json是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,因为其灵巧使得其在应用层开发以及接口层开发使用的十分广泛,最常用的莫过于协议交流使用json数据,比xml轻巧,又比二进制数据有规则。无论是各大公司的开放平台或者是动态网页,都大量的使用json串来传递以及交互信息,大多都是直接放在http的包体中使用。
具体的json的格式不多做介绍,因为其独特的结构,可以将其解析成树之后再使用,比如这段数据:
{"array":[{"code":0,"data":{"area":"34e5317","region":"eace02","isp":"535fe1"}}, {"id":"d2432"}, {"id":"d34234"}], "name":{"one":"zzh",""two":"hsc"}}
一般情况下,看到这段数据去想使用键值对来保存信息挺不错的,如果怕重复的话还可以使用stl中multimap来保存,不过这样会丢失一些信息,那就是键值对的父节点的信息,因此将其保存在树这样的数据结构中可以保存期完整的信息,但是如果存储为双亲表示法或者孩子表示法都不仅在语言语法的层面上实现,而且运行时也十分难以掌控,因此用孩子兄弟表示法来存储这些json信息是最理想的选择。
我们将值作为叶子节点,中途的数据作为非叶子节点,于是第二个问题出现,数组以及对象类型的json值应该也作为叶子节点吗?对于这个问题有两种方式解决,一个就是作为叶子节点,这个方法在我的第一篇博文中的数据结构就是这么解决的,这里使用第二种方法来解决:对于对象类型,直接将其看成一颗子树就好,至于数组类型,因为其内的值都只拥有一个键,这样建树似乎有些困难,这里使用一个辅助键array_p来作为数组中每一个值的键,然后将辅助键和数组中值看成真正键的孩子节点,这样就能够将数组融合在树中了,具体可以结合上面的json串转换的树来理解:
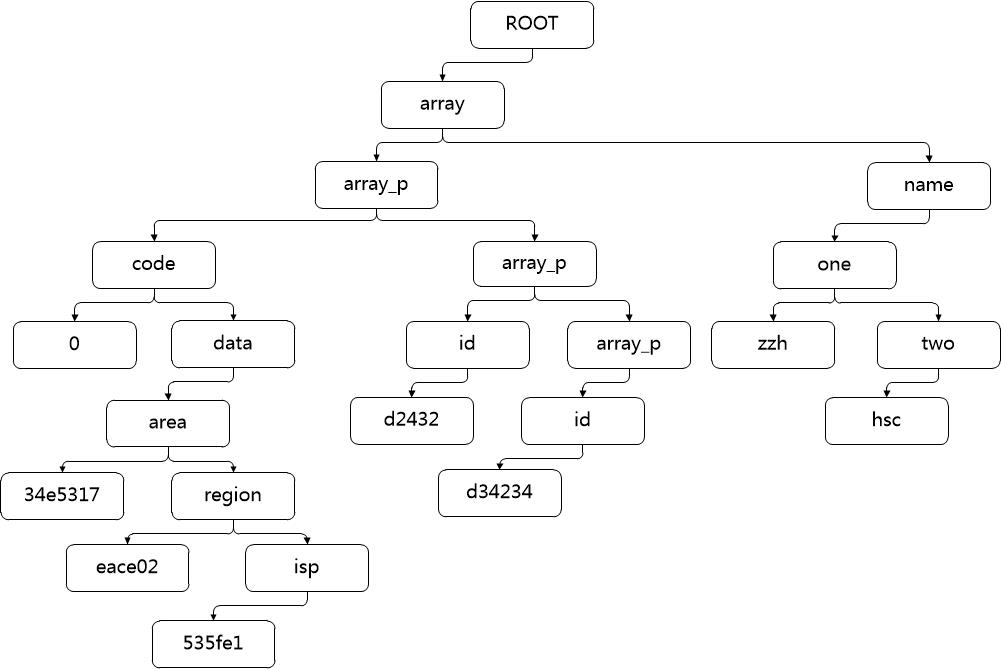
第三个问题仍然是存储问题,非叶子节点保存的数据都是字符串类型,但是叶子节点可能为整型 浮点型 字符串类型以及逻辑值型,总不能为了不同的存储数据而定义不同的节点类型,这样太过于冗余了。对于这个问题首先想到的是让所有类型都继承自一个父类,然后在节点中存储父类的引用或者指针,但是如果提供虚方法使用多态的特性来的话,存在的问题在于如果想要获得树节点中存放的信息,对于不同的类型,函数的返回类型必然是不同的,因此相同接口的不同实现方法被否定。实际上解决方法很简单,在节点中存放父类型的指针,但是每次给节点信息中保存的实际上是子类的指针,最后需要取出信息的时候转换过来就好了。
从上面分析的情形中先给出数据结构,几种不同的叶节点类型都是以其父类型来保存数据,因此大致如下:
typedef enum { STRDATA, INTDATA, BOOLDATA, DOUBLEDATA, }DATATYPE; class base_type { public: DATATYPE data_type_; }; class string_type:public base_type { //DATATYPE data_type_; std::string data; public: string_type(std::string d) { data = d; data_type_ = STRDATA; } std::string get_data() { return data; } }; class int_type:public base_type { //DATATYPE data int data; public: int_type(int d) { data = d; data_type_ = INTDATA; } int get_data() { return data; } }; class double_type:public base_type { double data; public: double_type(double d) { data = d; data_type_ = DOUBLEDATA; } double get_data() { return data; } }; class bool_type:public base_type { bool data; bool_type(bool d) { data = d; data_type_ = BOOLDATA; } bool get_data() { return data; } };
因为这次写的json解析模块只是简单的使用,所以只需要树节点就好,并没有提供一个整体管理数节点的树类,至于树节点的数据结构如下所示:
class tree_node { public: base_type* node_data; tree_node* first_child,* next_sib; tree_node(base_type* val) { node_data = val; first_child = NULL; next_sib = NULL; } ~tree_node() { if(node_data != NULL) delete node_data; if(first_child != NULL) delete first_child; if(next_sib) delete next_sib; } };
写到这里,整个json串解析就十分清晰了,需要做的就是读取json串,然后根据不同类型的键和值来新建节点然后缀在树根结点上就好,本来想写个解析jaon串的小库出来,应该可以结合栈来写些算法即可搞定,不过有现成的东西,这种跑大街的东西就不再重复造轮子了。所以需要一个json库,有很多库很强大,这是我写完树之后才了解到的,在这之前一直用的十分坑的json-c库,所以这里也用json-c库来读取好了,其他的库应该也有与下面想类似的方法来解决,下面贴出递归读取整个json-c串然后新建节点到树根上的代码:
void get_val(struct json_object* obj, tree_node* cur_root) { //temp作为当前节点 tree_node* temp = cur_root; //这里是个比较强大的宏定义,key和value都在宏定义中 json_object_object_foreach(obj, key, value) { string_type* d = new string_type(std::string(key)); if(cur_root->first_child == NULL) { tree_node* new_node = new tree_node(d); cur_root->first_child = new_node; temp = cur_root->first_child; } else { tree_node* new_node = new tree_node(d); temp->next_sib = new_node; temp = temp->next_sib; } enum json_type type; type = json_object_get_type(value); switch(type) { case json_type_string: { //const char* kee = json_object_get_string(key); const char* val = json_object_get_string(value); string_type* d = new string_type(std::string(val)); tree_node* leaf = new tree_node(d); temp->first_child = leaf; if(strcmp(key, "id")==0) did.push_back(std::string(val)); else normal.insert(std::make_pair(std::string(key), std::string(val))); break; } case json_type_int: { //const char* kee = json_object_get_string(key); int val = json_object_get_int(value); int_type* d = new int_type(val); tree_node* leaf = new tree_node(d); temp->first_child = leaf; //normal.insert(std::string(key), val_int); break; /* case json_type_boolean: boolean val = json_object_get_boolean(value); */ } case json_type_array: { //现在temp是数组中所有元素的父节点 //数组类型比较麻烦,将之放到树这样的数据结构中也不是很容易 tree_node* temp2 = temp; for(int i=0; i<json_object_array_length(value); i++) { if(temp->first_child == NULL) { tree_node* param = new tree_node(new string_type("array_p")); temp->first_child = param; temp2 = temp->first_child; } else { tree_node* param = new tree_node(new string_type("array_p")); temp2->next_sib = param; temp2 = temp2->next_sib; } json_object* obj = json_object_array_get_idx(value, i); if(json_object_get_type(obj) == json_type_object) get_val(obj, temp2); } break; } case json_type_object: get_val(value, temp); break; default: break; } } }
可能觉得自己技术不错的人都喜欢用到一些别人不常用的技术或者特性,json-c的作者也是如此,用了一个比较强大的宏来弥补遍历json串的缺陷,这个宏是:json_object_object_foreach(obj, key, value)
在json-c库中的宏是这样的:
# define json_object_object_foreach(obj,key,val) char *key; struct json_object *val; for(struct lh_entry *entry = json_object_get_object(obj)->head; ({ if(entry) { key = (char*)entry->k; val = (struct json_object*)entry->v; } ; entry; }); entry = entry->next )
将json串中的信息保存到树中才是开始,需要知道怎么用才是正道,所以顺便写个树的遍历,以及找到所有键值对的全路径,前者用递归或者栈来解决,后者用个能够看到栈中元素的栈,所以用vector来冒充一下就好:
void pre_order(tree_node* cur_root) { if(cur_root) { if(cur_root->node_data->data_type_ == STRDATA) { std::string info = (static_cast<string_type*>(cur_root->node_data))->get_data(); std::cout<<info<<" "; } else if(cur_root->node_data->data_type_ == INTDATA) { int info = (static_cast<int_type*>(cur_root->node_data))->get_data(); std::cout<<info<<" "; } else if(cur_root->node_data->data_type_ == DOUBLEDATA) { double info = (static_cast<int_type*>(cur_root->node_data))->get_data(); } pre_order(cur_root->first_child); pre_order(cur_root->next_sib); } } void pre_order_stack(tree_node* cur_root) { tree_node* temp = cur_root; std::stack<tree_node*> s; while(temp || !s.empty()) { while(temp) { if(temp->node_data->data_type_ == STRDATA) { std::string info = (static_cast<string_type*>(temp->node_data))->get_data(); std::cout<<info<<" "; } else if(temp->node_data->data_type_ == INTDATA) { int info = (static_cast<int_type*>(temp->node_data))->get_data(); std::cout<<info<<" "; } else if(temp->node_data->data_type_ == DOUBLEDATA) { double info = (static_cast<int_type*>(temp->node_data))->get_data(); std::cout<<info<<" "; } s.push(temp); temp = temp->first_child; } temp = s.top(); s.pop(); temp = temp->next_sib; } } //先序方式输出叶节点以及其路径 void pre_order_pwd(tree_node* cur_root) { tree_node* temp = cur_root; std::vector<tree_node*> v; while(temp || !v.empty()) { while(temp) { v.push_back(temp); temp = temp->first_child; } //只有在叶节点的情况下才打印出路径 在json中可以配合来判断整个路径得到最终的值 if(v.at(v.size()-1)->first_child == NULL) { std::vector<tree_node*>::iterator it; for(it=v.begin(); it!=v.end(); it++) { if((*it)->node_data->data_type_ == STRDATA) { std::string info = (static_cast<string_type*>((*it)->node_data))->get_data(); std::cout<<info<<" "; } else if((*it)->node_data->data_type_ == INTDATA) { int info = (static_cast<int_type*>((*it)->node_data))->get_data(); std::cout<<info<<" "; } else if((*it)->node_data->data_type_ == DOUBLEDATA) { double info = (static_cast<int_type*>((*it)->node_data))->get_data(); std::cout<<info<<" "; } } std::cout<<std::endl; } temp = v.at(v.size()-1); v.pop_back(); temp = temp->next_sib; } }
给出示例:
int main() { typedef std::vector<std::string>::iterator iterator; char* input = "{"array":[{"code":0,"data":{"ip":"210.75.225.254","country":"4e2","area":"34e5317","region":"53174eace02","city":"317eace02","county":"","isp":"535fe1","country_id":"86","id":"100000","id":"110000","id":"110000","id":"-1","isp_id":"100017"}}, {"id":"d2432"}, {"id":"d34234"}], "name":{"one":"zzh","two":"hsc"}}"; struct json_object* json_obj = json_tokener_parse(input); tree_node* root = new tree_node(new string_type("root")); get_val(json_obj, root); for(iterator it=did.begin(); it!=did.end(); it++) { std::cout<<*it<<" "; } pre_order_pwd(root); delete root; return 0; }
结果如下:
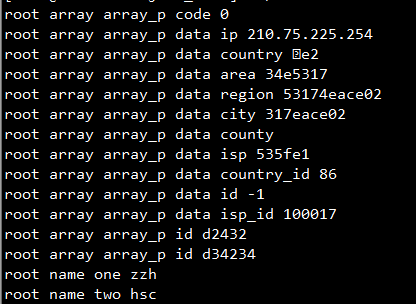
然后是测试代码以及json库的下载链接:https://files.cnblogs.com/files/beneathginkgo/json-tree.zip