我们知道Spring的IoC起到了一个容器的作用,其中装得都是各种各样的Bean。同时在我们刚刚开始学习Spring的时候都是通过xml文件来定义Bean,Spring会某种方式加载这些xml文件,然后根据这些信息绑定整个系统的对象,最终组装成一个可用的基于轻量级容器的应用系统。
Spring IoC容器整体可以划分为两个阶段,容器启动阶段,Bean实例化阶段。其中容器启动阶段主要包括加载配置信息、解析配置信息,装备到BeanDefinition中以及其他后置处理,而Bean实例化阶段主要包括实例化对象,装配依赖,生命周期管理已经注册回调。下面LZ先介绍容器的启动阶段的第一步,即定位配置文件。
我们使用编程方式使用DefaultListableBeanFactory时,首先是需要定义一个Resource来定位容器使用的BeanDefinition。
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("bean.xml");
通过这个代码,就意味着Spring会在类路径中去寻找bean.xml并解析为BeanDefinition信息。当然这个Resource并不能直接被使用,他需要被BeanDefinitionReader进行解析处理(这是后面的内容了)。
对于各种applicationContext,如FileSystemXmlApplicationContext、ClassPathXmlApplicationContext等等,我们从这些类名就可以看到他们提供了那些Resource的读入功能。下面我们以FileSystemXmlApplicationContext为例来阐述Spring IoC容器的Resource定位。
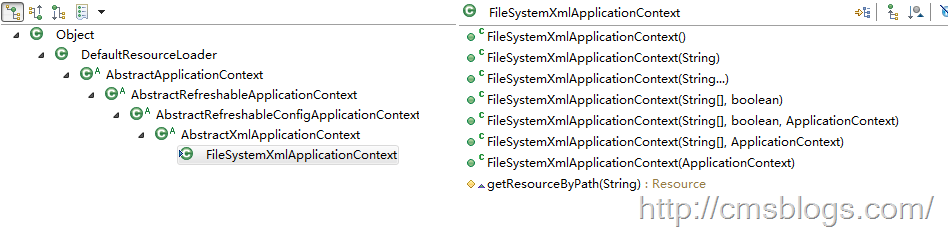
先看FileSystemXmlApplicationContext继承体系结构:
从图中可以看出FileSystemXMLApplicationContext继承了DefaultResourceLoader,具备了Resource定义的BeanDefinition的能力,其源代码如下:
public class FileSystemXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractXmlApplicationContext { /** * 默认构造函数 */ public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext() { } public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) { super(parent); } public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException { this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null); } public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException { this(configLocations, true, null); } public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { this(configLocations, true, parent); } public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh) throws BeansException { this(configLocations, refresh, null); } //核心构造器 public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { super(parent); setConfigLocations(configLocations); if (refresh) { refresh(); } } //通过构造一个FileSystemResource对象来得到一个在文件系统中定位的BeanDefinition //采用模板方法设计模式,具体的实现用子类来完成 protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) { if (path != null && path.startsWith("/")) { path = path.substring(1); } return new FileSystemResource(path); } }
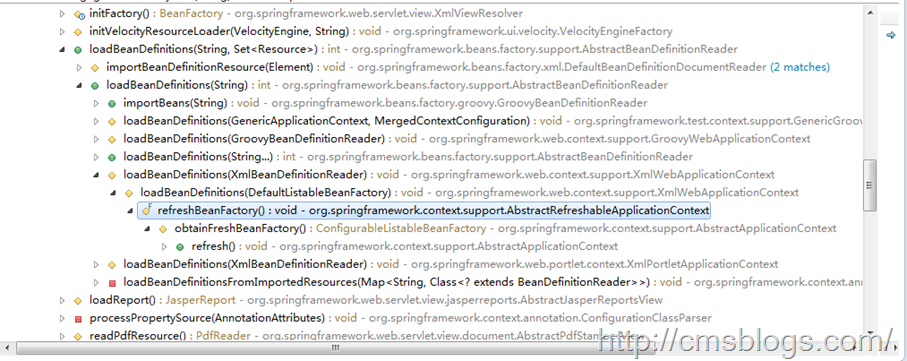
AbstractApplicationContext中的refresh()方法是IoC容器初始化的入口,也就是说IoC容器的初始化是通过refresh()方法来完成整个调用过程的。在核心构造器中就对refresh进行调用,通过它来启动IoC容器的初始化工作。getResourceByPath为一个模板方法,通过构造一个FileSystemResource对象来得到一个在文件系统中定位的BeanDEfinition。getResourceByPath的调用关系如下(部分):
refresh为初始化IoC容器的入口,但是具体的资源定位还是在XmlBeanDefinitionReader读入BeanDefinition时完成,loadBeanDefinitions() 加载BeanDefinition的载入。
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { //判断是否已经创建了BeanFactory,如果创建了则销毁关闭该BeanFactory if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { //创建DefaultListableBeanFactory实例对象 DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); //加载BeanDefinition信息 loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } }
DefaultListableBeanFactory作为BeanFactory默认实现类,其重要性不言而喻,而createBeanFactory()则返回该实例对象。
protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() { return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory()); }
loadBeanDefinition方法加载BeanDefinition信息,BeanDefinition就是在这里定义的。AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext对loadBeanDefinitions仅仅只是定义了一个抽象的方法,真正的实现类为其子类AbstractXmlApplicationContext来实现:
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext:
protected abstract void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException;
AbstractXmlApplicationContext:
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { //创建bean的读取器(Reader),即XmlBeanDefinitionReader,并通过回调设置到容器中 XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); // beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(getEnvironment()); //为Bean读取器设置Spring资源加载器 beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); //为Bean读取器设置SAX xml解析器 beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); //Bean读取器真正实现的地方 loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); }
程序首先首先创建一个Reader,在前面就提到过,每一类资源都对应着一个BeanDefinitionReader,BeanDefinitionReader提供统一的转换规则;然后设置Reader,最后调用loadBeanDefinition,该loadBeanDefinition才是读取器真正实现的地方:
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { //获取Bean定义资源的定位 Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); if (configResources != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); } //获取Bean定义资源的路径。在FileSystemXMLApplicationContext中通过setConfigLocations可以配置Bean资源定位的路径 String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); if (configLocations != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); } }
首先通过getConfigResources()获取Bean定义的资源定位,如果不为null则调用loadBeanDefinitions方法来读取Bean定义资源的定位。
loadBeanDefinitions是中的方法:
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null"); int counter = 0; for (String location : locations) { counter += loadBeanDefinitions(location); } return counter; }
继续:
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { return loadBeanDefinitions(location, null); }
再继续:
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { //获取ResourceLoader资源加载器 ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader(); if (resourceLoader == null) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available"); } // if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) { try { //调用DefaultResourceLoader的getResourceByPath完成具体的Resource定位 Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location); int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resources); if (actualResources != null) { for (Resource resource : resources) { actualResources.add(resource); } } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]"); } return loadCount; } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex); } } else { //调用DefaultResourceLoader的getResourceByPath完成具体的Resource定位 Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location); int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resource); if (actualResources != null) { actualResources.add(resource); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]"); } return loadCount; } }
在这段源代码中通过调用DefaultResourceLoader的getResource方法:
public Resource getResource(String location) { Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null"); if (location.startsWith("/")) { return getResourceByPath(location); } //处理带有classPath标识的Resource else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) { return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader()); } else { try { //处理URL资源 URL url = new URL(location); return new UrlResource(url); } catch (MalformedURLException ex) { return getResourceByPath(location); } } }
在getResource方法中我们可以清晰地看到Resource资源的定位。这里可以清晰地看到getResourceByPath方法的调用,getResourceByPath方法的具体实现有子类来完成,在FileSystemXmlApplicationContext实现如下:
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) { if (path != null && path.startsWith("/")) { path = path.substring(1); } return new FileSystemResource(path); }
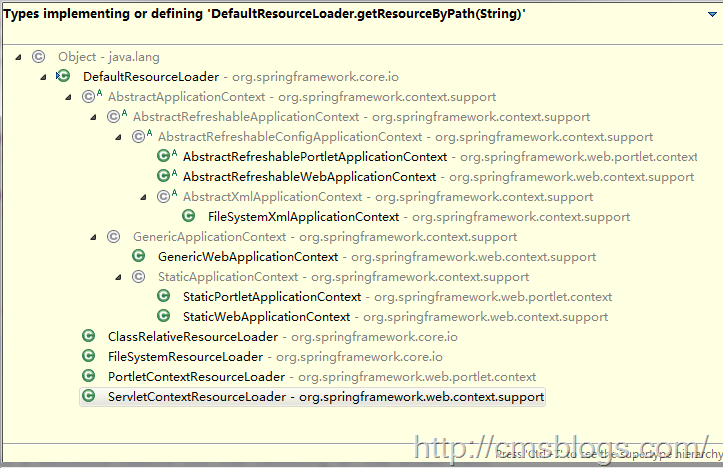
这样代码就回到了博客开初的FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 中来了,它提供了FileSystemResource 来完成从文件系统得到配置文件的资源定义。当然这仅仅只是Spring IoC容器定位资源的一种逻辑,我们可以根据这个步骤来查看Spring提供的各种资源的定位,如ClassPathResource、URLResource等等。下图是ResourceLoader的继承关系:
这里就差不多分析了Spring IoC容器初始化过程资源的定位,在BeanDefinition定位完成的基础上,就可以通过返回的Resource对象来进行BeanDefinition的载入、解析了。
下篇博客将探索Spring IoC容器初始化过程的解析,Spring Resource体系结构会在后面详细讲解。
参考文献
1、《Spring技术内幕 深入解析Spring架构与设计原理》--第二版