何为梯度下降,直白点就是,链式求导法则,不断更新变量值。
这里讲解的代码为李宏毅老师机器学习课程中 class 4 回归展示 中的代码demo
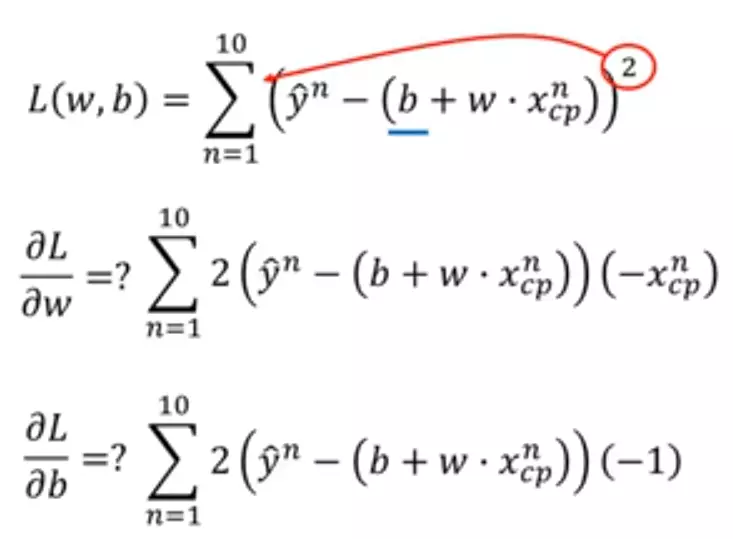
Loss函数
python代码如下
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # y_data = b + w * x_data x_data = [338., 333., 328., 207., 226., 25., 179., 60., 208., 606.] # 10 个数 y_data = [640., 633., 619., 393., 428., 27., 193., 66., 226., 1591.] # 10 个数 x = np.arange(-200, -100, 1) # bias y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.1) # weight z = np.zeros((len(x), len(y))) # zeros函数表示输出的数组为 100行 100列 #X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y) 个人感觉这句话没用。。。 for i in range(len(x)): for j in range(len(y)): b = x[i] w = y[j] z[j][i] = 0 for n in range(len(x_data)): # z[j][i]为 b=x[i] 及 w=y[j] 时,对应的 Loss Function 的大小 z[j][i] = z[j][i] + (y_data[n] - b - w * x_data[n]) ** 2 z[j][i] = z[j][i] / len(x_data) # 求 loss function 均值 # y_data = b + w * x_data b = -120 # initial b w = -4 # initial w lr = 0.0000001 # learning rate iteration = 100000 # 迭代运行次数 # store initial values for plotting b_history = [b] w_history = [w] # iterations for i in range(iteration): # 在 100000 次迭代下,看最后结果 b_grad = 0.0 # 对 b_grad 重新赋值为0 w_grad = 0.0 # 对 w_grad 重新赋值为0 for n in range(len(x_data)): # 此处应该注意的是,求导的是Loss函数,因此对应的变量是w、b,是看w、b在各自的轴上的移动 b_grad = b_grad + 2.0 * (y_data[n] - b - w * x_data[n]) * ( - 1.0) w_grad = w_grad + 2.0 * (y_data[n] - b - w * x_data[n]) * ( - x_data[n]) # update parameters b = b - lr * b_grad w = w - lr * w_grad # store parameters for plotting b_history.append(b) w_history.append(w) # plot the figure plt.contourf(x, y, z, 50, alpha = 0.5, cmap = plt.get_cmap('jet')) plt.plot([-188.4], [2.67], 'x', ms = 12, markeredgewidth = 3, color = 'orange') plt.plot(b_history, w_history, 'o-', ms = 3, lw = 1.5, color = 'black') plt.xlim(-200, -100) plt.ylim(-5, 5) plt.xlabel(r'$b$', fontsize=16) plt.ylabel(r'$w$', fontsize=16) plt.show()
当learning rate 即 lr = 0.0000001时
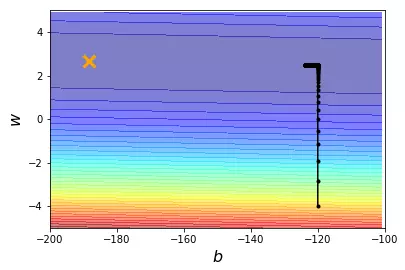
当learning rate 即 lr = 0.000001时

learning rate 即 lr = 0.00001时

可以看到效果不是很好 所以改变learning rate
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # y_data = b + w * x_data x_data = [338., 333., 328., 207., 226., 25., 179., 60., 208., 606.] # 10 个数 y_data = [640., 633., 619., 393., 428., 27., 193., 66., 226., 1591.] # 10 个数 x = np.arange(-200, -100, 1) # bias y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.1) # weight z = np.zeros((len(x), len(y))) # zeros函数表示输出的数组为 100 行 100 列 # X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y) for i in range(len(x)): for j in range(len(y)): b = x[i] w = y[j] z[j][i] = 0 for n in range(len(x_data)): # z[j][i]为 b=x[i] 及 w=y[j] 时,对应的 Loss Function 的大小 z[j][i] = z[j][i] + (y_data[n] - b - w * x_data[n]) ** 2 z[j][i] = z[j][i] / len(x_data) # 求 loss function 均值 # ydata = b + w * xdata b = -120 # initial b w = -4 # initial w lr = 1 # learning rate iteration = 100000 # 迭代运行次数 # store initial values for plotting b_history = [b] w_history = [w] # 个性化 w 和 b 的 learning rate lr_b = 0 lr_w = 0 # iterations for i in range(iteration): # 在 100000 次迭代下,看最后结果 b_grad = 0.0 # 对 b_grad 重新赋值为0 w_grad = 0.0 # 对 w_grad 重新赋值为0 for n in range(len(x_data)): # 此处应该注意的是,求导的是L函数,因此对应的变量是w、b,是看w、b在各自的轴上的移动 b_grad = b_grad + 2.0 * (y_data[n] - b - w * x_data[n]) * (- 1.0) w_grad = w_grad + 2.0 * (y_data[n] - b - w * x_data[n]) * (- x_data[n]) lr_b = lr_b + b_grad ** 2 lr_w = lr_w + w_grad ** 2 # update parameters b = b - lr / np.sqrt(lr_b) * b_grad w = w - lr / np.sqrt(lr_w) * w_grad # store parameters for plotting b_history.append(b) w_history.append(w) # plot the figure plt.contourf(x, y, z, 50, alpha=0.5, cmap=plt.get_cmap('jet')) plt.plot([-188.4], [2.67], 'x', ms=12, markeredgewidth=3, color='orange') plt.plot(b_history, w_history, 'o-', ms=3, lw=1.5, color='black') plt.xlim(-200, -100) plt.ylim(-5, 5) plt.xlabel(r'$b$', fontsize=16) plt.ylabel(r'$w$', fontsize=16) plt.show()
结果展示
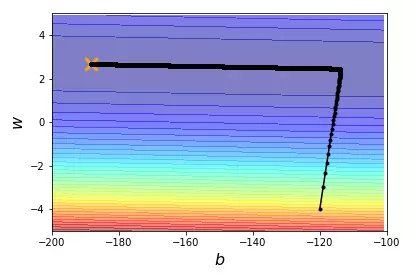
一些说明:
np.array np.asarray的区别
array和asarry都可以将结构数据转换为ndarray类型
但是主要的区别在于当数据源是ndarray时,array仍会copy出一个副本,占用新的内存,但asarray不会。
np.meshgrid的作用
生成网格点坐标矩阵