参考
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie
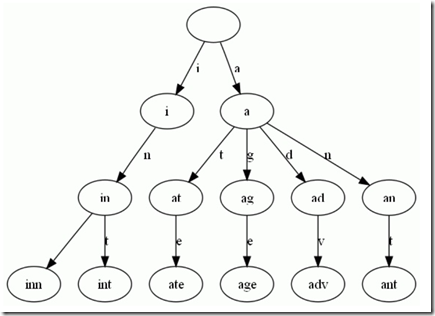
a trie, also called digital tree or prefix tree, is a kind of search tree—an ordered tree data structure used to store a dynamic set or associative array where the keys are usually strings
也叫前缀树, 特定情况下替代set 和map。这时候key是字符串。
LeetCode:208. Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)
LeetCode:211. Add and Search Word - Data structure design
LeetCode:212. Word Search II
下面我们就一步步来实现Trie,并做题
一、初步实现Trie树结构
208. Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)
https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-trie-prefix-tree/description/
非递归实现
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie* obj = new Trie();
* obj->insert(word);
* bool param_2 = obj->search(word);
* bool param_3 = obj->startsWith(prefix);
*/
const int letter_size=26;//字符集大小
struct TrieNode
{ TrieNode* children[letter_size]={0};bool isWord = false;
TrieNode(){}
~TrieNode(){for(int i=0; i<letter_size; i++) if(children[i]) delete children[i];
}
};
struct Trie {TrieNode* root;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
Trie() {root=new TrieNode();
}
~Trie(){delete root;
}
int idx(char c)
{return c - 'a';
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
void insert(string word) {TrieNode*p = root;
int len = word.length();
for(int i=0; i < len; i++){int c = idx(word[i]);
if(!p->children[c])
p->children[c] = new TrieNode();
p = p->children[c];
}
p->isWord = true;
}
//辅助函数
TrieNode * _search(string &word)
{TrieNode *p=root;
int len = word.length();
for(int i=0; i < len; i++){TrieNode *t = p->children[idx(word[i])];
if(!t)
return 0;
else
p = t;
}
return p;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
bool search(string word) {TrieNode *p=_search(word);
return p && p->isWord;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
bool startsWith(string word) {return _search(word);;
}
};
int main()
{Trie trie;
trie.insert("apple"); cout<< trie.search("apple") << endl; // returns true cout<< trie.search("app") << endl; // returns false cout<< trie.startsWith("app") << endl; // returns true trie.insert("app"); cout<< trie.search("app") << endl;; // returns truereturn 0;
}
递归实现:
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie* obj = new Trie();
* obj->insert(word);
* bool param_2 = obj->search(word);
* bool param_3 = obj->startsWith(prefix);
*/
const int letter_size=26;//字符集大小
struct TrieNode
{ TrieNode* children[letter_size]={0};bool isWord = false;
TrieNode(){}
~TrieNode(){for(int i=0; i<letter_size; i++) if(children[i]) delete children[i];
}
};
struct Trie {TrieNode* root;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
Trie() {root=new TrieNode();
}
// OJ上去掉析构会快很多
~Trie(){delete root;
}
int idx(char c)
{return c - 'a';
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
void insert(string word) {TrieNode*p = root;
int len = word.length();
for(int i=0; i < len; i++){int c = idx(word[i]);
if(!p->children[c])
p->children[c] = new TrieNode();
p = p->children[c];
}
p->isWord = true;
}
TrieNode* dfs(TrieNode *root, string &word, int pos)
{if(pos==word.length())
return root;
int c = word[pos];
TrieNode* p = root->children[idx(c)];
if(p)
return dfs(p, word, pos+1);
else
return 0;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
bool search(string word) {TrieNode *p = dfs(root, word, 0);
return p && p->isWord;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
bool startsWith(string word) {TrieNode *p = dfs(root, word, 0);
return p!=0;
}
};
int main()
{Trie trie;
trie.insert("apple"); cout<< trie.search("apple") << endl; // returns true cout<< trie.search("app") << endl; // returns false cout<< trie.startsWith("app") << endl; // returns true trie.insert("app"); cout<< trie.search("app") << endl;; // returns truereturn 0;
}
二、Trie树的运用:Trie树+回溯法
充分理解这道题后,就可以接着将这种数据结构投入运用了。
这一道题和上一题类似,需要你实现两个API,一个 插入,一个查找。插入和上一题相同,查找则需要实现“模糊查找”即:
addWord("bad")
addWord("dad")
addWord("mad")
search("pad") -> false
search("bad") -> true
search(".ad") -> true
search("b..") –> true
https://leetcode.com/problems/add-and-search-word-data-structure-design
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie* obj = new Trie();
* obj->insert(word);
* bool param_2 = obj->search(word);
* bool param_3 = obj->startsWith(prefix);
*/
const int letter_size=26;//字符集大小
struct TrieNode
{ TrieNode* children[letter_size]={0};bool isWord = false;
TrieNode(){}
~TrieNode(){for(int i=0; i<letter_size; i++) if(children[i]) delete children[i];
}
};
struct Trie {TrieNode* root;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
Trie() {root=new TrieNode();
}
// OJ上去掉析构会快很多
~Trie(){delete root;
}
int idx(char c)
{return c - 'a';
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
void insert(string word) {TrieNode*p = root;
int len = word.length();
for(int i=0; i < len; i++){int c = idx(word[i]);
if(!p->children[c])
p->children[c] = new TrieNode();
p = p->children[c];
}
p->isWord = true;
}
TrieNode* dfs(TrieNode *root, string &word, int pos)
{if(pos==word.length())
return root;
int c = word[pos];
// . 的话,匹配所有子节点
if(c=='.')
{for(auto p : root->children)
{if(p)
{TrieNode* t = dfs(p, word, pos+1);
if(t && t->isWord) return t;//如果找到一个,直接返回(需要判断是否是word,否则可能返回中间节点)
}
}
}
else// 否则,正常匹配
{TrieNode* p = root->children[idx(c)];
if(p)
return dfs(p, word, pos+1);
else
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
bool search(string word) {TrieNode *p = dfs(root, word, 0);
return p && p->isWord;
}
// /** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
// bool startsWith(string word) {// TrieNode *p = dfs(root, word, 0);
// return p!=0;
// }
};
//["WordDictionary","addWord","addWord","addWord","addWord","addWord","addWord","addWord","addWord","search","search","search","search","search","search","search","search","search","search"]
//[[],["ran"],["rune"],["runner"],["runs"],["add"],["adds"],["adder"],["addee"],["r.n"],["ru.n.e"],["add"],["add."],["adde."],[".an."],["...s"],["....e."],["......."],["..n.r"]]
int main()
{Trie trie;
vector<string> input={"ran","rune","runner","runs","add","adds","adder","addee"};for(string s: input)
{cout<<s<<endl;
trie.insert(s);
}
vector<string> search={"r.n","ru.n.e","add","add.","adde.",".an.","...s","....e.",".......","..n.r"};for(string s: search)
{cout<< trie.search(s) << endl;
}
cout<< trie.search("add.") << endl; // returns truereturn 0;
}
三、Trie树的运用:Trie树+深度优先搜索
Word Search II - LeetCodeleetcode.com此题咋一看,很简单嘛,把针对每个单词进行一次深度优先搜索不就行了?这个思路是可行的,但十有八九会超时。因为深度优先搜索本身就是一种比较耗时间和内存的算法。
但这道题似乎也只好用深度优先搜索,那么,有没有可能只进行一次搜索,就查明白所有的单词是否存在于这个二维矩阵中?
是的,这个时候你需要Trie树。而且题目也有提示,你看,output里面不是按字典顺序输出的吗?哈哈。 所以思路如下:
1、所有单词建立Trie树
2、dfs每个board位置, 去和Trie路径匹配。Tire当前位置有这个字母时候,才继续dfs下去。
Example:
Input: board = [ ['o','a','a','n'], ['e','t','a','e'], ['i','h','k','r'], ['i','f','l','v'] ] words =["oath","pea","eat","rain"]Output:["eat","oath"]
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class TrieNode{//树节点结构public:
TrieNode*next[26]={0};int isexist = -1;//-1表示节点表示的单词不存在,0及以上的数表示此单词存在且与vector<string>>words的序号对应
TrieNode(){}
~TrieNode(){ for(int i=0;i<26;i++){if(next[i])delete next[i];
}
}
};
#include <unordered_set>
class Solution {public:
TrieNode* root=0;
int arr[4][2]={{1,0},{-1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};//搜索的四个方向int idx(char c)
{return c - 'a';
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
void insert(string word, int index) {TrieNode*p = root;
int len = word.length();
for(int i=0; i < len; i++){int c = idx(word[i]);
if(!p->next[c])
p->next[c] = new TrieNode();
p = p->next[c];
}
p->isexist = index;
}
void dfs(int r,int c,TrieNode*pNode,unordered_set<int>&res,vector<vector<char>>b){b[r][c]='0';//标记已经搜索过得地方为‘0’
if(pNode && pNode->isexist>=0){//如果isexist>=0表示word[isexist]存在于此节点。res.insert(pNode->isexist);
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){//向上下左右四个方向搜索int newr=r+arr[i][0],newc=c+arr[i][1];
if(newr>=0&&newc>=0&&newr<b.size()&&newc<b[0].size()&&b[newr][newc]!='0'&&pNode->next[b[newr][newc]-'a']){dfs(newr,newc,pNode->next[b[newr][newc]-'a'],res,b);
}
}
}
vector<string> findWords(vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<string>& words) {//所有单词建立Tire
root=new TrieNode();
for(int i=0; i<words.size(); i++)
insert(words[i], i);
unordered_set<int>res;//用于保存在board中查找到的words的序号
for(int r=0;r<(int)board.size();r++){ for(int c=0;c<(int)board[r].size();c++){if(root->next[board[r][c]-'a'])dfs(r,c,root->next[board[r][c]-'a'],res,board);
}
}
vector<string>ress;//根据res中的序号制作string数组返回
for(auto it:res){ress.push_back(words[it]);
}
return ress;
}
};
int main()
{ vector<vector<char>> board={ {'o','a','a','n'}, {'e','t','a','e'}, {'i','h','k','r'}, {'i','f','l','v'}};
vector<string> words = {"oath","pea","eat","rain"};Solution s;
vector<string> result = s.findWords(board, words);
for(auto it:result){cout << it <<endl;
}
return 0;
}