系统初始化期间,Linux 都首先要在内存当中构造一棵VFS的目录树,实际上便是在内存中建立相应的数据结构。
文件系统注册
在 Linux 源代码中,每种实际的文件系统用以下的数据结构表示:
struct file_system_type { const char *name; int fs_flags; int (*get_sb) (struct file_system_type *, int, const char *, void *, struct vfsmount *); void (*kill_sb) (struct super_block *); struct module *owner; struct file_system_type * next; struct list_head fs_supers; struct lock_class_key s_lock_key; struct lock_class_key s_umount_key; };
注册过程实际上将表示各实际文件系统的 struct file_system_type数据结构的实例化,然后形成一个链表,内核中用一个名为 file_systems的全局变量来指向该链表的表头.
rootfs注册
rootfs 的注册是通过init_rootfs()这一初始化函数来完成,这意味着rootfs的注册过程是 Linux 内核初始化阶段不可分割的一部分。
init_rootfs_fs->register_filesystem
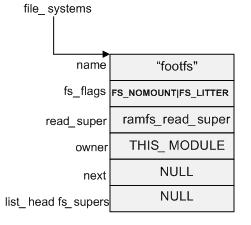
static struct file_system_type rootfs_fs_type = { .name = "rootfs", .get_sb = rootfs_get_sb, /* 创建superblock*/ .kill_sb = kill_litter_super, }; int __init init_rootfs(void) { return register_filesystem(&rootfs_fs_type); }
把rootfs挂在到全局file_systems链表上。
int register_filesystem(struct file_system_type * fs) { int res = 0; struct file_system_type ** p; if (!fs) return -EINVAL; if (fs->next) return -EBUSY; INIT_LIST_HEAD(&fs->fs_supers); write_lock(&file_systems_lock); p = find_filesystem(fs->name); if (*p) res = -EBUSY; else *p = fs; write_unlock(&file_systems_lock); return res; } static struct file_system_type *file_systems; static struct file_system_type **find_filesystem(const char *name) { struct file_system_type **p; for (p=&file_systems; *p; p=&(*p)->next) if (strcmp((*p)->name,name) == 0) break; return p; }
注册之后的 file_systems 链表结构如下图所示:
VFS根目录建立
init_mount_tree() 函数会调用 do_kern_mount(“rootfs”, 0, “rootfs”, NULL) 来挂载前面已经注册了的 rootfs 文件系统。这看起来似乎有点奇怪,因为根据前面的说法,似乎是应该先有挂载目录,然后再在其上挂载相应的文件系统,然而此时 VFS 似乎并没有建立其根目录。没关系,这是因为这里我们调用的是 do_kern_mount(),这个函数内部自然会创建我们最关心也是最关键的根目录(在 Linux 中,目录对应的数据结构是 struct dentry)。
命名空间
每个进程可拥有自己的已安装文件树——叫做进程的命名空间(namespace)。
对于每一个进程都有自己的namespace,这可以理解为这个进程的地盘。在这里,所有的文件系统都要挂上来统一管理。
通常大多数进程共享一个命名空间,即位于系统的根文件系统且被init进程使用的已安装文件系统树。
不过如果clone()系统调用以CLONE_NEWNS标志创建一个新进程,那么进程将获取一个新的命名空间,这个新的命名空间随后由子进程继承(如果父进程没有以CLONE_NEWNS标志创建这些进程)。
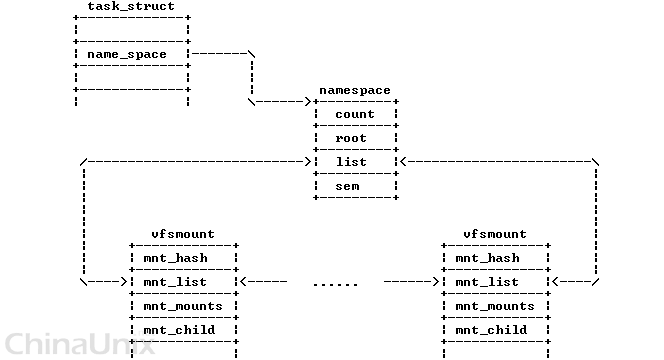
struct namespace { atomic_t count; /* 引用计数 */ struct vfsmount * root; /* 根目录的 vfsmount */ struct list_head list; /* 所有已mount的文件系统都挂载这链表上 */ wait_queue_head_t poll; int event; };
vfsmount
已安装文件系统描述符vfsmount。
对于每一个命名空间,所有属于此命名空间的已安装的文件系统描述符形成了一个双向循环链表。
下图vfs_tree_1,namespace结构的list字段存放链表的头,vfsmount描述符的mnt_list字段包含链表中指向相邻元素的指针:
vfs_tree_2
建立根目录
在初始化阶段是如何建立根结点的,即 “/“目录。这其中会包括挂载 rootfs 文件系统到根目录 “/“ 的具体过程。
构造根目录的代码是在 init_mount_tree函数中。
- init_mount_tree()函数会调用do_kern_mount(“rootfs”, 0, “rootfs”, NULL)来挂载前面已经注册了的 rootfs 文件系统。
- do_kern_mount()函数内部创建VFS的根目录(在 Linux 中,目录对应的数据结构是 struct dentry)。
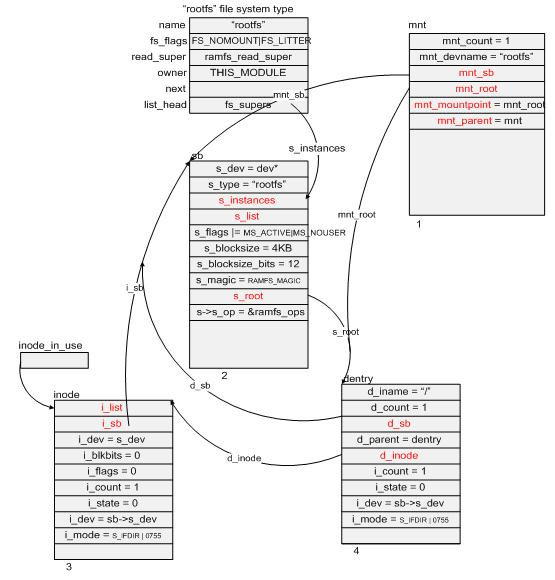
static void __init init_mount_tree(void) { struct vfsmount *mnt; struct namespace *namespace; struct task_struct *g, *p; //do_kern_mount函数主要作用: //1.在内存里申请了一块该类型的内存空间(struct vfsmount *mnt),并初始化其部分成员变量 //2.调用rootfs->get_sb_nodev函数在内存中分配一个超级块结构 (struct super_block) sb, // 并初始化其部分成员变量,将成员s_instances插入到rootfs中的fs_supers指向的双向链表中 //3.调用rootfs->get_sb_nodev->fill_super->simple_fill_super函数: // 在内存中分配了一个inode (struct inode) ,并初始化其部分成员变量(i_op、i_fop等) // 还有生成根目录dentry。root = d_alloc_root(inode); mnt = do_kern_mount("rootfs", 0, "rootfs", NULL); if (IS_ERR(mnt)) panic("Can't create rootfs"); //在内存里申请命名空间 namespace = kmalloc(sizeof(*namespace), GFP_KERNEL); if (!namespace) panic("Can't allocate initial namespace"); atomic_set(&namespace->count, 1); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&namespace->list); init_waitqueue_head(&namespace->poll); namespace->event = 0; //如上图vfs_tree_1所示,把mnt_list挂在到namespace->list上 list_add(&mnt->mnt_list, &namespace->list); namespace->root = mnt; mnt->mnt_namespace = namespace; //为系统最开始的进程(即init_task进程)准备它的进程数据块中的namespace //将mnt和dentry信息记录在了init_task进程的进程数据块中, //这样所有以后从init_task进程fork出来的进程也都先天地继承了这一信息 init_task.namespace = namespace; read_lock(&tasklist_lock); do_each_thread(g, p) { get_namespace(namespace); p->namespace = namespace; } while_each_thread(g, p); read_unlock(&tasklist_lock); //下面两行就是把mnt和dentry信息记录在了当前进程的 fs结构中 //namespace->root指向roofs的vfsmount //namespace->root->mnt_root指向根目录dentry set_fs_pwd(current->fs, namespace->root, namespace->root->mnt_root); set_fs_root(current->fs, namespace->root, namespace->root->mnt_root); }
函数init_mount_tree调用完毕后,结构如下图:
一旦VFS目录树建立,就可以通过系统调用sys_mkdir在这棵树上建立新的叶子节点等。
VFS目录树中各目录的主要用途是为以后挂载文件系统提供挂载点,所以将rootfs文件系统挂载到了这棵树的根目录上,而真正的文件操作还是要通过挂载后的文件系统提供的功能接口来进行。
VFS建立新目录
VFS目录树建立,就可以通过系统调用sys_mkdir在这棵树上建立新的叶子节点等。
下面我们用一个实际例子来看看Linux是如何在 VFS 的根目录下建立一个新的目录 “/dev” 的。
sys_mkdir
系统调用sys_mkdir(“/dev/“, 0700)->do_path_lookup
asmlinkage long sys_mkdir(const char __user *pathname, int mode) { return sys_mkdirat(AT_FDCWD, pathname, mode); } struct nameidata { struct dentry *dentry; struct vfsmount *mnt; struct qstr last; unsigned int flags; int last_type; unsigned depth; char *saved_names[MAX_NESTED_LINKS + 1]; /* Intent data */ union { struct open_intent open; } intent; }; asmlinkage long sys_mkdirat(int dfd, const char __user *pathname, int mode) { int error = 0; char * tmp; tmp = getname(pathname); error = PTR_ERR(tmp); if (!IS_ERR(tmp)) { struct dentry *dentry; struct nameidata nd; error = do_path_lookup(dfd, tmp, LOOKUP_PARENT, &nd); if (error) goto out; dentry = lookup_create(&nd, 1); error = PTR_ERR(dentry); if (!IS_ERR(dentry)) { if (!IS_POSIXACL(nd.dentry->d_inode)) mode &= ~current->fs->umask; error = vfs_mkdir(nd.dentry->d_inode, dentry, mode); dput(dentry); } mutex_unlock(&nd.dentry->d_inode->i_mutex); path_release(&nd); out: putname(tmp); } return error; }
转载自:地址