介绍
一种自动化运维工具,基于paramiko开发的,并且基于模块化工作,Ansible是一种集成IT系统的配置管理、应用部署、执行特定任务的开源平台,它是基于python语言,由Paramiko和PyYAML两个关键模块构建。集合了众多运维工具的优点,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能.ansible是基于模块工作的,本身没有批量部署的能力.真正具有批量部署的是ansible所运行的模块,ansible只是提供一种框架.ansible不需要在远程主机上安装client/agents,
因为它们是基于ssh来和远程主机通讯的.
功能
确保所依赖的软件包已经被安装
配置文件包含正确的内容和正确的权限
相关服务被正确运行
常见的自动化运维工具区别

组成
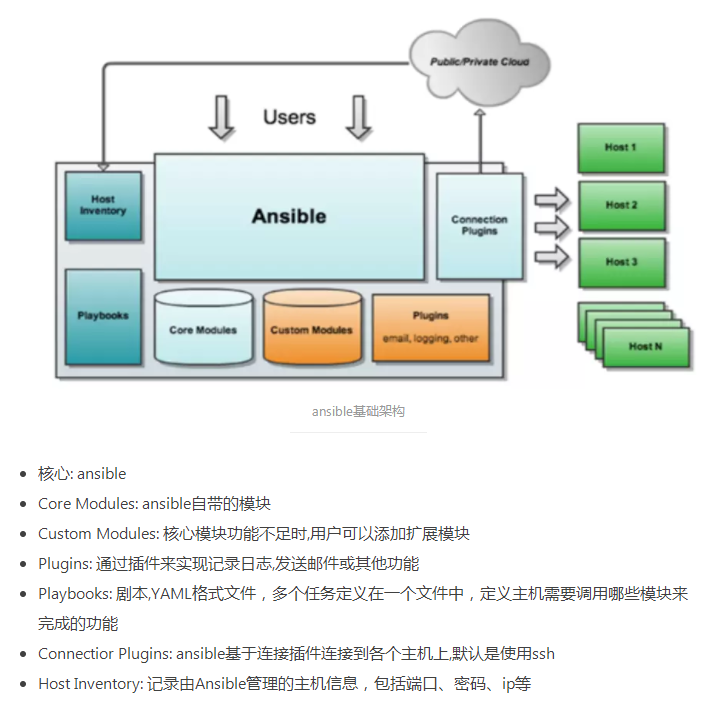
特点
部署简单, 只需要在控制主机上部署ansible环境,被控制端上只要求安装ssh和python 2.5以上版本,这个对于类unix系统来说相当与无需配置.
- no angents: 被管控节点无需安装agent
- no server: 无服务端,使用是直接调用命名
- modules in any languages: 基于模块工作, 可以使用任意语言开发模块
- 易读的语法: 基于yaml语法编写playbook
- 基于推送模式: 不同于puppet的拉取模式,直接由调用者控制变更在服务器上发生的时间
- 模块是幂等性的:定义的任务已存在则不会做任何事情,意味着在同一台服务器上多次执行同一个playbook是安全的
安装
pip install ansible -i https://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
提示的没有pip
安装pip yum -y install python-pip
提示错误
更新epel
sudo yum -y install epel-release
然后在安装pip
在安装ansible
程序目录结构
配置文件: /etc/ansible/
执行文件目录: /usr/bin/
lib依赖库: /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible/
help文件: /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible
inventory文件格式
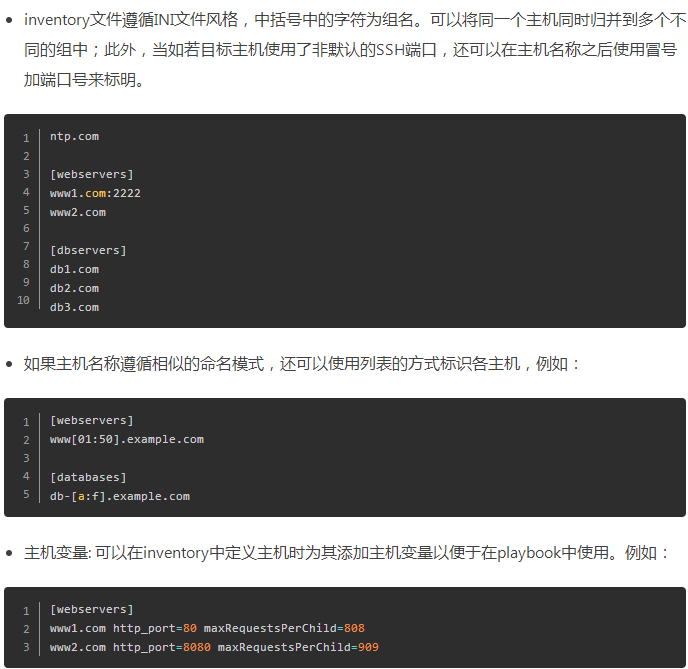
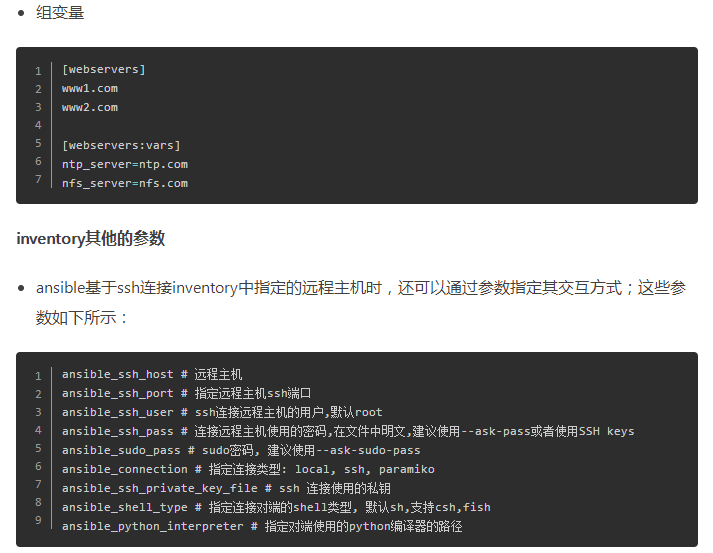
基于ad-hoc模式运行
ansible通过ssh实现配置管理、应用部署、任务执行等功能,因此,需要事先配置ansible端能基于密钥认证的方式联系各被管理节点。
ansible命令使用语法:
ansible
-m module:默认为command
列出支持的模块
ansible-doc -l
ping # 主机连通性测试
command # 在远程主机上执行命令,不支持管道
shell # 在远程主机上调用shell解析器,支持管道命令个
copy # 用于将文件复制到远程主机,支持设定内容和修改权限.
file # 创建文件,创建连接文件,删除文件等
fetch # 从远程复制文件到本地
cron # 管理cron计划任务
yum # 用于模块的安装
service # 管理服务
user # 管理用户账号
group # 用户组管理
script # 将本地的脚本在远端服务器运行
setup # 该模块主要用于收集信息,是通过调用facts组件来实现的,以变量形式存储主机上的信息
查看相应模块的使用方法
ansible -s
# ansible-doc -s service
- name: Manage services
service:
arguments: # Additional arguments provided on the command line
enabled: # Whether the service should start on boot. *At least one of state and enabled are required.*
name: # (required) Name of the service.
pattern: # If the service does not respond to the status command, name a substring to look for as would be
found in the output of the `ps' command as a stand-in for a
status result. If the string is found, the service will be
assumed to be running.
runlevel: # For OpenRC init scripts (ex: Gentoo) only. The runlevel that this service belongs to.
sleep: # If the service is being `restarted' then sleep this many seconds between the stop and start
command. This helps to workaround badly behaving init scripts
that exit immediately after signaling a process to stop.
state: # `started'/`stopped' are idempotent actions that will not run commands unless necessary.
`restarted' will always bounce the service. `reloaded' will
always reload. *At least one of state and enabled are required.*
Note that reloaded will start the service if it is not already
started, even if your chosen init system wouldn't normally.
use: # The service module actually uses system specific modules, normally through auto detection, this
setting can force a specific module. Normally it uses the value
of the 'ansible_service_mgr' fact and falls back to the old
'service' module when none matching is found.
-m ping
定义好inventory文件后可以调用ping来检测网络是否可达
# ansible all -m ping
192.168.57.22 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.57.11 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
-m command 执行命令 默认的
# 如果/etc/passwd文件存在就执行grep命令
# ansible all -m command -a 'removes=/etc/passwd grep root /etc/passwd'
192.168.57.22 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
192.168.57.11 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
-m script 执行脚本
-m raw -a "执行源生的linux命令"
ansible -i 指定hosts文件 -m raw -a "要批量在主机上执行的命令"
hosts文件中可以进行分组指定组参数
[11.vars]
ssh_user = root
ssh_passw = xxx
[11]
10.10.10.10
xxxxxxxxx
基于playbook执行
playbook是由一个或多个“play”组成的列表。play的主要功能在于将事先归并为一组的主机装扮成事先通过ansible中的task定义好的角色。从根本上来讲,所谓task无非是调用ansible的一个module。将多个play组织在一个playbook中,即可以让它们联同起来按事先编排的机制同唱一台大戏。