| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 10 | 10 |
| • Estimate | • 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 440 | 540 |
| Development | • 开发 | 410 | 500 |
| • Analysis | • 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 120 | 180 |
| • Design Spec | • 生成设计文档 | 10 | 10 |
| • Design Review | • 设计复审 | 10 | 10 |
| • Coding Standard | • 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 10 | 10 |
| • Design | • 具体设计 | 20 | 20 |
| • Coding | • 具体编码 | 180 | 120 |
| • Code Review | • 代码复审 | 30 | 60 |
| • Test | • 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 30 | 90 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 30 | 40 |
| • Test Repor | • 测试报告 | 10 | 10 |
| • Size Measurement | • 计算工作量 | 10 | 10 |
| • Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | • 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 10 | 20 |
| 合计 | 450 | 550 |
解题思路
这次的需求是关于读写文件的,所以可以大致分为读文件,数据处理,写数据三个模块。读写文件方面,我觉得java自带的方法就可以完成,所以这一块的任务就是查找该怎么用java自带的方法。数据处理方面,主要需要关注的是单词数的统计,我的思路是将先将单词全部转为小写,过滤掉长度不足的字符串,并判断前四位是否是字母,这样就留下了符合要求的字符。
接口的设计与实现过程
代码有三个类,一个是文件相关的FileUtil类,目前只有通过路径取得文件的功能,一个是lib类,里面有主要的实现方法,最后是Main类,用于运行代码。
- FileUtil.java
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
/**
* @author 031602435 xyq
* @version 1
*
*/
public class FileUtil {
/**
* @param path
* @return file
*/
public File getFile(String path) {
File file = new File(path);
if (!file.exists()) {
System.out.println("file not found");
}
System.out.println("locate:"+path);
return file;
}
}
- lib.java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author 031602435 xyq
* @version 1
*
*/
public class lib {
public static String encoding = "UTF-8";
/**字符数量计数器
*
* @param file
* @return charnum
* @throws Exception
* @throws FileNotFoundException
*/
public int charCounter(File file) throws Exception,FileNotFoundException {
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file), encoding);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
int charnum = 0;
String str = null;
while ((str = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
//String s = bufferedReader.readLine();
charnum += str.length();
}
//System.out.println("char:"+charnum);
inputStreamReader.close();
return charnum;
}
/**行数计数器
*
* @param file
* @return linenum
* @throws Exception
* @throws FileNotFoundException
*/
public int lineCounter(File file) throws Exception, FileNotFoundException {
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file), encoding);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
int linenum = 0;
String str = null;
while ((str = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
//String s = bufferedReader.readLine();
if (!str.isEmpty()) {
linenum ++;
}
}
//System.out.println("line:"+linenum);
inputStreamReader.close();
return linenum;
}
/**单词数量计数器
*
* @param file
* @return wordsnum
* @throws Exception
* @throws FileNotFoundException
*/
public int wordsCounter(File file) throws Exception, FileNotFoundException {
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file), encoding);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
int wordsnum = 0;
String str = null;
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
while ((str = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
//String s = bufferedReader.readLine();
String splited[] = str.split(",|\.| |\?|\!|\'");
for (int i = 0; i < splited.length; i++) {
if (splited[i].length() >= 4 ) {
String temp = splited[i].substring(0, 4);
temp = temp.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z]", "");
if (temp.length() >= 4) {
if (map.containsKey(splited[i].toLowerCase())) {
map.put(splited[i].toLowerCase(), map.get(splited[i].toLowerCase())+1);
}
else {
map.put(splited[i].toLowerCase(), 1);
}
}
}
}
}
wordsnum = map.size();
//System.out.println("words:"+wordsnum);
inputStreamReader.close();
return wordsnum;
}
/**单词统计器
*
* @param file
* @return List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>
* @throws Exception
* @throws FileNotFoundException
*/
public List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> wordsNumCounter(File file) throws Exception, FileNotFoundException {
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file), encoding);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
String str = null;
while ((str = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
//String s = bufferedReader.readLine();
String splited[] = str.split(",|\.| |\?|\!|\'");
for (int i = 0; i < splited.length; i++) {
if (splited[i].length() >= 4 ) {
String temp = splited[i].substring(0, 4);
temp = temp.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z]", "");
if (temp.length() >= 4) {
if (map.containsKey(splited[i].toLowerCase())) {
map.put(splited[i].toLowerCase(), map.get(splited[i].toLowerCase())+1);
}
else {
map.put(splited[i].toLowerCase(), 1);
}
}
}
}
}
List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>(map.entrySet());
// 通过比较器来实现排序
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>() {
@Override
public int compare(Map.Entry<String, Integer> o1, Map.Entry<String, Integer> o2) {
// 降序排序
return o2.getValue().compareTo(o1.getValue());
}
});
inputStreamReader.close();
return list;
}
/**写入文件
*
* @param charcount
* @param linecount
* @param wordscount
* @param list
* @return
* @throws Exception
*
*/
public void writeFile(int charcount,int linecount,int wordscount,List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> list) throws Exception {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder("");
result.append("characters:");
result.append(charcount+linecount-1);
result.append("
");
result.append("words");
result.append(wordscount);
result.append("
");
result.append("lines");
result.append(linecount);
result.append("
");
int count = 0;
for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> map : list) {
count++;
result.append("<" + map.getKey() + ">:" + map.getValue());
if (count>9) {
break;
}
result.append("
");
}
//String pathname = "D:\java_project\wordcount_0910\src\result.txt";
String pathname = System.getProperty("user.dir")+"\result.txt";
//System.out.println("out.locate:"+pathname);
File file = new File(pathname);
if (!file.exists()) {
System.out.println("not found result.txt");
System.out.println("create result.txt");
file.createNewFile();
}
FileWriter filewriter = new FileWriter(file.getAbsoluteFile());
//System.out.println("absolutely path:"+file.getAbsolutePath());
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(filewriter);
bufferedWriter.write(result.toString());
bufferedWriter.close();
}
}
- Main.java
import java.io.File;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author 031602435 xyq
* @version 1
*
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
lib l = new lib();
FileUtil fileUtil = new FileUtil();
//String path = "D:\java_project\wordcount_0910\src\wordcount_0910\input.txt";
String path = args[0];
File file = fileUtil.getFile(path);
int charcount = l.charCounter(file);
int wordscount = l.wordsCounter(file);
int linecount = l.lineCounter(file);
List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> list = l.wordsNumCounter(file);
l.writeFile(charcount, linecount, wordscount, list);
System.out.println("finished");
}
}
接口部分的性能改进
大概就是把数据处理的接口分开写了吧。考虑到以后可能有的改进要求,所以几个数据项的统计功能单独写,方便以后修改。
单元测试
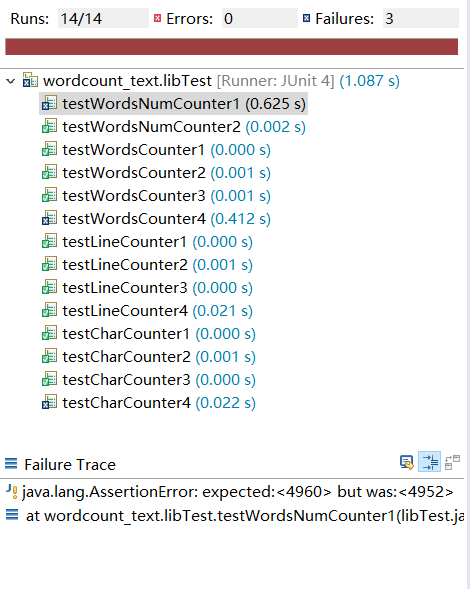
共进行了13个单元测试,其中字符,行数,单词数测试三次自己写的测试文档,和一次助教发在群中的测试文本;词频测试自己写的和群文件中的测试文本各一次。
出错的都是进行的群文件中的测试,大概知道错误原因是漏了一些分隔符的判断,添加了一些分隔符之后结果更接近答案了但还是差一点点,接着会继续找缺了哪些分隔符吧。。如果老师能直接给出所有具体的分隔符就更好了。。
心得体会
收获大概有以下几点
- 学习了java文件读写方法的使用
以前并没有怎么用过java读写过文件,这次的实践让我了解了一些常用方法的用法。 - 学习了如何不用IDE运行代码
之前都是在用eclipse来编写/运行java程序,没有想过使用命令行运行,这次学会了如何将eclipse上的java projection变成一个可用命令行执行的file system。 - 继续学习了github的使用方法
了解了GitHub关于fork,pull request的相关操作
除了收获还有其他不足的地方吧,因为之前做Mapreduce测试的时候有用过自带的Wordcount测试样例,所以潜意识觉得这次作业花不了多少时间就能完成,导致预留的时间不够,转眼就发现快到DDL了。。这次的实践可以说就是草草地收场,只把代码写了出来,至于像代码优化,单元测试,都没有做,作业博客也没有时间认真写了。还有就是在编码的过程中还是没有做到有进展就pull到仓库里面,到最后写完才一起pull进去。
以后的实践任务会尽量留足时间去完成的好一些吧,也希望在接下来的实践任务中能够养成良好的编码习惯。