1 import multiprocessing 2 import queue 3 def foo(num,num2,q): 4 num2 +=444 5 num+=1 6 num+=1 7 q.put((num,num2)) # 可以传数据 8 9 10 if __name__ == '__main__': 11 # q = queue.Queue() # 创建的是线程队列 12 q = multiprocessing.Queue() # 进程队列 13 num = 1 14 num2 = 3 15 p = multiprocessing.Process(target=foo,args=(num,num2,q)) 16 p.start() 17 print(q.get()[1]) 18 # print(id(q)) 19 # print(q.get()) 20 # print(q.get()) 21 输出: 22 447
管道:
import time from multiprocessing import Pipe,Process def f(conn): conn.send('hello') time.sleep(2) response = conn.recv() print('response',response) conn.close() print('q_id',id(conn)) if __name__ == '__main__': parent_conn,child_conn = Pipe() p = Process(target=f,args=(child_conn,)) p.start() print(parent_conn.recv()) parent_conn.send('who n你是 you') 输出: hello response who n你是 you q_id 62791536
进程信息共享》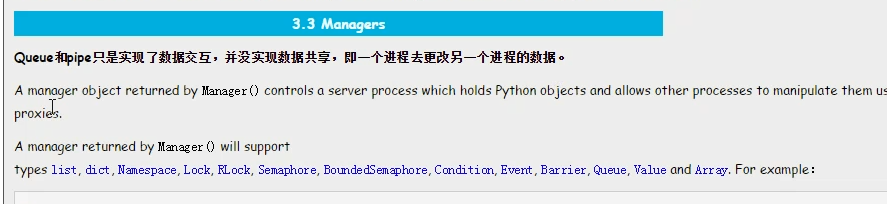
1 from multiprocessing import Manager,Process 2 3 4 def add(a,b,c): 5 a['1'] = 'hello' 6 a[c] = 1 7 b.append(1000) 8 print(c) 9 10 if __name__ == '__main__': 11 with Manager() as f: 12 dict_f = f.dict() 13 l = f.list(range(5)) 14 l_lsit = [] 15 for i in range(10): 16 p = Process(target=add,args=(dict_f,l,i)) 17 p.start() 18 l_lsit.append(p) 19 for i in l_lsit: 20 i.join() 21 print(dict_f) 22 print(l) 23 输出: 24 1 25 0 26 2 27 3 28 5 29 4 30 6 31 7 32 8 33 9 34 {'1': 'hello', 1: 1, 0: 1, 2: 1, 3: 1, 5: 1, 4: 1, 6: 1, 7: 1, 8: 1, 9: 1} 35 [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 1000, 1000, 1000, 1000, 1000, 1000, 1000, 1000, 1000, 1000]