


节点代码
完整代码:
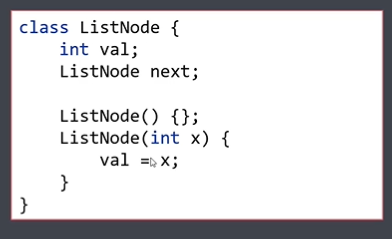
<1> 链表实现代码
class ListNode { int val; // 数据域 ListNode next; // 指针域,指向下⼀个节点 ListNode() { } ListNode(int x) { val = x; } }
<2>存在 long 类型溢出的问题,需要⼿动测试
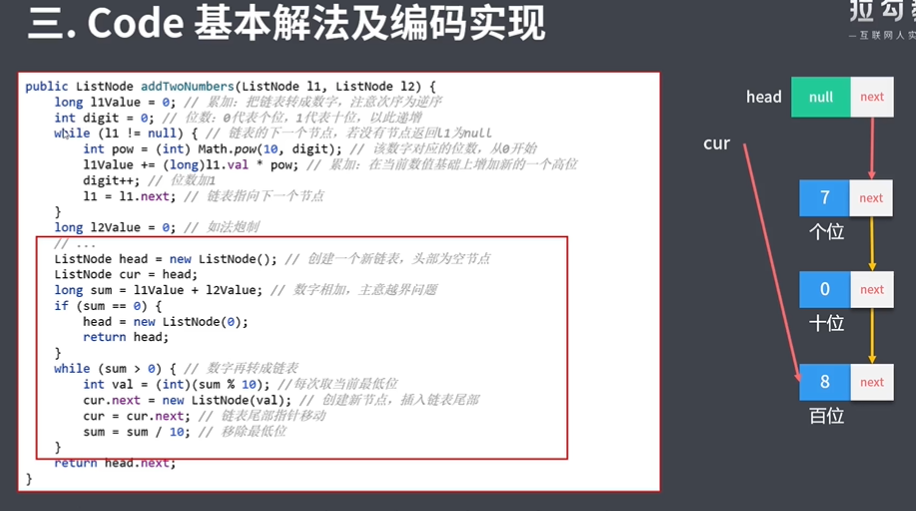
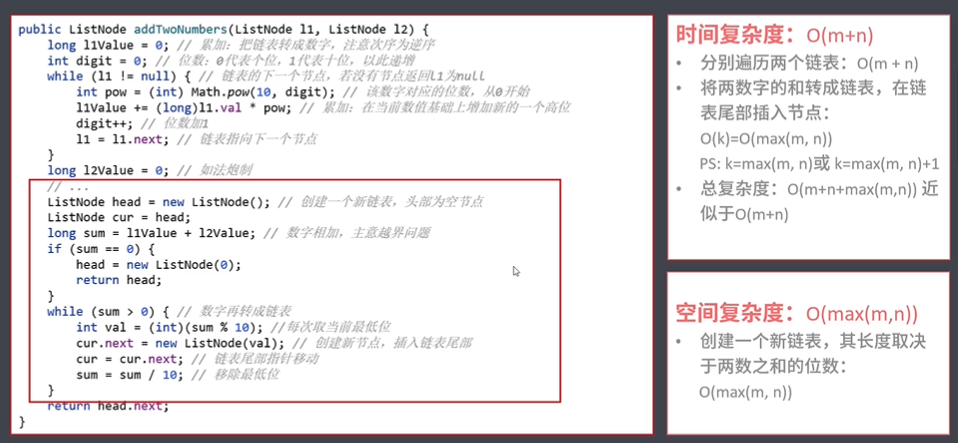
/** * 暴⼒解法: * 遍历两个链表使⽤数学思维分别将他们转成整数 * 对两个整数进⾏求和得到sum * 将sum按照数学思维再转成链表 * ⼿动测试: * 若超过语⾔⽀持的数据类型范围,则报错 * 解决办法:BigInteger * * * @param l1 * @param l2 * @return */ public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { //把链表转成数字,注意次序为逆序 long l1Value = 0; int digit = 0; while (l1 != null) { //该位对应的 单位 int pow = (int) Math.pow(10, digit); //在当前数值基础上增加新的⼀个⾼位 l1Value += (long)l1.val * pow; digit++; //链表指向下⼀个节点 l1 = l1.next; } long l2Value = 0; digit = 0; while (l2 != null) { //该位对应的 单位 int pow = (int) Math.pow(10, digit); //在当前数值基础上增加新的⼀个⾼位 l2Value += (long)l2.val * pow; digit++; //链表指向下⼀个节点 l2 = l2.next; } //创建⼀个新链表,头部为空节点 ListNode head = new ListNode(); ListNode cur = head; //数字相加 long sum = l1Value + l2Value; if (sum == 0) { head = new ListNode(0); return head; } //数字再转成链表 while (sum > 0) { //每次取当前最低位 int val = (int) (sum % 10); //移除最低位 sum = sum / 10; //创建新节点 ListNode node = new ListNode(val); //插⼊链表尾部 cur.next = node; //链表尾部指针移动 cur = cur.next; } return head.next; }
<3>解决办法:⽤ java.math.BigInteger 替代 long 类型。注意全类名写法。
/** * 暴⼒解法:存在的问题:使⽤long也会存在溢出 * 解决办法:java.math.BigInteger * 该类在leetcode默认环境没有导⼊,所以使⽤全类名编写 * * @param l1 * @param l2 * @return */ public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { //把链表转成数字,注意次序为逆序 java.math.BigInteger l1Value = java.math.BigInteger.valueOf(0); int digit = 0; while (l1 != null) { java.math.BigInteger carry = java.math.BigInteger.valueOf(10).pow(digit); l1Value = l1Value.add(carry.multiply(java.math.BigInteger.valueOf(l1.val))); digit++; l1 = l1.next; } java.math.BigInteger l2Value = java.math.BigInteger.valueOf(0); digit = 0; while (l2 != null) { java.math.BigInteger carry = java.math.BigInteger.valueOf(10).pow(digit); l2Value = l2Value.add(carry.multiply(java.math.BigInteger.valueOf(l2.val))); digit++; l2 = l2.next; } ListNode head = new ListNode(); ListNode cur = head; //数字相加,然后再转成链表 java.math.BigInteger sum = l1Value.add(l2Value); if (sum.compareTo(java.math.BigInteger.valueOf(0)) == 0) { head = new ListNode(0); return head; } while (sum.compareTo(java.math.BigInteger.valueOf(0)) > 0) { int val = sum.mod(java.math.BigInteger.valueOf(10)).intValue(); sum = sum.divide(java.math.BigInteger.valueOf(10)); ListNode node = new ListNode((int) val); cur.next = node; cur = cur.next; } return head.next; }


完整代码:
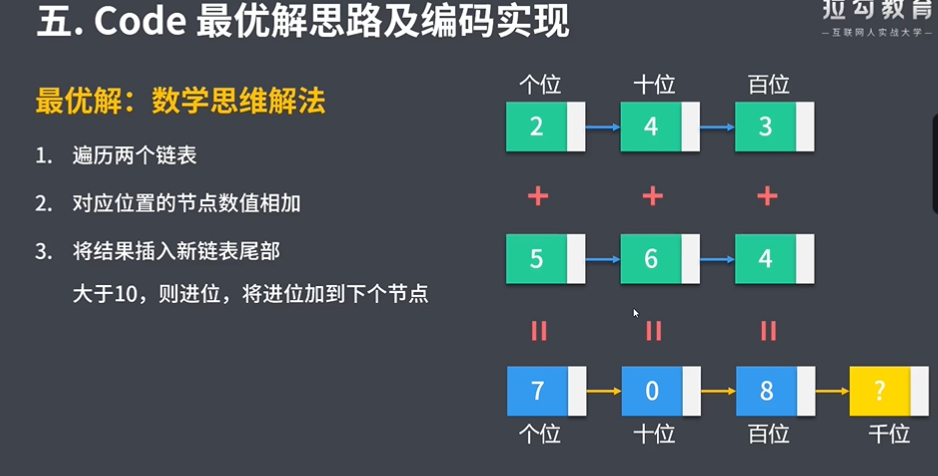
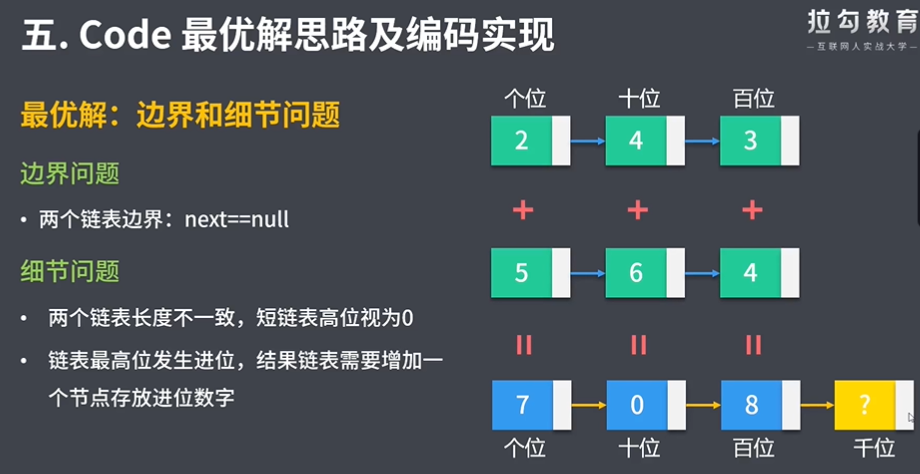
/** * 最优解:数学思维解法 * 1.遍历两个链表 * 2.对应位置的节点数值相加 * 3.将计算结果插⼊新链表尾部 * ⼤于10,则进位,将进位加到下个节点 * * 边界问题 * 两个链表边界:next==null * 细节问题 * 两个链表⻓度不⼀致,短链表⾼位视为0 * 链表最⾼位发⽣进位,结果链表需要增加⼀个节点存放进位数字 * * @param l1 * @param l2 * @return */ public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode p = l1, q = l2; // 原链表的两个遍历指针 ListNode resultHead = new ListNode(-1); // 结果链表的头结点head ListNode curr = resultHead; // 结果链表的遍历指针,代表当前操作的节点 int carry = 0; // 进位 // 1.遍历两个链表 while (p != null || q != null) { // 以⻓链表为准 // 获取当前节点的值:链表较短,已⽆节点,取0 int x = p != null ? p.val : 0; int y = q != null ? q.val : 0; // 2.对应位置的节点数值相加 int sum = x + y + carry; carry = sum / 10; // 如何得到进位:和对10求整,得到此次计算的进位 int num = sum % 10; // 存放到新链表节点中的数值 // 3.将计算结果插⼊新链表尾部 curr.next = new ListNode(num); // 创建新节点 curr = curr.next; p = p == null ? p : p.next; q = q == null ? q : q.next; } if (carry > 0) { // 处理进位节点 curr.next = new ListNode(carry); } return resultHead.next; }
测试用例
<1>辅助数据结构:链表。代码如下:
class ListNode { int val; // 数据域 ListNode next; // 指针域,指向下⼀个节点 ListNode() { } ListNode(int x) { val = x; } }
<2>测试⽤例:
输⼊:(2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4) 输出:7 -> 0 -> 8 原因:342 + 465 = 807
<3>测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { Solution solution=new AddTwoNumbers2().new Solution(); int[] arr1 = {2, 4, 3}; int[] arr2 = {5, 6, 4}; ListNode l1 = new AddTwoNumbers2().new ListNode(); ListNode l2 = new AddTwoNumbers2().new ListNode(); ListNode l1Cur = l1; ListNode l2Cur = l2; for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) { ListNode node1 = new AddTwoNumbers2().new ListNode(arr1[i]); ListNode node2 = new AddTwoNumbers2().new ListNode(arr2[i]); l1Cur.next = node1; l1Cur = node1; l2Cur.next = node2; l2Cur = node2; } ListNode result = solution.addTwoNumbers(l1.next, l2.next); while (result != null) { System.out.print(result.val + " "); // 输出:7 0 8 result = result.next; } }


练习题
Leetcode 67 - 二进制求和
给你两个二进制字符串,返回它们的和(用二进制表示)。
输入为 非空 字符串且只包含数字 1 和 0。
代码:
class Solution { public String addBinary(String a, String b) { StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer(); // 二进制相加,末尾对齐,逐位相加,逢二进一 int n = Math.max(a.length(), b.length()), carry = 0;//carry表示上一位置的进位,初始为0 //从低位开始遍历相加,a、b中短的位置补0 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { carry += i < a.length() ? (a.charAt(a.length() - 1 - i) - '0') : 0; carry += i < b.length() ? (b.charAt(b.length() - 1 - i) - '0') : 0; ans.append((char) (carry % 2 + '0')); carry /= 2; } //进位有值,存入答案字符串中 if (carry > 0) { ans.append('1'); } //最终将答案串反转 ans.reverse(); return ans.toString(); } }
Leetcode 371 - 两整数之和
不使用运算符 + 和 - ,计算两整数 a 、b 之和。
示例 1:
输入: a = 1, b = 2
输出: 3
示例 2:
输入: a = -2, b = 3
输出: 1
说明:
- 输入输出的取值范围为[-2^31,2^31-1]
- 如果计算结果溢出,我们将你的计算结果以二进制补码表示,并只取低32位作为输出
代码
//无进位加法使用异或运算计算得出,进位结果使用与运算和移位运算计算得出; class Solution { public int getSum(int a, int b) { if (b!=0){ int xor=a^b; int and = (a&b)<<1; return getSum(xor,and); }else{ return a; } } }
Leetcode 445 - 两数相加 II
给你两个 非空 链表来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。它们的每个节点只存储一位数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
示例:
输入:(7 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出:7 -> 8 -> 0 -> 7
代码:
class Solution { public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { Deque<Integer> stack1 = new LinkedList<Integer>(); Deque<Integer> stack2 = new LinkedList<Integer>(); // 把L1、L2中的数字依次压入栈中 while (l1 != null) { stack1.push(l1.val); l1 = l1.next; } while (l2 != null) { stack2.push(l2.val); l2 = l2.next; } int carry = 0; ListNode ans = null; //再依次取出来相加,存到节点中 while (!stack1.isEmpty() || !stack2.isEmpty() || carry != 0) { int a = stack1.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack1.pop(); int b = stack2.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack2.pop(); int cur = a + b + carry; carry = cur / 10; cur %= 10; ListNode curnode = new ListNode(cur); curnode.next = ans; ans = curnode; } return ans; } }
Leetcode 989 - 数组形式的整数加法
对于非负整数 X 而言,X 的数组形式是每位数字按从左到右的顺序形成的数组。例如,如果 X = 1231,那么其数组形式为 [1,2,3,1]。
给定非负整数 X 的数组形式 A,返回整数 X+K 的数组形式。
示例 1:
输入:A = [1,2,0,0], K = 34
输出:[1,2,3,4]
解释:1200 + 34 = 1234
示例 2:
输入:A = [2,7,4], K = 181
输出:[4,5,5]
解释:274 + 181 = 455
示例 3:
输入:A = [2,1,5], K = 806
输出:[1,0,2,1]
解释:215 + 806 = 1021
示例 4:
输入:A = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9], K = 1
输出:[1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]
解释:9999999999 + 1 = 10000000000
提示:
1 <= A.length <= 10000
0 <= A[i] <= 9
0 <= K <= 10000
如果 A.length > 1,那么 A[0] != 0
代码
//将整个加数加入数组表示的数的最低位,通过求余数计算留下来的数值,求除数计算进位数值; class Solution { public List addToArrayForm(int[] A, int K) { int N = A.length; int cur = K; List ans = new ArrayList(); int i = N; while (--i >= 0 || cur > 0) { if (i >= 0) cur += A[i]; ans.add(cur % 10); cur /= 10; } Collections.reverse(ans); return ans; } }