转到基本查询
一、多表查询
笛卡尔积:每张表的列数相加,行数相乘。
连接条件:得出笛卡尔积后需要用where条件筛选出正确的数据。连接条件至少需要n张表减1个
1.等值连接
连接条件为等号
select t1.a,t1.b,t1.c,t2.d from table t1,t2 where t1.c=t2.c
2.不等值连接
select t1.a,t1.b,t1.c,t2.d from table t1,t2 where t1.c between t2.e and t2.f --between and 小值在前,大值在后
3.外连接(把对于连接条件不成立的数据包含在最近的结果中)
SELECT 语句必须拥有相同数量的列,相似的数据类型,和相同的顺序。这种条件下能合并表
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name1 UNION SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name2
union 去重,union all不去重
inner join(join)内连接
左外连接:当连接条件不成立时,等号左边的表依然被包含在结果中
left join
右外连接:当连接条件不成立时,等号右边的表依然被包含在结果中
right join
full join
4.自连接
一张表起两个别名,当做两张表来用。
自接连不适合查询大表
5.层次查询
对于树型结构的单表查询
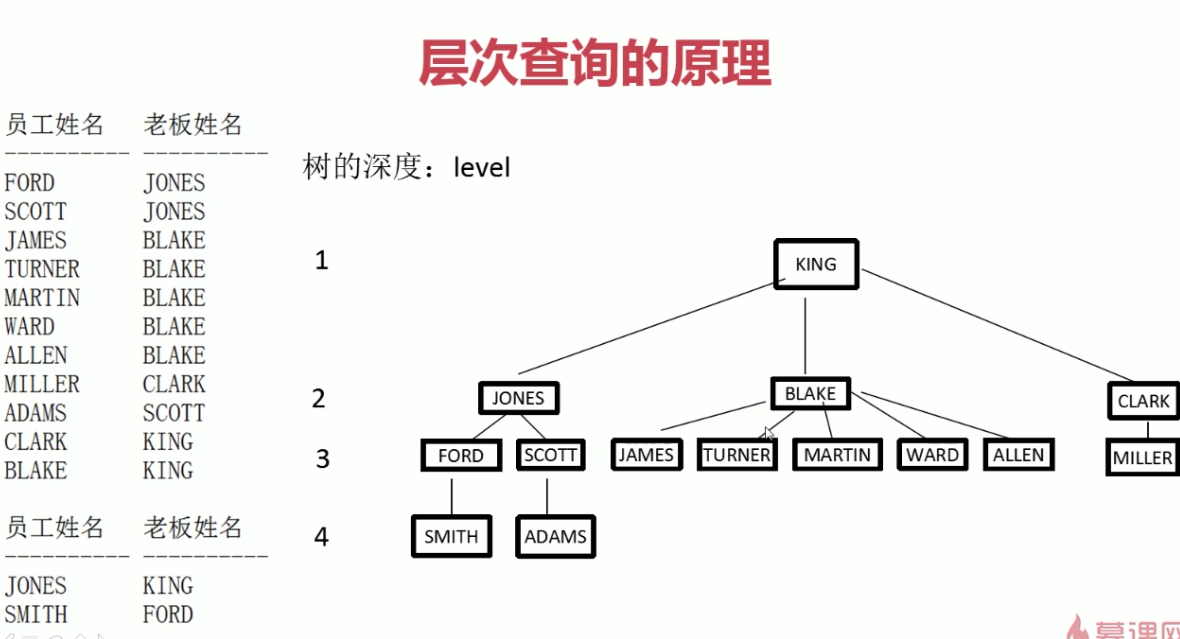
select * from table connect by 上一层字段=本层字段 start with 分支的定点字段=xxx;
如果从根节点开始查询还可以写成 : start with 上层字段 is null
select * from table connect by 上一层字段=本层字段 start with 上层字段 is null;
注意 :上层字段和本层字段是不同的两个列
二、行转列
先建表,插入数据
create table fruits(id int,name varchar(20),place varchar(20),amount int); ---- 创建表 / insert into fruits values(1, '苹果','河北', 1000); / insert into fruits values(2, '苹果','浙江', 1000); / insert into fruits values(3, '苹果','河北', 1000); / insert into fruits values(4, '橘子','浙江', 1000); / insert into fruits values(5, '橘子','河北', 1000); / insert into fruits values(6, '葡萄','浙江', 1000); / insert into fruits values(7, '芒果','浙江', 1000); / insert into fruits values(8, '芒果','浙江', 1000); /
行转列sql
select * from (select PLACE,NAME,AMOUNT from FRUITS) pivot (sum(AMOUNT) for NAME in('苹果','橘子' as 橙子,'葡萄' 葡萄))
![]()
pivot(聚合函数 for 列名 in(类型)
等同于
WITH t AS (SELECT PLACE, NAME, AMOUNT FROM FRUITS) SELECT * FROM t PIVOT (SUM (AMOUNT) FOR NAME IN ('苹果', '橘子' AS 橙子, '葡萄' 葡萄))
使用 with as 的原因:1优化速度 2方便阅读
三、条件控制
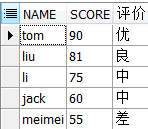
SELECT name, score, CASE --如果 WHEN score >= 90 THEN '优' --当...那么... WHEN (80 <= score AND score < 90) THEN '良' WHEN (60 <= score AND score < 80) THEN '中' ELSE '差' END --结束 AS 评价 FROM student WHERE 1 = 1 ORDER BY score DESC
四、分组查询
分组函数
1.avg()平均(avg函数会过滤掉空值), sum()求和
select avg(字段名) ,sum(字段名) from table
2.min()最小值,max()最大值
select min(字段名), max(字段名) from table
3.count()统计个数
select count(*) from table select count(字段名) from table
select count( distinct 字段名) from table --去掉某字段重复数据后,再统计行数
4.nvl() 为空时替换
select count(nvl(字段名,0)) from table --当字段名有数据为空时,会把他替换成第二个参数
5.gourp by
select 需要分组的字段, 分组函数(需要统计的字段) from table group by 需要分组的字段 select a,b,c, max(x) from table group by a,b,c --所有未包含在分组函数的列,都必须在 group by 中表示出来
当执行多个列分组时,先执行 a分组,分组后b如果有重复再执行b分组。
6. having
where 和 having 都是筛选条件,区别是 where 子句中不能使用分组函数
select a,avg(b) from table group by a having avg(b) ;
其他条件下通用
select a,avg(b) from table group a by having a=10; select a,avg(b) from table where=10 group by a;
在sql的优化角度考虑尽量使用where
7.分组查询的中order by
可以按照: 列,别名,表达式,序号排列
select a,avg(b) from table group by a order by avg(b) ; --按b升序排列 select a,avg(b) as 平均工资 from table group by a order by 平均工资 ;--按别名 select a,avg(b) as from table group by a order by 2; --按序号
8.分组嵌套
平均工资的最大值
select max(avg(b)) from table group by b;
9.group by 增强语句
group by rollup(a,b)
五、子查询
select * from t1 where t1.a>(select t2.b from t2 where ...);
注意问题
.可以写子查询的位置: where ,select ,having,from
.不可以使用子查询的位置 group by
六、排重
select PROD_NORM_CODE,REMARK from T_MD_PROD_NORM GROUP BY PROD_NORM_CODE,REMARK having count(PROD_NORM_CODE)>1
正则表达式 查询所有是数字的
REGEXP_LIKE(列名,'(^[+-]?d{0,}.?d{0,}$)');
剔除改字段下非数字数据,然后转成数字,四舍五入保留三位小数
select round (to_number(列名),3) as 列名 from table1 where REGEXP_LIKE(列名,'(^[+-]?d{0,}.?d{0,}$)');