1.什么是表达式目录树 :简单的说是一种语法树,或者说是一种数据结构(Expression)
2.用Lambda声明表达式目录树:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
Expression<Func<int, int, int>> exp = (n, m) => n * m + 2; //表达试目录树的方法体只能是一行,不能有大括号。比如: //Expression<Func<int, int, int>> exp1 = (m, n) => // { // return m * n + 2; // }; |
3.Expression.Compile();
|
1
2
3
4
|
Func<int, int, int> func = (m, n) => m * n + 2;Expression<Func<int, int, int>> exp = (m, n) => m * n + 2;int iResult1 = func.Invoke(99, 99);int iResult2 = exp.Compile().Invoke(99, 99); |
iResult1 和iResult2的结果一样,但是能Compile()的只有LambdaExpression。 Compile() 是将表达式树描述的 Lambda 表达式编译为可执行代码,并生成表示该 lambda 表达式的委托。exp.Compile().Invoke(99,99) 相当于这样调用 exp.Compile()();
4.認識表达式目录树结构。把上面的表达式拆分就是如下图,小学数学知识里的,按照运算符优先级别,先算乘法,m*n,得出结果再算加法,加上2。
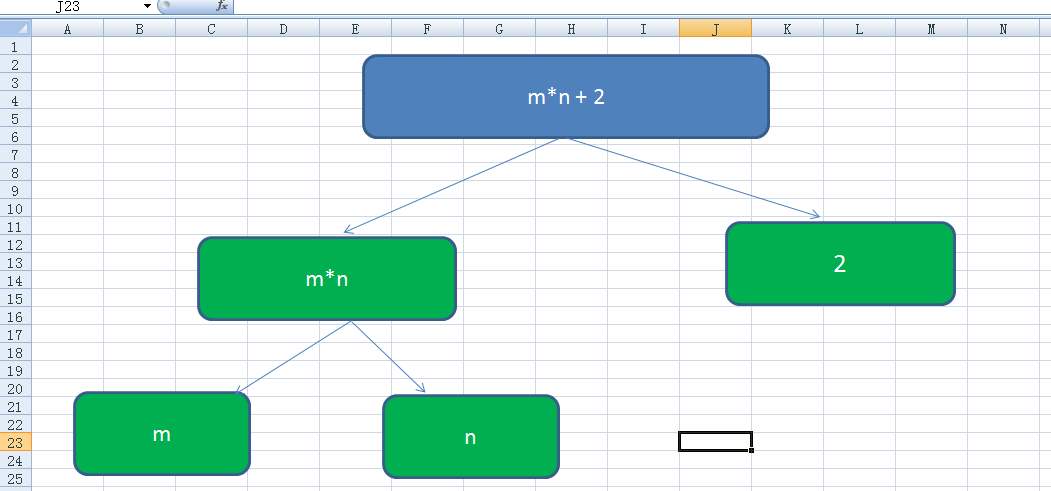
如代码所示,m和n是参数,所以类型为ParameterExpression ,2是常量,常量类型是ConstantExpression ,MultiplyAssign 乘法,Add加法。第六步中只能执行表示Lambda表达式的表达式目录树,即LambdaExpression或者Expression<TDelegate>类型。如果表达式目录树不是表示Lambda表达式,需要调用Lambda方法创建一个新的表达式。actExpression.Compile()成委托,再调用。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
{ ParameterExpression left = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "m");//左边的参数 ParameterExpression right = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "n");//右边的参数 ConstantExpression constantlExp = Expression.Constant(2,typeof(int));//常量2 BinaryExpression binaryExpMult = Expression.MultiplyAssign(left, right);//两个参数相乘 BinaryExpression binaryExpAdd=Expression.Add(binaryExpMult, constantlExp);//相乘的结果再加2 Expression<Func<int, int,int>> actExpression = Expression.Lambda<Func<int, int, int>>(binaryExpAdd, left, right); int result= actExpression.Compile()(2, 1);//调用 Console.WriteLine(result+"");} |
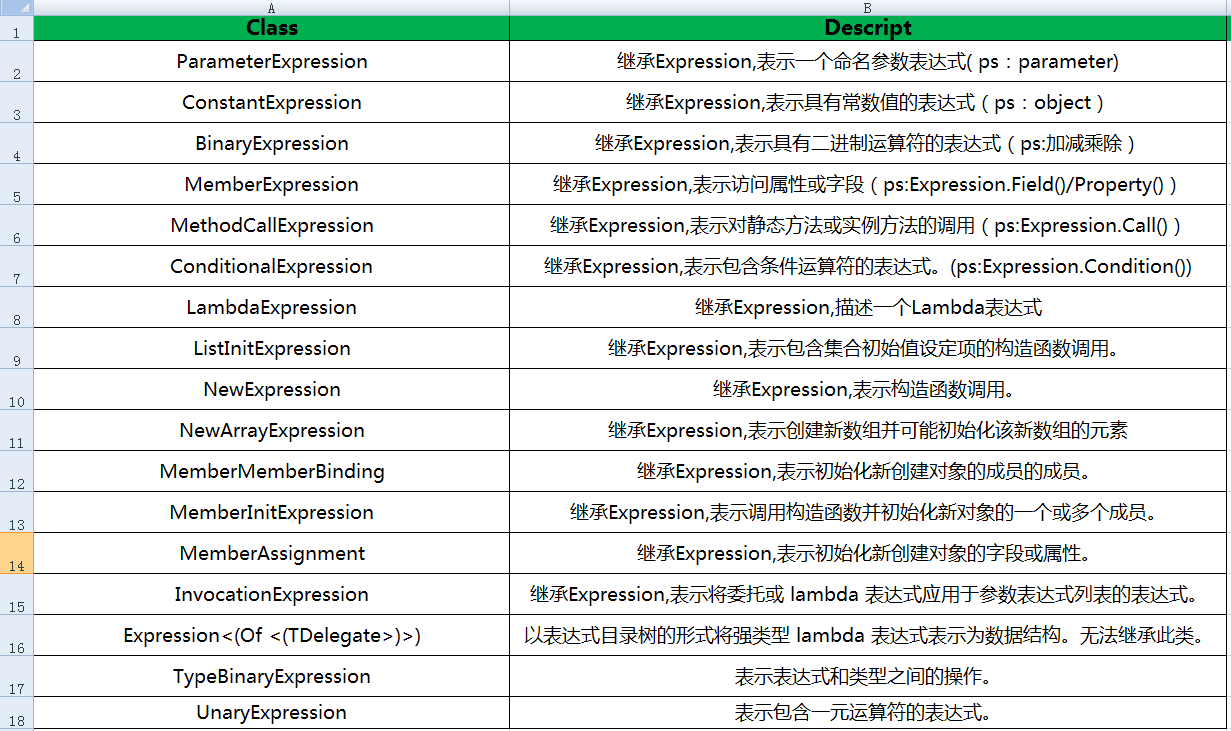
一些表达式目录树常用的类型
5.表达式目录树+缓存
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ThreeHomeWork.Model{ public class Student { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } } public class StudentDto { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } }} |
有时候一些业务模型和实体模型不太一样,比如Student 于StudentDto实体的转换
一般的写法,new 一个实体然后把值赋给另一个实体,有一个就写一个,有十个就写是个,代码写死了,硬编码性能高
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
{ Student student = new Student() { Age = 12, Id=1, Name="晴天" }; StudentDto studentDto = new StudentDto() { Name = student.Name, Id = student.Id, Age = student.Age }; } |
第二种:使用Expression表达式目录树
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
Expression<Func<Student, StudentDto>> lambda = p => new StudentDto { Age = p.Age, Id = p.Id, Name = p.Name }; lambda.Compile().Invoke(student); |
01.使用字典缓存表达式树,第一步是实例化了一个命令参数,parameterExpression, List<MemberBinding> memberBindingList = new List<MemberBinding>();是一个对象成员集合列表,循环TOut的所有公共的属性和字段,Add到memberBindingList集合中,然后使用MemberInitExpression初始化多个对象拼装再调用。第一次调用动态拼装,组装了一个key放入字典中,缓存之后,就直接调用字典中的数据。缓存后的就是硬编码所以性能高。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Linq.Expressions;using System.Text;using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ThreeHomeWork.MappingExtend{ /// <summary> /// 生成表达式目录树。字典缓存 /// </summary> public class ExpressionMapper { private static Dictionary<string, object> _DIC = new Dictionary<string, object>(); /// <summary> /// 字典缓存表达式树 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="TIn"></typeparam> /// <typeparam name="TOut"></typeparam> /// <param name="tIn"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static TOut Trans<TIn, TOut>(TIn tIn) { string key = string.Format("funckey_{0}_{1}", typeof(TIn).FullName, typeof(TOut).FullName); if (!_DIC.ContainsKey(key)) { ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(TIn), "p"); List<MemberBinding> memberBindingList = new List<MemberBinding>(); foreach (var item in typeof(TOut).GetProperties()) { MemberExpression property = Expression.Property(parameterExpression, typeof(TIn).GetProperty(item.Name)); MemberBinding memberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, property); memberBindingList.Add(memberBinding); } foreach (var item in typeof(TOut).GetFields()) { MemberExpression property = Expression.Field(parameterExpression, typeof(TIn).GetField(item.Name)); MemberBinding memberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, property); memberBindingList.Add(memberBinding); } MemberInitExpression memberInitExpression = Expression.MemberInit(Expression.New(typeof(TOut)), memberBindingList.ToArray()); Expression<Func<TIn, TOut>> lambda = Expression.Lambda<Func<TIn, TOut>>(memberInitExpression, new ParameterExpression[] { parameterExpression }); Func<TIn, TOut> func = lambda.Compile();//拼装是一次性的 _DIC[key] = func; } return ((Func<TIn, TOut>)_DIC[key]).Invoke(tIn); } }} |
02.泛型+反射,接收一个TIn类型的,返回一个TOut类型的反射,通过反射遍历赋值。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ThreeHomeWork.MappingExtend{ public class ReflectionMapper { /// <summary> /// 反射 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="TIn"></typeparam> /// <typeparam name="TOut"></typeparam> /// <param name="tIn"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static TOut Trans<TIn, TOut>(TIn tIn) { TOut tOut = Activator.CreateInstance<TOut>();//创建对象 foreach (var itemOut in tOut.GetType().GetProperties())//遍历属性 { foreach (var itemIn in tIn.GetType().GetProperties()) { if (itemOut.Name.Equals(itemIn.Name)) { itemOut.SetValue(tOut, itemIn.GetValue(tIn)); break; } } } foreach (var itemOut in tOut.GetType().GetFields())//遍历字段 { foreach (var itemIn in tIn.GetType().GetFields()) { if (itemOut.Name.Equals(itemIn.Name)) { itemOut.SetValue(tOut, itemIn.GetValue(tIn)); break; } } } return tOut; } }} |
03.使用第三方序列化反序列化工具,Newtonsoft.Json是比较好的一个工具,这种方式序列化代码虽然一行搞定,但是序列化和反序列化的动作比反射动作大点,耗时会比较高。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
using Newtonsoft.Json;using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ExpressionDemo.MappingExtend{ public class SerializeMapper { /// <summary> /// 序列化反序列化方式 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="TIn"></typeparam> /// <typeparam name="TOut"></typeparam> public static TOut Trans<TIn, TOut>(TIn tIn) { return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<TOut>(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(tIn)); } }} |
04.生成表达式目录树,泛型缓存,使用泛型缓存性能是最高的。动态实现Student与StudentDto的转换。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Linq.Expressions;using System.Text;using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ThreeHomeWork.MappingExtend{ /// <summary> /// 生成表达式目录树 泛型缓存 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="TIn"></typeparam> /// <typeparam name="TOut"></typeparam> public class ExpressionGenericMapper<TIn, TOut>//Mapper`2 { private static Func<TIn, TOut> _FUNC = null; static ExpressionGenericMapper() { ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(TIn), "p"); List<MemberBinding> memberBindingList = new List<MemberBinding>(); foreach (var item in typeof(TOut).GetProperties()) { MemberExpression property = Expression.Property(parameterExpression, typeof(TIn).GetProperty(item.Name)); MemberBinding memberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, property); memberBindingList.Add(memberBinding); } foreach (var item in typeof(TOut).GetFields()) { MemberExpression property = Expression.Field(parameterExpression, typeof(TIn).GetField(item.Name)); MemberBinding memberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, property); memberBindingList.Add(memberBinding); } MemberInitExpression memberInitExpression = Expression.MemberInit(Expression.New(typeof(TOut)), memberBindingList.ToArray()); Expression<Func<TIn, TOut>> lambda = Expression.Lambda<Func<TIn, TOut>>(memberInitExpression, new ParameterExpression[] { parameterExpression }); _FUNC = lambda.Compile();//拼装是一次性的 } public static TOut Trans(TIn t) { return _FUNC(t); } }} |