Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,null,2,3] Output: [1,3,2]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1] Output: [1]
Example 4:

Input: root = [1,2] Output: [2,1]
Example 5:

Input: root = [1,null,2] Output: [1,2]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
二叉树的中序遍历。
中序遍历我记为 左 - 根 - 右。
还是用GeeksforGeeks的例子来描述如何做中序遍历吧。
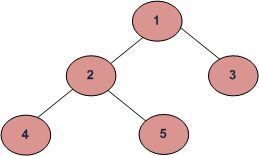
Inorder (Left, Root, Right) : 4 2 5 1 3
树的遍历大部分都是可以给出迭代和递归两种做法的,此题我也给出两种做法。两种做法的时间和空间复杂度一样,时间都是O(n),空间都是O(h)。
迭代
(配合例子看)迭代的做法是需要将所有的左孩子先放进栈,这样弹出的时候(15行),最小的左孩子4就被存入结果集了。此时cur指针在stack顶端,2的位置,所以此时才会有17行去看2是否有右孩子。有的话,下一次while循环的一开头,这个右孩子5就会被再次放进栈。
JavaScript实现
1 /** 2 * @param {TreeNode} root 3 * @return {number[]} 4 */ 5 var inorderTraversal = function(root) { 6 let res = []; 7 if (root === null) return res; 8 let stack = []; 9 let cur = root; 10 while (cur !== null || stack.length) { 11 while (cur !== null) { 12 stack.push(cur); 13 cur = cur.left; 14 } 15 cur = stack.pop(); 16 res.push(cur.val); 17 cur = cur.right; 18 } 19 return res; 20 };
Java实现
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) return res; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); TreeNode cur = root; while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { while (cur != null) { stack.push(cur); cur = cur.left; } cur = stack.pop(); res.add(cur.val); cur = cur.right; } return res; } }
递归
递归的做法很直观,既然是中序遍历,所以根节点需要放在左孩子和右孩子的helper函数中间。
JavaScript实现
1 /** 2 * @param {TreeNode} root 3 * @return {number[]} 4 */ 5 var inorderTraversal = function(root) { 6 let res = []; 7 if (root === null) return res; 8 helper(res, root); 9 return res; 10 }; 11 12 var helper = function(res, root) { 13 if (root === null) return; 14 helper(res, root.left); 15 res.push(root.val); 16 helper(res, root.right); 17 };
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode() {} 8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { 10 * this.val = val; 11 * this.left = left; 12 * this.right = right; 13 * } 14 * } 15 */ 16 class Solution { 17 public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { 18 List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); 19 if (root == null) { 20 return res; 21 } 22 helper(res, root); 23 return res; 24 } 25 26 public static void helper(List<Integer> res, TreeNode root) { 27 if (root == null) { 28 return; 29 } 30 helper(res, root.left); 31 res.add(root.val); 32 helper(res, root.right); 33 } 34 }
关于为什么很多树的题目的空间复杂度是O(h) - 树的高度,我这里给一个discussion里面看到的截图。我看到这个截图我彻底懂了为什么是跟树的高度有关了。
树的遍历
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
