的值减少 1。
如果符合下列情况之一,则数组 A 就是 锯齿数组:
- 每个偶数索引对应的元素都大于相邻的元素,即
A[0] > A[1] < A[2] > A[3] < A[4] > ... - 或者,每个奇数索引对应的元素都大于相邻的元素,即
A[0] < A[1] > A[2] < A[3] > A[4] < ...
返回将数组 nums 转换为锯齿数组所需的最小操作次数。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:2 解释:我们可以把 2 递减到 0,或把 3 递减到 1。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [9,6,1,6,2] 输出:4
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10001 <= nums[i] <= 1000

1 import copy 2 class Solution: 3 def movesToMakeZigzag(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: 4 nums_len = len(nums) 5 ans0 = 0 6 ans1 = 0 7 nums_copy0 = copy.deepcopy(nums) 8 nums_copy1 = copy.deepcopy(nums) 9 #奇数索引 10 for index in range(nums_len): 11 if index %2 == 1: 12 d1 = d2 = 0 13 if nums_copy1[index] <= nums_copy1[index-1]: 14 d1 = (nums_copy1[index-1] - (nums_copy1[index] - 1)) 15 nums_copy1[index-1] = (nums_copy1[index] - 1) 16 17 if (index+1< nums_len) and nums_copy1[index] <= nums_copy1[index+1]: 18 d2 = nums_copy1[index+1] - (nums_copy1[index] - 1) 19 nums_copy1[index+1] = (nums_copy1[index] - 1) 20 21 ans1 += (d1+d2) 22 23 #偶数索引 24 for index in range(nums_len): 25 if index %2 == 0: 26 d1 = d2 = 0 27 if index > 0 and nums_copy0[index] <= nums_copy0[index-1]: 28 d1 = (nums_copy0[index-1] - (nums_copy0[index] - 1)) 29 nums_copy0[index-1] = (nums_copy0[index] - 1) 30 31 if (index+1< nums_len) and nums_copy0[index] <= nums_copy0[index+1]: 32 d2 = nums_copy0[index+1] - (nums_copy0[index] - 1) 33 nums_copy0[index+1] = (nums_copy0[index] - 1) 34 35 ans0 += (d1+d2) 36 37 return min(ans0, ans1)
406. 根据身高重建队列
假设有打乱顺序的一群人站成一个队列。 每个人由一个整数对(h, k)表示,其中h是这个人的身高,k是排在这个人前面且身高大于或等于h的人数。 编写一个算法来重建这个队列。
注意:
总人数少于1100人。
示例
输入: [[7,0], [4,4], [7,1], [5,0], [6,1], [5,2]] 输出: [[5,0], [7,0], [5,2], [6,1], [4,4], [7,1]]

1 class Solution: 2 def reconstructQueue(self, people: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: 3 people.sort(key=lambda x:((-x[0],x[1]))) 4 res = list() 5 for peo in people: 6 res.insert(peo[1], peo) 7 8 return res
582. 杀死进程
给 n 个进程,每个进程都有一个独一无二的 PID (进程编号)和它的 PPID (父进程编号)。
每一个进程只有一个父进程,但是每个进程可能会有一个或者多个孩子进程。它们形成的关系就像一个树状结构。只有一个进程的 PPID 是 0 ,意味着这个进程没有父进程。所有的 PID 都会是唯一的正整数。
我们用两个序列来表示这些进程,第一个序列包含所有进程的 PID ,第二个序列包含所有进程对应的 PPID。
现在给定这两个序列和一个 PID 表示你要杀死的进程,函数返回一个 PID 序列,表示因为杀这个进程而导致的所有被杀掉的进程的编号。
当一个进程被杀掉的时候,它所有的孩子进程和后代进程都要被杀掉。
你可以以任意顺序排列返回的 PID 序列。
示例 1:
输入:
pid = [1, 3, 10, 5]
ppid = [3, 0, 5, 3]
kill = 5
输出: [5,10]
解释:
3
/
1 5
/
10
杀掉进程 5 ,同时它的后代进程 10 也被杀掉。
注意:
- 被杀掉的进程编号一定在 PID 序列中。
- n >= 1.

1 class Solution: 2 def killProcess(self, pid: List[int], ppid: List[int], kill: int) -> List[int]: 3 graph = defaultdict(list) 4 5 for p, pp in zip(pid, ppid): 6 graph[pp].append(p) 7 8 ans = [] 9 d = deque() 10 d.append(kill) 11 while d: 12 cur = d.popleft() 13 ans.append(cur) 14 d.extend(graph[cur]) 15 16 return ans
56. 合并区间
给出一个区间的集合,请合并所有重叠的区间。
示例 1:
输入: [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]] 输出: [[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]] 解释: 区间 [1,3] 和 [2,6] 重叠, 将它们合并为 [1,6].
示例 2:
输入: [[1,4],[4,5]] 输出: [[1,5]] 解释: 区间 [1,4] 和 [4,5] 可被视为重叠区间。

1 class Solution: 2 def merge(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: 3 4 intervals.sort(key=lambda x: x[0]) 5 6 merged = [] 7 for interval in intervals: 8 # if the list of merged intervals is empty or if the current 9 # interval does not overlap with the previous, simply append it. 10 if not merged or merged[-1][1] < interval[0]: 11 merged.append(interval) 12 else: 13 # otherwise, there is overlap, so we merge the current and previous 14 # intervals. 15 merged[-1][1] = max(merged[-1][1], interval[1]) 16 17 return merged
75. 颜色分类
给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色,一共 n 个元素的数组,原地对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
此题中,我们使用整数 0、 1 和 2 分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。
注意:
不能使用代码库中的排序函数来解决这道题。
示例:
输入: [2,0,2,1,1,0] 输出: [0,0,1,1,2,2]
进阶:
- 一个直观的解决方案是使用计数排序的两趟扫描算法。
首先,迭代计算出0、1 和 2 元素的个数,然后按照0、1、2的排序,重写当前数组。 - 你能想出一个仅使用常数空间的一趟扫描算法吗?

1 class Solution: 2 def sortColors(self, nums: List[int]) -> None: 3 """ 4 Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead. 5 """ 6 if not nums: 7 return 8 9 start = 0 10 11 for index in range(len(nums)): 12 if nums[index] == 0: 13 nums[index] = nums[start] 14 nums[start] = 0 15 start += 1 16 17 for index in range(len(nums)): 18 if nums[index] == 1: 19 nums[index] = nums[start] 20 nums[start] = 1 21 start += 1 22 23 return
820. 单词的压缩编码
给定一个单词列表,我们将这个列表编码成一个索引字符串 S 与一个索引列表 A。
例如,如果这个列表是 ["time", "me", "bell"],我们就可以将其表示为 S = "time#bell#" 和 indexes = [0, 2, 5]。
对于每一个索引,我们可以通过从字符串 S 中索引的位置开始读取字符串,直到 "#" 结束,来恢复我们之前的单词列表。
那么成功对给定单词列表进行编码的最小字符串长度是多少呢?
示例:
输入: words =["time", "me", "bell"]输出: 10 说明: S ="time#bell#" , indexes = [0, 2, 5] 。
提示:
1 <= words.length <= 20001 <= words[i].length <= 7- 每个单词都是小写字母 。

1 class Solution(object): 2 def minimumLengthEncoding(self, words): 3 good = set(words) 4 for word in words: 5 for k in range(1, len(word)): 6 good.discard(word[k:]) 7 8 return sum(len(word) + 1 for word in good)
163. 缺失的区间
给定一个排序的整数数组 nums ,其中元素的范围在 闭区间 [lower, upper] 当中,返回不包含在数组中的缺失区间。
示例:
输入: nums =[0, 1, 3, 50, 75], lower = 0 和 upper = 99, 输出:["2", "4->49", "51->74", "76->99"]

1 class Solution: 2 def findMissingRanges(self, nums: List[int], lower: int, upper: int) -> List[str]: 3 4 res = [] 5 low = lower - 1 6 nums.append(upper + 1) 7 8 for num in nums: 9 dif = num - low 10 if dif == 2: 11 res.append(str(low+1)) 12 elif dif > 2: 13 res.append(str(low+1) + "->" + str(num-1)) 14 15 low = num 16 17 return res
1162. 地图分析
你现在手里有一份大小为 N x N 的『地图』(网格) grid,上面的每个『区域』(单元格)都用 0 和 1 标记好了。其中 0 代表海洋,1 代表陆地,你知道距离陆地区域最远的海洋区域是是哪一个吗?请返回该海洋区域到离它最近的陆地区域的距离。
我们这里说的距离是『曼哈顿距离』( Manhattan Distance):(x0, y0) 和 (x1, y1) 这两个区域之间的距离是 |x0 - x1| + |y0 - y1| 。
如果我们的地图上只有陆地或者海洋,请返回 -1。
示例 1:
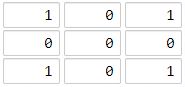
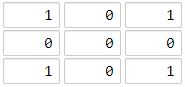
输入:[[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]] 输出:2 解释: 海洋区域 (1, 1) 和所有陆地区域之间的距离都达到最大,最大距离为 2。
示例 2:

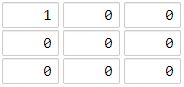
输入:[[1,0,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,0]] 输出:4 解释: 海洋区域 (2, 2) 和所有陆地区域之间的距离都达到最大,最大距离为 4。

1 from collections import deque 2 class Solution: 3 def maxDistance(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int: 4 # 地图规模 5 n, m = len(grid), len(grid[0]) 6 # 每个点到陆地的曼哈顿距离 7 dist = [[float('inf') for _ in range(m)] for _ in range(n)] 8 # 该点是否被访问过 9 visited = [[False for _ in range(m)] for _ in range(n)] 10 # 队列 11 q = deque() 12 # 陆地计数 13 cnt = 0 14 ans = 0 15 tot = n * m 16 for i in range(n): 17 for j in range(m): 18 if grid[i][j]: 19 dist[i][j] = 0 20 visited[i][j] = True 21 q.append((i, j)) 22 cnt += 1 23 # 如果都是陆地或者都是海洋,则返回-1 24 if cnt == tot or cnt == 0: 25 return -1 26 27 while q: 28 x, y = q.popleft()# 出列 29 for i, j in [(x + 1, y), (x - 1, y), (x, y + 1), (x, y - 1)]: 30 # 如果坐标合法并且没被访问过 31 if 0 <= i < n and 0 <= j < m and not visited[i][j]: 32 dist[i][j] = min(dist[i][j], dist[x][y] + 1) # 取最小值 33 ans = max(ans, dist[i][j]) # 更新答案 34 visited[i][j] = True 35 q.append((i, j)) # 入列 36 return ans
957. N 天后的牢房
8 间牢房排成一排,每间牢房不是有人住就是空着。
每天,无论牢房是被占用或空置,都会根据以下规则进行更改:
- 如果一间牢房的两个相邻的房间都被占用或都是空的,那么该牢房就会被占用。
- 否则,它就会被空置。
(请注意,由于监狱中的牢房排成一行,所以行中的第一个和最后一个房间无法有两个相邻的房间。)
我们用以下方式描述监狱的当前状态:如果第 i 间牢房被占用,则 cell[i]==1,否则 cell[i]==0。
根据监狱的初始状态,在 N 天后返回监狱的状况(和上述 N 种变化)。
示例 1:
输入:cells = [0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1], N = 7 输出:[0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0] 解释: 下表概述了监狱每天的状况: Day 0: [0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1] Day 1: [0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] Day 2: [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0] Day 3: [0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0] Day 4: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0] Day 5: [0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0] Day 6: [0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0] Day 7: [0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]
示例 2:
输入:cells = [1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0], N = 1000000000 输出:[0,0,1,1,1,1,1,0]
提示:
cells.length == 8cells[i]的值为0或11 <= N <= 10^9

1 class Solution: 2 def prisonAfterNDays(self, cells: List[int], N: int) -> List[int]: 3 4 def nextday(cells): 5 return [int(i>0 and i< 7 and cells[i-1]==cells[i+1]) for i in range(8)] 6 7 seen = {} 8 while N > 0: 9 cells_tuple = tuple(cells) 10 if cells_tuple in seen: 11 N %= (seen[cells_tuple] - N) 12 13 seen[cells_tuple] = N 14 15 if N > 0: 16 N -= 1 17 cells = nextday(cells) 18 19 return cells
1030. 距离顺序排列矩阵单元格
给出 R 行 C 列的矩阵,其中的单元格的整数坐标为 (r, c),满足 0 <= r < R 且 0 <= c < C。
另外,我们在该矩阵中给出了一个坐标为 (r0, c0) 的单元格。
返回矩阵中的所有单元格的坐标,并按到 (r0, c0) 的距离从最小到最大的顺序排,其中,两单元格(r1, c1) 和 (r2, c2) 之间的距离是曼哈顿距离,|r1 - r2| + |c1 - c2|。(你可以按任何满足此条件的顺序返回答案。)
示例 1:
输入:R = 1, C = 2, r0 = 0, c0 = 0 输出:[[0,0],[0,1]] 解释:从 (r0, c0) 到其他单元格的距离为:[0,1]
示例 2:
输入:R = 2, C = 2, r0 = 0, c0 = 1 输出:[[0,1],[0,0],[1,1],[1,0]] 解释:从 (r0, c0) 到其他单元格的距离为:[0,1,1,2] [[0,1],[1,1],[0,0],[1,0]] 也会被视作正确答案。
示例 3:
输入:R = 2, C = 3, r0 = 1, c0 = 2 输出:[[1,2],[0,2],[1,1],[0,1],[1,0],[0,0]] 解释:从 (r0, c0) 到其他单元格的距离为:[0,1,1,2,2,3] 其他满足题目要求的答案也会被视为正确,例如 [[1,2],[1,1],[0,2],[1,0],[0,1],[0,0]]。

1 class Solution: 2 def allCellsDistOrder(self, R, C, r0, c0): 3 dist_list = [[] for i in range(200)] 4 for i in range(R): 5 for j in range(C): 6 distinct = abs(r0-i) + abs(c0-j) 7 dist_list[distinct].append([i, j]) 8 9 result = [] 10 for dist in dist_list: 11 if dist: 12 result.extend(dist) 13 else: 14 break 15 16 return result
