1.ArrayBlockingQueue介绍

1.1BlockingQueue接口
支持阻塞等待的队列:当取出元素的时候,若队列为空,wait直到队列非空;当存储元素的时候,若队列满,wait直到队列有空闲。
对于BlockingQueue,当执行操作的条件不满足时,有四种形式。
|
Throws exception |
Special value |
Blocks |
Times out |
|
|
Insert |
(若队列未满,添加,返回true; 若队列满,抛出IllegalStateException) |
(若队列未满,添加,返回true; 若队列满,返回false) |
(若队列未满,添加,无返回值; 若队列满,wait直到队列有空闲) |
(若队列未满,添加,返回true; 若队列满,wait指定时间后队列还是满,返回false) |
|
Remove |
(若队列非空,移除,返回true; 若队列空,返回false) |
(若队列非空,移除; 若队列空,返回null) |
(若队列非空,移除; 若队列空,wait直到队列非空) |
(若队列非空,移除; 若队列空,wait指定时间后队列还是空,返回null) |
|
Examine |
not applicable |
not applicable |
使用样例——典型的(多)生产者、(多)消费者模型
//生产者线程 class Producer implements Runnable { private final BlockingQueue queue;//阻塞队列 Producer(BlockingQueue q) { queue = q; } public void run() { try { while (true) { queue.put(produce()); }//生产,并入队 } catch (InterruptedException ex) { ... handle ...} } Object produce() { ... } } //消费者线程 class Consumer implements Runnable { private final BlockingQueue queue;//阻塞队列 Consumer(BlockingQueue q) { queue = q; } public void run() { try { while (true) { consume(queue.take()); }//出队,消费 } catch (InterruptedException ex) { ... handle ...} } void consume(Object x) { ... } } class Setup { void main() { BlockingQueue q = new SomeQueueImplementation(); //启动1个生产者线程,2个消费者线程 Producer p = new Producer(q); Consumer c1 = new Consumer(q); Consumer c2 = new Consumer(q); new Thread(p).start(); new Thread(c1).start(); new Thread(c2).start(); } }
1.2ArrayBlockingQueue
ArrayBlockingQueue是数组实现的线程安全的有界的阻塞队列。
1.数组实现:使用数组实现循环队列。

2.线程安全:使用了ReentrantLock来保证线程安全。
3.有界:可存储的元素的个数固定的。因内部为数组实现,一旦创建完成,数组的长度不能再改变。
4.阻塞队列:先进先出。当取出元素的时候,若队列为空,wait直到队列非空;当存储元素的时候,若队列满,wait直到队列有空闲。
2.ArrayBlockingQueue源码分析
2.1创建
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) { if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); this.items = new Object[capacity];//数组存储元素 lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);//锁保证线程安全 notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); notFull = lock.newCondition(); }
2.2生产者消费者模型
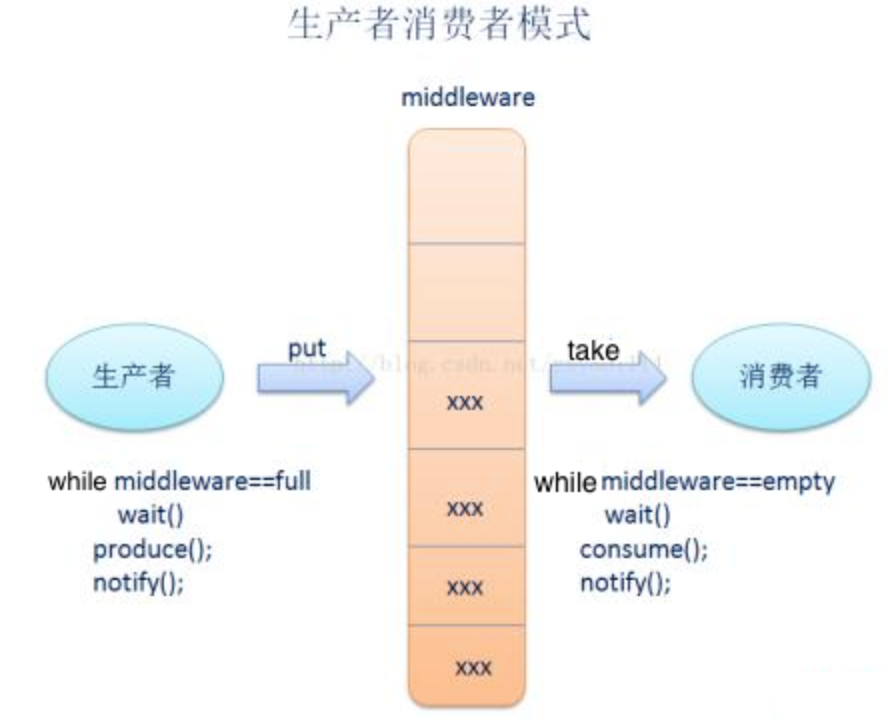
2.2.1生产者生产元素——put方法元素进队
put方法
如何实现【生产者】和【消费者】线程之间的同步
1.若队列满,调用notFull.await()方法,使当前【生产者】线程阻塞等待
2.元素进队后,调用notEmpty.signal()方法,唤醒阻塞的【消费者】线程
//插入指定的element到队列的尾部 //若队列满,当前线程等待,直到队列有空闲 public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException { checkNotNull(e); final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; //获得锁 lock.lockInterruptibly(); try { //若队列满,当前线程等待,直到队列有空闲 while (count == items.length) notFull.await(); //队列有空闲,元素进队 enqueue(e); } finally { //释放锁 lock.unlock(); } } private void enqueue(E x) { // assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1; // assert items[putIndex] == null; //元素进队 final Object[] items = this.items; items[putIndex] = x; if (++putIndex == items.length) putIndex = 0; count++; //唤醒阻塞在notEmepty上的线程 notEmpty.signal(); }
2.2.2消费者消费元素——take方法元素出队
take方法
如何实现【生产者】和【消费者】线程同步
1.若队列为空,调用notEmpty.await()方法,使当前【消费者】线程阻塞等待
2.元素进队后,调用notFull.signal()方法,唤醒阻塞的【生产者】线程
//返回队列头部的元素 //若队列为空,等待,直到队列非空 public E take() throws InterruptedException { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; //获得锁 lock.lockInterruptibly(); try { //若队列为空,等待,直到队列非空 while (count == 0) notEmpty.await(); //队列非空,返回队头元素 return dequeue(); } finally { //释放锁 lock.unlock(); } } private E dequeue() { // assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1; // assert items[takeIndex] != null; //返回队头元素 final Object[] items = this.items; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E x = (E) items[takeIndex]; items[takeIndex] = null; if (++takeIndex == items.length) takeIndex = 0; count--; if (itrs != null) itrs.elementDequeued(); //唤醒阻塞在notFull上的线程 notFull.signal(); return x; }