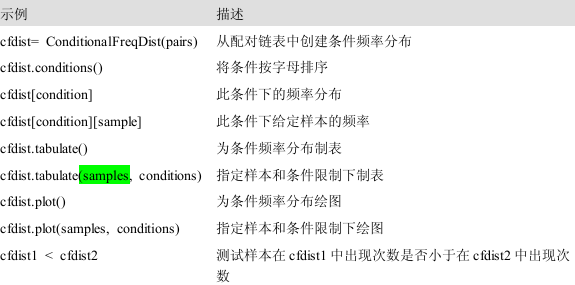
条件概率分布是频率分布的集合,每个频率分布有一个不同的条件。这个条件通常是文本的类别。它的每对的形式是:(条件、事件)
按文体计数词汇
#先从语料库中设置条件频率分布 From nltk.corpus import brown Cfd=nltk.ConditionalFreqDist( (genre,word) For genre in brown.categories() For word in brown.words(categories=genre) #可以选择自己感兴趣的进行查看,组成一个以对为元素的链表 Genre_word=[(genre,word) For genre in [‘news’,’romance’] For word in brown.words(categories=genre) Len(genre_word) #有了这个配对链表,也可以用这种方式,进行设置条件频率分布 Cfd=nltk.ConditionalFreqDist(genre_word) Cfd.conditions()-查看我们设置的条件 List(cfd[‘romance’])-查看所有的条件下的单词 Cfd[‘romance’][‘could’]-查看具体的数值
绘制分布图和分布表
这两种方法分别是cfd.plot()和cfd.tabulate()
还有一些其他的参数。Conditions=parameter,来制定选择哪些条件显示
Samples=parameter,来限制要显示的样本,例如:
Cfd.tabulate(conditions=[‘English’,’German_Deutsch’],samples=range(10),cumulative=True)
使用双连词生成随机文本
>>>sent = ['In', 'the', 'beginning', 'God', 'created', 'the', 'heaven', ... 'and', 'the', 'earth', '.'] >>>nltk.bigrams(sent) [('In', 'the'), ('the', 'beginning'), ('beginning', 'God'), ('God', 'created'), ('created', 'the'), ('the', 'heaven'), ('heaven', 'and'), ('and', 'the'), ('the', 'earth'), ('earth', '.')] #现在我们将要写一个函数,使用这个函数随机生成文本。需要来构建一个条件频率分布,来记录哪些词汇最有可能跟在定词的后面。 Def generate_model(cfdist,word,num=15): For i in range(num): Print word, Word=cfdist([word]).max() Text=nltk.corpus.genesis.words(‘english-kjv.txt’) Bigrams=nltk.bigrams(text) Cfd=nltk.ConditionalFreeqDist(bigrams) Print cfd[living] <FreqDist:'creature': 7, 'thing': 4, 'substance': 2, ',': 1, '.': 1, 'soul': 1> Generate_model(cfd,”living”) living creature that hesaid , and the land ofthe land ofthe land #常用的关于条件频率分布的方法