1.ShouldBindJson vs ShouldBindBodyWith
ShouldBindJSON方法是最常用解析JSON数据的方法之一,但在重复调用的情况下会出现EOF的报错,这个原因出在ShouldBindJSON在调用过一次之后context.request.body.sawEOF的值是false导致,所以如果要多次绑定多个变量,需要使用ShouldBindBodyWith。
至于为什么单次绑定不优选使用BindJSON方法,主要因为BindJSON方法会强制抛出错误,影响正常流程。
简单总结:
- 1.单次解析,追求性能使用
ShouldBindJson,因为多次绑定解析会出现EOF - 2.多次解析,避免报EOF,使用
ShouldBindBodyWith
下面是代码示例:
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin/binding"
"log"
"net/http"
)
type MyMsg struct {
Username string `json:"username"`
Password string `json:"password"`
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.POST("/json", bindJson)
r.POST("/json2", bindJson2)
r.POST("/jsonBody2", bindBodyWith)
r.Run(":8080")
}
// HandlerFunc
func bindJson(c *gin.Context) {
var mymsg MyMsg
// first call ShouldBindJson
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&mymsg); err != nil {
log.Println(err)
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"msg": "bind json is ok"})
}
func bindJson2(c *gin.Context) {
var mymsg MyMsg
// first call ShouldBindJson
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&mymsg); err != nil {
log.Println(err)
}
log.Printf("username: %s, password: %s", mymsg.Username, mymsg.Password)
// second call ShouldBindJson
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&mymsg); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": err.Error()}) // EOF
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"msg": "bind json is ok"})
}
func bindBodyWith(c *gin.Context) {
var mymsg MyMsg
// first call bind
if err := c.ShouldBindBodyWith(&mymsg, binding.JSON); err !=nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
// second call bind
if err := c.ShouldBindBodyWith(&mymsg, binding.JSON); err !=nil { // ok
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"msg": "Bind body with is ok"})
}
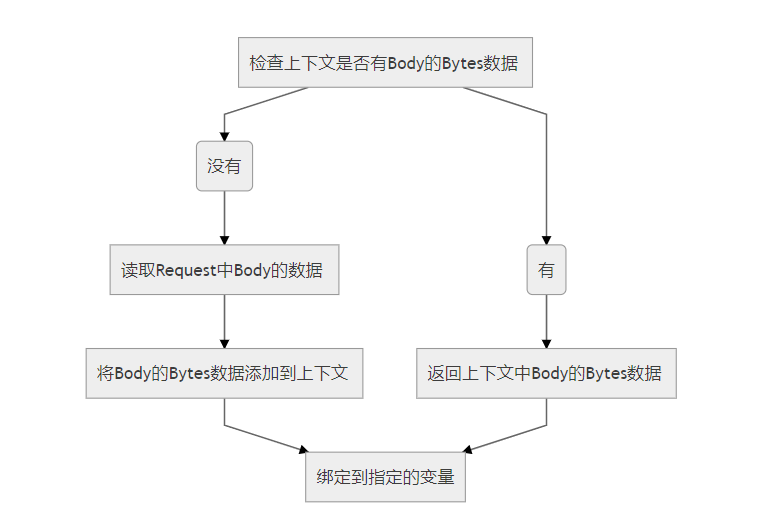
2.gin 源码分析
ShouldBindBodyWith和ShouldBindWith很像,但它保存了requests的Body到上下文,允许Body被继续调用。
注意:这个方法会先读取Body然后绑定,如果只绑定一次,建议使用ShouldBindWith来获得更好的性能(因为后者会直接读取并写到指定变量,而没有写入上下文)。
ShouldBindBodyWith
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/yes169yes123/article/details/106204252