Given a binary tree where node values are digits from 1 to 9. A path in the binary tree is said to be pseudo-palindromic if at least one permutation of the node values in the path is a palindrome.
Return the number of pseudo-palindromic paths going from the root node to leaf nodes.
Example 1:
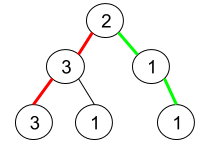
Input: root = [2,3,1,3,1,null,1] Output: 2 Explanation: The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the red path [2,3,3], the green path [2,1,1], and the path [2,3,1]. Among these paths only red path and green path are pseudo-palindromic paths since the red path [2,3,3] can be rearranged in [3,2,3] (palindrome) and the green path [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
Example 2:
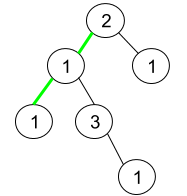
Input: root = [2,1,1,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,1] Output: 1 Explanation: The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the green path [2,1,1], the path [2,1,3,1], and the path [2,1]. Among these paths only the green path is pseudo-palindromic since [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
Example 3:
Input: root = [9] Output: 1
Constraints:
- The given binary tree will have between
1and10^5nodes. - Node values are digits from
1to9.
二叉树中的伪回文路径。
给你一棵二叉树,每个节点的值为 1 到 9 。我们称二叉树中的一条路径是 「伪回文」的,当它满足:路径经过的所有节点值的排列中,存在一个回文序列。
请你返回从根到叶子节点的所有路径中 伪回文 路径的数目。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pseudo-palindromic-paths-in-a-binary-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路是DFS + 回溯。这道题跟113题很像,你需要去找到树中每一条从根节点到叶子节点的路径,然后再多一步判断,判断每一条路径是不是满足题目定义的伪回文。判断伪回文额外写一个函数判断即可。这里我提供两种做法,思路差不多,第一种方法速度快一些,第二种方法不使用全局变量。两种做法的时间空间复杂度均为O(n)。
DFS + 回溯
count是全局变量而且hashmap是被带入helper函数往下一层去递归的,所以需要回溯
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode() {} 8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { 10 * this.val = val; 11 * this.left = left; 12 * this.right = right; 13 * } 14 * } 15 */ 16 class Solution { 17 int count = 0; 18 19 public int pseudoPalindromicPaths(TreeNode root) { 20 int[] map = new int[10]; 21 helper(root, map); 22 return count; 23 } 24 25 private void helper(TreeNode root, int[] map) { 26 // base case 27 if (root == null) { 28 return; 29 } 30 map[root.val]++; 31 if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { 32 if (isPalindrome(map)) { 33 count++; 34 } 35 } 36 37 helper(root.left, map); 38 helper(root.right, map); 39 map[root.val]--; 40 } 41 42 private boolean isPalindrome(int[] map) { 43 int single = 0; 44 for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) { 45 if (map[i] % 2 == 1) { 46 single++; 47 } 48 } 49 return single > 1 ? false : true; 50 } 51 }
更像前序遍历的一种做法,没有回溯
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode() {} 8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { 10 * this.val = val; 11 * this.left = left; 12 * this.right = right; 13 * } 14 * } 15 */ 16 class Solution { 17 public int pseudoPalindromicPaths(TreeNode root) { 18 return helper(root, new HashSet<>()); 19 } 20 21 private int helper(TreeNode root, HashSet<Integer> set) { 22 if (root == null) { 23 return 0; 24 } 25 if (set.contains(root.val)) { 26 set.remove(root.val); 27 } else { 28 set.add(root.val); 29 } 30 if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { 31 return set.size() <= 1 ? 1 : 0; 32 } 33 // 注意这里hashset的细节 34 int left = helper(root.left, new HashSet<>(set)); 35 int right = helper(root.right, new HashSet<>(set)); 36 return left + right; 37 } 38 }
相关题目