sklearn数据集划分方法有如下方法:
KFold,GroupKFold,StratifiedKFold,LeaveOneGroupOut,LeavePGroupsOut,LeaveOneOut,LeavePOut,ShuffleSplit,GroupShuffleSplit,StratifiedShuffleSplit,PredefinedSplit,TimeSeriesSplit,
①数据集划分方法——K折交叉验证:KFold,GroupKFold,StratifiedKFold,
- 将全部训练集S分成k个不相交的子集,假设S中的训练样例个数为m,那么每一个自己有m/k个训练样例,相应的子集为{s1,s2,...,sk}
- 每次从分好的子集里面,拿出一个作为测试集,其他k-1个作为训练集
- 在k-1个训练集上训练出学习器模型
- 把这个模型放到测试集上,得到分类率的平均值,作为该模型或者假设函数的真实分类率
这个方法充分利用了所以样本,但计算比较繁琐,需要训练k次,测试k次
KFold:
import numpy as np #KFold from sklearn.model_selection import KFold X=np.array([[1,2],[3,4],[5,6],[7,8],[9,10],[11,12]]) y=np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6]) kf=KFold(n_splits=2) #分成几个组 kf.get_n_splits(X) print(kf)
for train_index,test_index in kf.split(X):
print("Train Index:",train_index,",Test Index:",test_index)
X_train,X_test=X[train_index],X[test_index]
y_train,y_test=y[train_index],y[test_index]
#print(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
#KFold(n_splits=2, random_state=None, shuffle=False) #Train Index: [3 4 5] ,Test Index: [0 1 2] #Train Index: [0 1 2] ,Test Index: [3 4 5]
GroupKFold:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import GroupKFold
X=np.array([[1,2],[3,4],[5,6],[7,8],[9,10],[11,12]])
y=np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6])
groups=np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6])
group_kfold=GroupKFold(n_splits=2)
group_kfold.get_n_splits(X,y,groups)
print(group_kfold)
for train_index,test_index in group_kfold.split(X,y,groups):
print("Train Index:",train_index,",Test Index:",test_index)
X_train,X_test=X[train_index],X[test_index]
y_train,y_test=y[train_index],y[test_index]
#print(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
#GroupKFold(n_splits=2)
#Train Index: [0 2 4] ,Test Index: [1 3 5]
#Train Index: [1 3 5] ,Test Index: [0 2 4]
StratifiedKFold:保证训练集中每一类的比例是相同的
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
X=np.array([[1,2],[3,4],[5,6],[7,8],[9,10],[11,12]])
y=np.array([1,1,1,2,2,2])
skf=StratifiedKFold(n_splits=3)
skf.get_n_splits(X,y)
print(skf)
for train_index,test_index in skf.split(X,y):
print("Train Index:",train_index,",Test Index:",test_index)
X_train,X_test=X[train_index],X[test_index]
y_train,y_test=y[train_index],y[test_index]
#print(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
#StratifiedKFold(n_splits=3, random_state=None, shuffle=False)
#Train Index: [1 2 4 5] ,Test Index: [0 3]
#Train Index: [0 2 3 5] ,Test Index: [1 4]
#Train Index: [0 1 3 4] ,Test Index: [2 5]
②数据集划分方法——留一法:LeaveOneGroupOut,LeavePGroupsOut,LeaveOneOut,LeavePOut,
- 留一法验证(Leave-one-out,LOO):假设有N个样本,将每一个样本作为测试样本,其他N-1个样本作为训练样本,这样得到N个分类器,N个测试结果,用这N个结果的平均值来衡量模型的性能
- 如果LOO与K-fold CV比较,LOO在N个样本上建立N个模型而不是k个,更进一步,N个模型的每一个都是在N-1个样本上训练的,而不是(k-1)*n/k。两种方法中,假定k不是很大而且k<<N,LOO比k-fold CV更耗时
- 留P法验证(Leave-p-out):有N个样本,将每P个样本作为测试样本,其它N-P个样本作为训练样本,这样得到
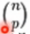 个train-test pairs,不像LeaveOneOut和KFold,当P>1时,测试集将会发生重叠,当P=1的时候,就变成了留一法
个train-test pairs,不像LeaveOneOut和KFold,当P>1时,测试集将会发生重叠,当P=1的时候,就变成了留一法
leaveOneOut:测试集就留下一个
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import LeaveOneOut
X=np.array([[1,2],[3,4],[5,6],[7,8],[9,10],[11,12]])
y=np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6])
loo=LeaveOneOut()
loo.get_n_splits(X)
print(loo)
for train_index,test_index in loo.split(X,y):
print("Train Index:",train_index,",Test Index:",test_index)
X_train,X_test=X[train_index],X[test_index]
y_train,y_test=y[train_index],y[test_index]
#print(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
#LeaveOneOut()
#Train Index: [1 2 3 4 5] ,Test Index: [0]
#Train Index: [0 2 3 4 5] ,Test Index: [1]
#Train Index: [0 1 3 4 5] ,Test Index: [2]
#Train Index: [0 1 2 4 5] ,Test Index: [3]
#Train Index: [0 1 2 3 5] ,Test Index: [4]
#Train Index: [0 1 2 3 4] ,Test Index: [5
LeavePOut:测试集留下P个
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import LeavePOut
X=np.array([[1,2],[3,4],[5,6],[7,8],[9,10],[11,12]])
y=np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6])
lpo=LeavePOut(p=3)
lpo.get_n_splits(X)
print(lpo)
for train_index,test_index in lpo.split(X,y):
print("Train Index:",train_index,",Test Index:",test_index)
X_train,X_test=X[train_index],X[test_index]
y_train,y_test=y[train_index],y[test_index]
#print(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
#LeavePOut(p=3)
#Train Index: [3 4 5] ,Test Index: [0 1 2]
#Train Index: [2 4 5] ,Test Index: [0 1 3]
#Train Index: [2 3 5] ,Test Index: [0 1 4]
#Train Index: [2 3 4] ,Test Index: [0 1 5]
#Train Index: [1 4 5] ,Test Index: [0 2 3]
#Train Index: [1 3 5] ,Test Index: [0 2 4]
#Train Index: [1 3 4] ,Test Index: [0 2 5]
#Train Index: [1 2 5] ,Test Index: [0 3 4]
#Train Index: [1 2 4] ,Test Index: [0 3 5]
#Train Index: [1 2 3] ,Test Index: [0 4 5]
#Train Index: [0 4 5] ,Test Index: [1 2 3]
#Train Index: [0 3 5] ,Test Index: [1 2 4]
#Train Index: [0 3 4] ,Test Index: [1 2 5]
#Train Index: [0 2 5] ,Test Index: [1 3 4]
#Train Index: [0 2 4] ,Test Index: [1 3 5]
#Train Index: [0 2 3] ,Test Index: [1 4 5]
#Train Index: [0 1 5] ,Test Index: [2 3 4]
#Train Index: [0 1 4] ,Test Index: [2 3 5]
#Train Index: [0 1 3] ,Test Index: [2 4 5]
#Train Index: [0 1 2] ,Test Index: [3 4 5]
③数据集划分方法——随机划分法:ShuffleSplit,GroupShuffleSplit,StratifiedShuffleSplit
- ShuffleSplit迭代器产生指定数量的独立的train/test数据集划分,首先对样本全体随机打乱,然后再划分出train/test对,可以使用随机数种子random_state来控制数字序列发生器使得讯算结果可重现
- ShuffleSplit是KFlod交叉验证的比较好的替代,他允许更好的控制迭代次数和train/test的样本比例
- StratifiedShuffleSplit和ShuffleSplit的一个变体,返回分层划分,也就是在创建划分的时候要保证每一个划分中类的样本比例与整体数据集中的原始比例保持一致
#ShuffleSplit 把数据集打乱顺序,然后划分测试集和训练集,训练集额和测试集的比例随机选定,训练集和测试集的比例的和可以小于1
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import ShuffleSplit
X=np.array([[1,2],[3,4],[5,6],[7,8],[9,10],[11,12]])
y=np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6])
rs=ShuffleSplit(n_splits=3,test_size=.25,random_state=0)
rs.get_n_splits(X)
print(rs)
for train_index,test_index in rs.split(X,y):
print("Train Index:",train_index,",Test Index:",test_index)
X_train,X_test=X[train_index],X[test_index]
y_train,y_test=y[train_index],y[test_index]
#print(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
print("==============================")
rs=ShuffleSplit(n_splits=3,train_size=.5,test_size=.25,random_state=0)
rs.get_n_splits(X)
print(rs)
for train_index,test_index in rs.split(X,y):
print("Train Index:",train_index,",Test Index:",test_index)
#ShuffleSplit(n_splits=3, random_state=0, test_size=0.25, train_size=None)
#Train Index: [1 3 0 4] ,Test Index: [5 2]
#Train Index: [4 0 2 5] ,Test Index: [1 3]
#Train Index: [1 2 4 0] ,Test Index: [3 5]
#==============================
#ShuffleSplit(n_splits=3, random_state=0, test_size=0.25, train_size=0.5)
#Train Index: [1 3 0] ,Test Index: [5 2]
#Train Index: [4 0 2] ,Test Index: [1 3]
#Train Index: [1 2 4] ,Test Index: [3 5]
#StratifiedShuffleSplitShuffleSplit 把数据集打乱顺序,然后划分测试集和训练集,训练集额和测试集的比例随机选定,训练集和测试集的比例的和可以小于1,但是还要保证训练集中各类所占的比例是一样的
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedShuffleSplit
X=np.array([[1,2],[3,4],[5,6],[7,8],[9,10],[11,12]])
y=np.array([1,2,1,2,1,2])
sss=StratifiedShuffleSplit(n_splits=3,test_size=.5,random_state=0)
sss.get_n_splits(X,y)
print(sss)
for train_index,test_index in sss.split(X,y):
print("Train Index:",train_index,",Test Index:",test_index)
X_train,X_test=X[train_index],X[test_index]
y_train,y_test=y[train_index],y[test_index]
#print(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
#StratifiedShuffleSplit(n_splits=3, random_state=0, test_size=0.5,train_size=None)
#Train Index: [5 4 1] ,Test Index: [3 2 0]
#Train Index: [5 2 3] ,Test Index: [0 4 1]
#Train Index: [5 0 4] ,Test Index: [3 1 2]
