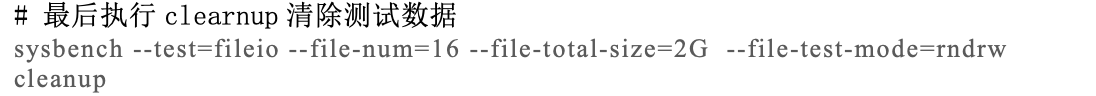1. sysbench 介绍
sysbench是一个模块化的、跨平台、多线程基准测试工具,主要用于评估测试各种不同系统参数 下的数据库负载情况。
它主要包括以下几种方式的测试:
- cpu性能
- 磁盘io性能
- 调度程序性能
- 内存分配及传输速度
- POSIX线程性能
- 数据库性能(OLTP基准测试)
目前sysbench主要支持MySQL,Pgsql和Oracle这3种数据库。
2、开始测试
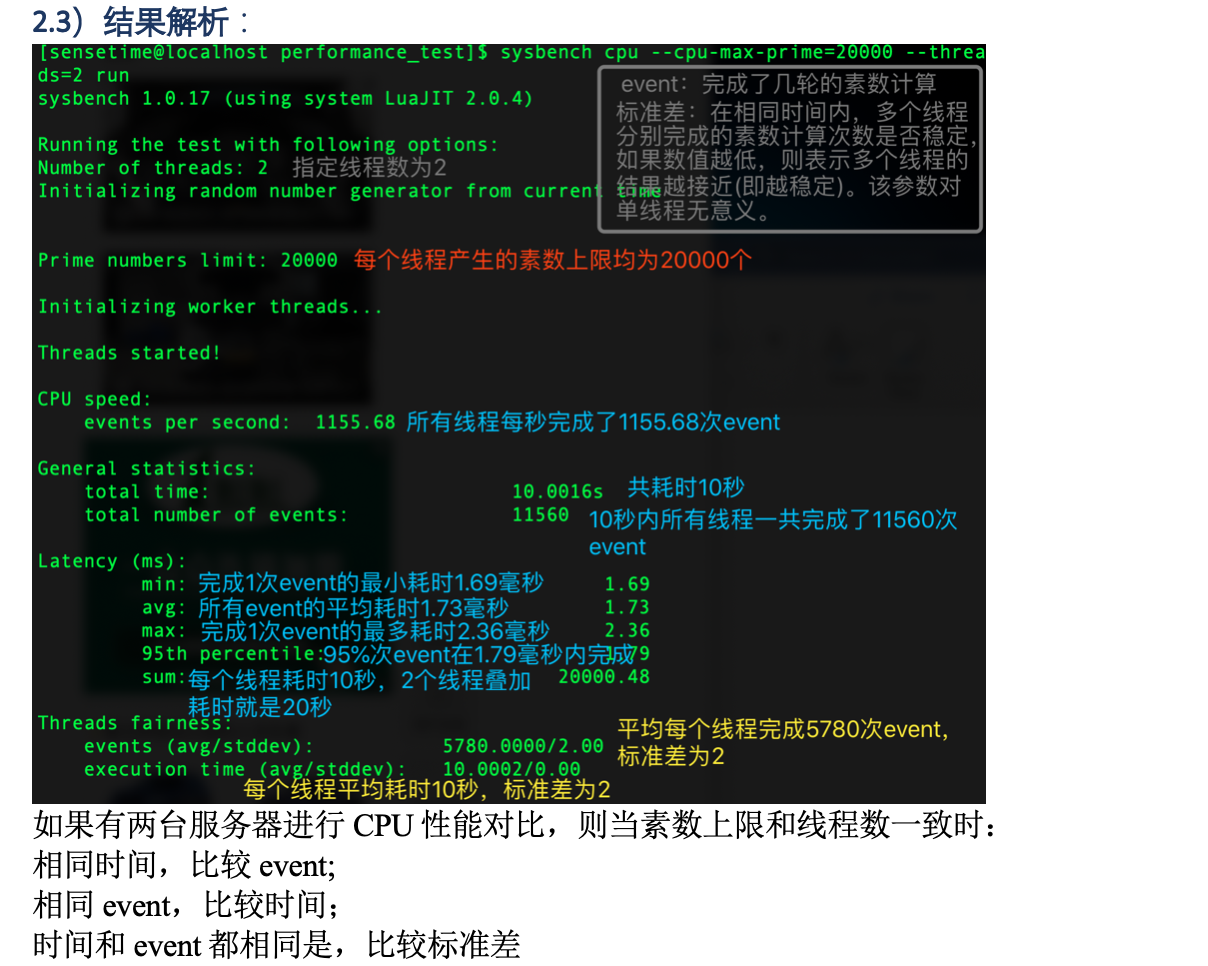
2.1 CPU性能测试
根据官网的介绍可知:CPU测试使用64位整数,测试计算素数直到某个最大值所需要的时间。
sysbench --test=cpu --cpu-max-prime=20000 run
输出如下:
Maximum prime number checked in CPU test: 200000 Test execution summary: total time: 286.5703s total number of events: 10000 total time taken by event execution: 285197.4463 per-request statistics: min: 109.67ms avg: 28519.74ms max: 36760.02ms approx. 95 percentile: 31751.56ms Threads fairness: events (avg/stddev): 9.7656/0.81 execution time (avg/stddev): 278.5131/6.05
我们只需要关心测试的总时间(total time)即可。
CPU性能测试有一个需要注意的地方,上面的测试只使用了一个线程,如果在两个cpu processor不同的电脑上做比较,这是不公平的。公平的做法是指定合理的线程数,如下所示:
sysbench --test=cpu --num-threads=`grep "processor" /proc/cpuinfo | wc -l` --cpu-max-prime=200000 run
补充知识:
查看CPU核数的方法:
1、查看物理cpu个数
grep "physical id" /proc/cpuinfo | sort -u | wc -l
2、查看核心数量
grep "core id" /proc/cpuinfo | sort -u | wc -l
3、查看线程数量
grep "processor" /proc/cpuinfo | sort -u | wc -l
在sysbench的测试中,--num-threads取值为"线程数量"即可,再大的值没有什么意义,对测试结果也没有什么影响。
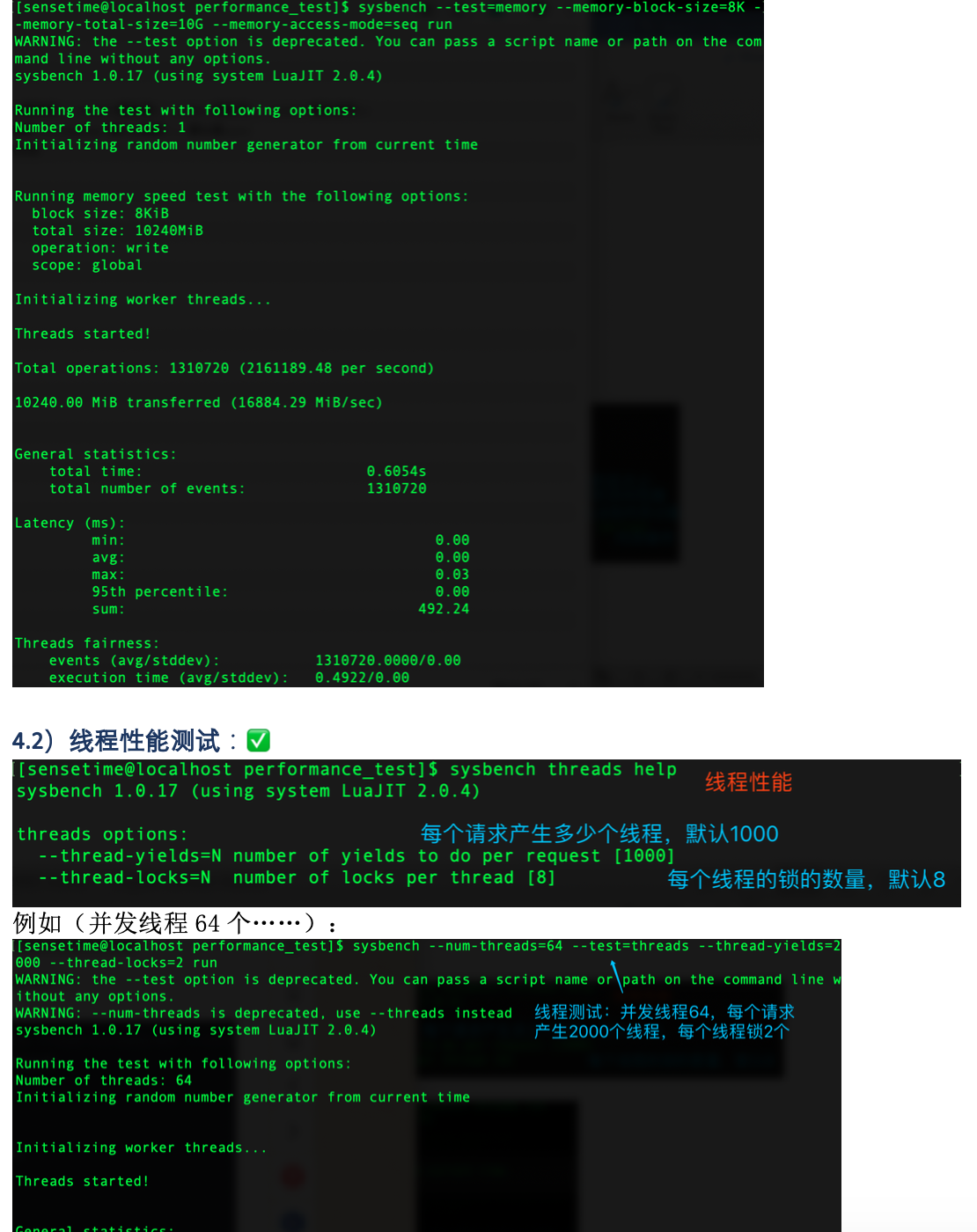
2.2 线程(thread)测试
测试线程调度器的性能。对于高负载情况下测试线程调度器的行为非常有用。
sysbench --test=threads --num-threads=64 run
下面是输出结果:
Number of threads: 64 Doing thread subsystem performance test Thread yields per test: 1000 Locks used: 8 Threads started! Done. Test execution summary: total time: 4.5845s total number of events: 10000 total time taken by event execution: 291.9995 per-request statistics: min: 0.76ms avg: 29.20ms max: 152.71ms approx. 95 percentile: 71.11ms Threads fairness: events (avg/stddev): 156.2500/5.81 execution time (avg/stddev): 4.5625/0.02
说实话,我也不怎么会分析这个测试结果,网上搜了半天也没有搜到,几乎所有的资料都是简单的罗列出测试结果, 也不告诉我们应该怎么分析,实在是太不照顾新手了。 我自己是通过(total time:)判断线程调度的性能的,下面是我在服务器上运行这个测试的输出:
Number of threads: 64 Doing thread subsystem performance test Thread yields per test: 1000 Locks used: 8 Threads started! Done. Test execution summary: total time: 2.4829s total number of events: 10000 total time taken by event execution: 157.3468 per-request statistics: min: 0.21ms avg: 15.73ms max: 166.69ms approx. 95 percentile: 119.14ms Threads fairness: events (avg/stddev): 156.2500/22.25 execution time (avg/stddev): 2.4585/0.02
可以看到total time 比在我自己电脑上少了一半,服务器的线程调度肯定比普通电脑快多了。
2.3 互斥锁(mutex)
测试互斥锁的性能,方式是模拟所有线程在同一时刻并发运行,并都短暂请求互斥锁。
sysbench --test=mutex --num-threads=16 --mutex-num=2048 --mutex-locks=1000000 --mutex-loops=5000 run
输出结果如下:
Number of threads: 16 Doing mutex performance test Threads started! Done. Test execution summary: total time: 3.6123s total number of events: 16 total time taken by event execution: 57.6636 per-request statistics: min: 3580.79ms avg: 3603.98ms max: 3610.94ms approx. 95 percentile: 10000000.00ms Threads fairness: events (avg/stddev): 1.0000/0.00 execution time (avg/stddev): 3.6040/0.01
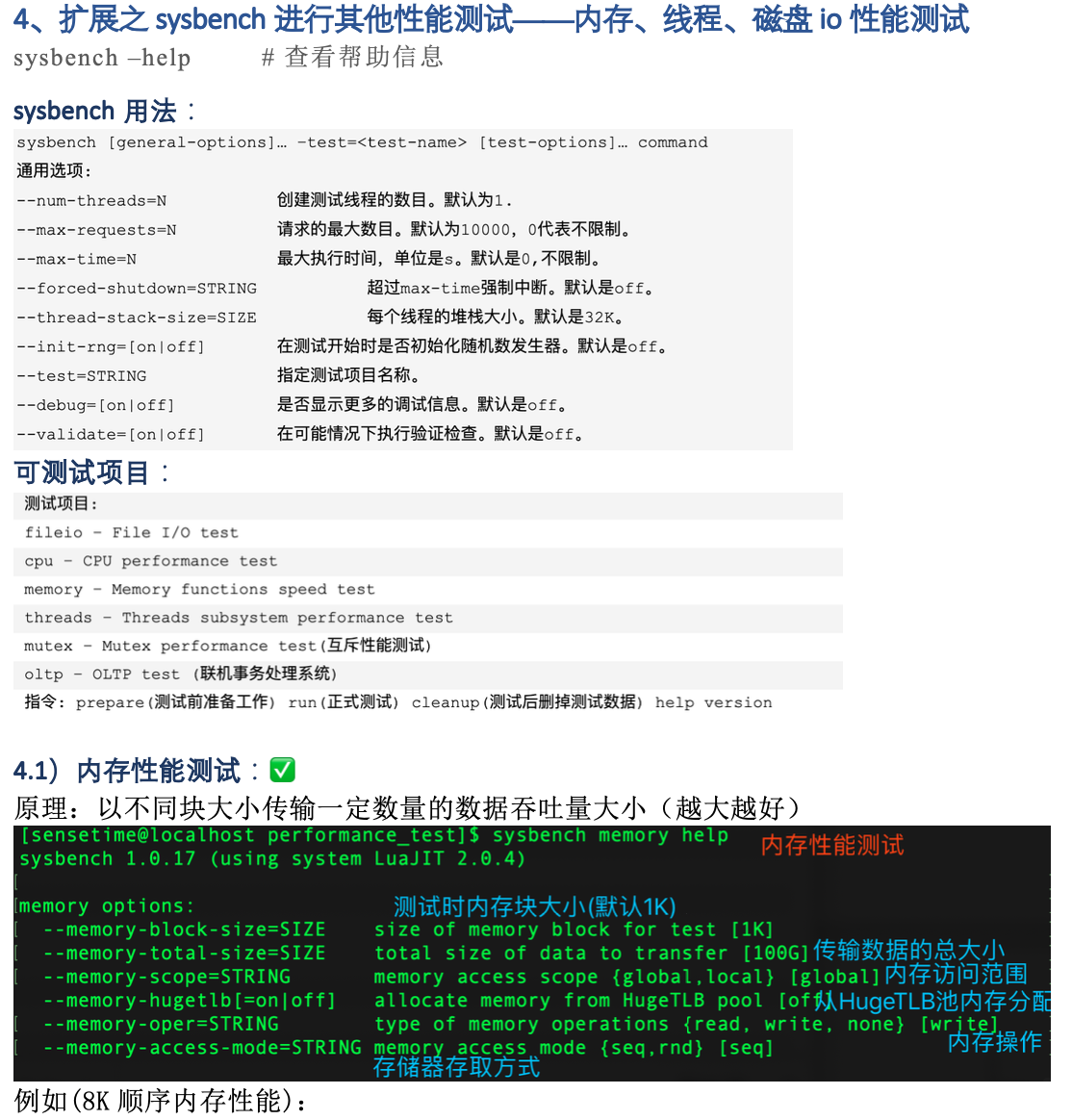
2.4 内存测试
内存测试测试了内存的连续读写性能。
sysbench --test=memory --memory-block-size=8K --memory-total-size=2G --num-threads=16 run
上面这条语句指定了整个测试过程中,传输2G的数据量,每个block的大小为8K(大写的K)。 测试结果如下所示,我们最关心的是吞吐量(8030.45MB/sec),和后面的磁盘io 测试结果比较可知,内存的连续读写比磁盘的连续读写快十几倍。
Number of threads: 16 Doing memory operations speed test Memory block size: 8K Memory transfer size: 2048M Memory operations type: write Memory scope type: global Threads started! Done. Operations performed: 262144 (1027897.89 ops/sec) 2048.00 MB transferred (8030.45 MB/sec) Test execution summary: total time: 0.2550s total number of events: 262144 total time taken by event execution: 3.1911 per-request statistics: min: 0.00ms avg: 0.01ms max: 29.55ms approx. 95 percentile: 0.00ms Threads fairness: events (avg/stddev): 16384.0000/926.14 execution time (avg/stddev): 0.1994/0.02
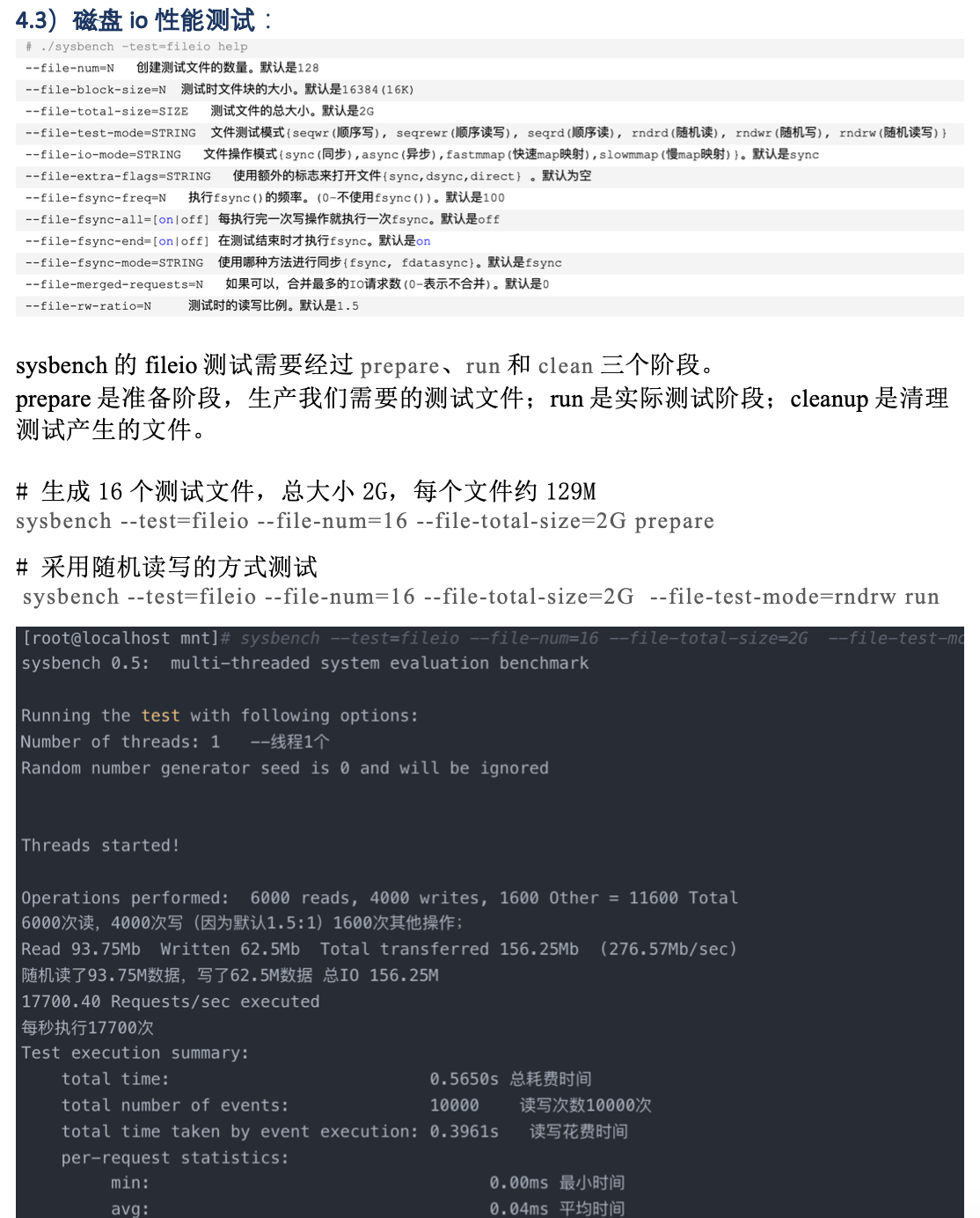
2.5 文件IO基准测试
文件IO(fileio)基准测试可以测试系统在不同IO负载下的性能。这对于比较不同的硬盘驱动器,不同的RAID 卡,不同的RAID 模式,都很有帮助。可以根据测试结果调整IO子系统。文件IO基准测试模拟了很多InnoDB 的IO特性。
测试的第一步是准备(Prepare)阶段,生成测试用到的数据文件,生成的数据文件至少要比内存大。 如果文件中的数据能完全放入内存中,则操作系统 缓存大部分的数据,导致测试结果无法体现IO密集型的工作负载。首先通过下面的命令创建一个数据集:
sysbench --test=fileio --file-total-size=40G prepare
这个命令会在当前工作目录下创建测试文件,后续的运行(run)阶段将通过读写这些文件进行测试。 第二步就是运行(run)阶段,针对不同的IO 类型有不同的测试选项:
- seqwr 顺序写入
- seqrewr 顺序重写
- seqrd 顺序读取
- rndrd 随机读取
- rndwr 随机写入
- rndrw 混合随机读/写
下面的命令运行文件I/O混合随机读/写基准测试:
sysbench --test=fileio --file-total-size=40G --file-test-mode=rndrw --init-rng=on --max-time=300 --max-requests=0 run
结果如下:
Extra file open flags: 0 128 files, 240Mb each 30Gb total file size Block size 16Kb Number of random requests for random IO: 0 Read/Write ratio for combined random IO test: 1.50 Periodic FSYNC enabled, calling fsync() each 100 requests. Calling fsync() at the end of test, Enabled. Using synchronous I/O mode Doing random r/w test Threads started! Time limit exceeded, exiting... Done. Operations performed: 15900 Read, 10600 Write, 33842 Other = 60342 Total Read 248.44Mb Written 165.62Mb Total transferred 414.06Mb (1.3802Mb/sec) 88.33 Requests/sec executed Test execution summary: total time: 300.0074s total number of events: 26500 total time taken by event execution: 164.1563 per-request statistics: min: 0.01ms avg: 6.19ms max: 315.51ms approx. 95 percentile: 15.83ms Threads fairness: events (avg/stddev): 26500.0000/0.00 execution time (avg/stddev): 164.1563/0.00
输出结果中包含了大量的信息。和IO子系统密切相关的包括每秒请求数和总吞吐量。在上述例子中, 每秒请求数是88.33 Requests/sec , 吞吐量是1.3802Mb/sec 。另外,时间信息也非常有用, 尤其是大约95%的时间分布。这些数据对于评估磁盘性能十分有用。
测试完成以后,运行清除(cleanup)操作删除第一步生成的测试文件。
sysbench --test=fileio --fil-total-size=30G cleanup
2.6 oltp
下面来看最重要也是最复杂的测试————oltp。oltp 基准测试模拟了一个简单的事物处理系统的工作负载。 下面的例子使用的是一张超过百万行记录的表,第一步是先生成这张表:
sysbench --test=oltp --oltp-table-size=1000000 --mysql-db=test --mysql-user=root prepare
生成数据只需要上面这条简单的命令即可。这条命令在test 数据库中新建了一个表(sbtest),并在表中插入了1000000条记录。
对于非默认安装的mysql,需要指定连接到msyql服务器的socket(my.cnf中的socket值),如下所示:
sysbench --test=oltp --oltp-table-size=1000000 --mysql-user=root --mysql-db=test --mysql-socket=/data/ntse/lmx/sysbench/var/mysqld.sock prepare
数据加载完成以后就可以开始测试了,这个例子采用了16个线程,测试时长为720秒:
sysbench --test=oltp --oltp-table-size=1000000 --mysql-db=test --mysql-user=root --max-time=720 --max-requests=0 --num-threads=16 --oltp-test-mode=complex run
与插入记录时一样,如果mysql是非默认安装,还需要指定--mysql-socket的值。
Number of threads: 16 Doing OLTP test. Running mixed OLTP test Using Special distribution (12 iterations, 1 pct of values are returned in 75 pct cases) Using "BEGIN" for starting transactions Using auto_inc on the id column Threads started! Time limit exceeded, exiting... (last message repeated 15 times) Done. OLTP test statistics: queries performed: read: 26225724 write: 9366330 other: 3746532 total: 39338586 transactions: 1873266 (2601.71 per sec.) deadlocks: 0 (0.00 per sec.) read/write requests: 35592054 (49432.47 per sec.) other operations: 3746532 (5203.42 per sec.) Test execution summary: total time: 720.0136s total number of events: 1873266 total time taken by event execution: 11506.8251 per-request statistics: min: 2.37ms avg: 6.14ms max: 400.48ms approx. 95 percentile: 14.90ms Threads fairness: events (avg/stddev): 117079.1250/275.62 execution time (avg/stddev): 719.1766/0.01
如上所示,结果中包含了相当多的信息。其中最有价值的信息如下;
- 总的事务数
- 每秒事务数
- 时间统计信息(最小,平均,最大响应时间,以及95%百分比响应时间)
- 线程公平性统计信息
最最重要的当然是每秒事务数(2601.71 per sec.)。
oltp 测试注意事项:
1、--max-requests --max-requests 默认值为10000 ,如果设置了--max-requests 或者使用默认值 ,分析结果的时候主要查看运行时间(total time),一般情况下,都将--max-requests 赋值为0 ,即不限制请求数量,通过--max-time 来指定测试时长,然后查看系统的每秒事务数。
2、--oltp-test-mode
--oltp-test-mode用以指定测试模式,取值有(simeple,complex,nontrx),默认是complex。不同模式会执行不同的语句。 具体执行语句如下所示:
1)Simple 这种模式只是简单的执行selec语句。
SELECT c FROM sbtest WHERE id=N
2)complex(Advanced transactional) 在事务中,可能包含下列语句。
Point queries:
SELECT c FROM sbtest WHERE id=N
Range queries:
SELECT c FROM sbtest WHERE id BETWEEN N AND M
Range SUM() queries:
SELECT SUM(K) FROM sbtest WHERE id BETWEEN N and M
Range ORDER BY queries:
SELECT c FROM sbtest WHERE id between N and M ORDER BY c
Range DISTINCT queries:
SELECT DISTINCT c FROM sbtest WHERE id BETWEEN N and M ORDER BY c
UPDATEs on index column:
UPDATE sbtest SET k=k+1 WHERE id=N
UPDATEs on non-index column:
UPDATE sbtest SET c=N WHERE id=M
DELETE queries:
DELETE FROM sbtest WHERE id=N
INSERT queries:
INSERT INTO sbtest VALUES (...)
3)nontrx(Non-transactional) 这种模式包含下列SQL语句。
Point queries:
SELECT pad FROM sbtest WHERE id=N
UPDATEs on index column:
UPDATE sbtest SET k=k+1 WHERE id=N
UPDATEs on non-index column:
UPDATE sbtest SET c=N WHERE id=M
DELETE queries:
DELETE FROM sbtest WHERE id=N
INSERT queries:
NSERT INTO sbtest (k, c, pad) VALUES(N, M, S)
3、simple 与 --oltp-read-only 的区别
simple模式和在complex模式下开启read-only选项都只包含select语句。但是 simple 模式只包含最简单的select语句,相反地,complex 模式中,如果我们开启read-only 选项,即--oltp-read-only=on,则会包含复杂的SQL语句。如:
SELECT SUM(K) FROM sbtest WHERE id BETWEEN N and M SELECT DISTINCT c FROM sbtest WHERE id BETWEEN N and M ORDER BY c
4、测试自有的存储引擎
测试自有的存储引擎需要告诉sysbench,这个存储引擎是否支持事务。
如下所示:
1)准备:
sysbench --test=oltp --mysql-table-engine=tnt --mysql-engine-trx=yes --oltp-table-size=100000 --mysql-user=root --mysql-db=test --mysql-socket=/data/ntse/lmx/sysbench/var/mysqld.sock prepare
2)测试:
sysbench --test=oltp --mysql-table-engine=tnt --mysql-engine-trx=yes --oltp-table-size=100000 --mysql-user=root --mysql-db=test --mysql-socket=/data/ntse/lmx/sysbench/var/mysqld.sock --oltp-test-mode=complex --num-threads=16 --max-time=720 --max-requests=0 run
3)清除:
sysbench --test=oltp --mysql-table-engine=tnt --mysql-engine-trx=yes --oltp-table-size=100000 --mysql-user=root --mysql-db=test --mysql-socket=/data/ntse/lmx/sysbench/var/mysqld.sock clean
3. sysbench 0.5
1)下载:
bzr branch lp:sysbench
2)安装依赖库:
sudo apt-get install libtool
3)安装:
tar -zxvf sysbench.tar.gz cd sysbench ./autogen.sh ./configure make #make install #可选
4)开始测试:
cd sysbench/sysbench ./sysbench --test=./tests/db/oltp.lua --debug=yes --mysql-host=localhost --mysql-socket=PATH/mysqld.sock --mysql-db=test --mysql-table-engine=innodb --mysql-engine-trx=yes --mysql-user=root --max-requests=0 --max-time=60 --num-threads=16 --oltp-table-size=100000 --report-interval=10 [prepare|run|cleanup]
5)解释:
--debug 参数用以打印更加详细的调试信息 --report-interval 用以打印中间结果 除了测试oltp,sysbench 0.5还可以进行插入操作的性能测试(insert.lua),选择操作的性能测试(select.lua)等。
6)sysbench原生命令输出:
Missing required command argument. Usage: sysbench [general-options]... --test=<test-name> [test-options]... command General options: --num-threads=N number of threads to use [1] --max-requests=N limit for total number of requests [10000] --max-time=N limit for total execution time in seconds [0] --forced-shutdown=STRING amount of time to wait after --max-time before forcing shutdown [off] --thread-stack-size=SIZE size of stack per thread [64K] --tx-rate=N target transaction rate (tps) [0] --report-interval=N periodically report intermediate statistics with a specified interval in seconds. 0 disables intermediate reports [0] --report-checkpoints=[LIST,...]dump full statistics and reset all counters at specified points in time. The argument is a list of comma-separated values representing the amount of time in seconds elapsed from start of test when report checkpoint(s) must be performed. Report checkpoints are off by default. [] --test=STRING test to run --debug=[on|off] print more debugging info [off] --validate=[on|off] perform validation checks where possible [off] --help=[on|off] print help and exit --version=[on|off] print version and exit [off] --rand-init=[on|off] initialize random number generator [off] --rand-type=STRING random numbers distribution {uniform,gaussian,special,pareto} [special] --rand-spec-iter=N number of iterations used for numbers generation [12] --rand-spec-pct=N percentage of values to be treated as 'special' (for special distribution) [1] --rand-spec-res=N percentage of 'special' values to use (for special distribution) [75] --rand-seed=N seed for random number generator, ignored when 0 [0] --rand-pareto-h=N parameter h for pareto distibution [0.2] Log options: --verbosity=N verbosity level {5 - debug, 0 - only critical messages} [3] --percentile=N percentile rank of query response times to count [95] Compiled-in tests: fileio - File I/O test cpu - CPU performance test memory - Memory functions speed test threads - Threads subsystem performance test mutex - Mutex performance test Commands: prepare run cleanup help version See 'sysbench --test=<name> help' for a list of options for each test.
4、输出结果详解:
1)CPU

2)内存Memory
3)磁盘io