定义一个数组类,要求包含构造方法,增加数据,输出数据的成员方法,并利用数组实现动态内存的分配,
在此基础上定义以下子类:
1)排序类,实现排序。
2)反转类,实现数据反向存放。
分析
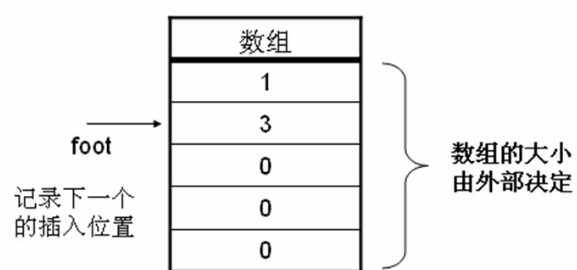
本程序要求数组实现动态的内存分配,也就是说里面数组大小是由程序外部决定的。即根据对象实例化: 类 对象=new 类(参数,参数,,);
所以应该在构造方法中,为类的数组进行初始化操作(数组大小通过构造方法里的参数代入初始化。)。
之后每次增加数据的时候都应该判断数组的内容是否已经满了。如果满了不能增加。
另外如果要增加数据的时候肯定需要一个指向可以插入的下标,用于记录插入的位置。
class Array{ // 表示数组 private int temp[] ; // 整型数组 private int foot ; // 定义添加位置 public Array(int len){ if(len>0){ this.temp = new int[len] ; }else{ this.temp = new int[1] ; // 最少维持空间是1个 } } public boolean add(int i){ // 增加元素 if(this.foot<this.temp.length){ // 还有空间 this.temp[foot] = i ; // 增加元素 this.foot ++ ;// 修改脚标 return true ; }else{ return false ; } } public int[] getArray(){ return this.temp ; } }; class SortArray extends Array{ // 排序类 public SortArray(int len){ super(len) ; } public int[] getArray(){ // 覆写方法 java.util.Arrays.sort(super.getArray()) ; // 排序操作 return super.getArray() ; } }; class ReverseArray extends Array{ // 反转操作类 public ReverseArray(int len){ super(len) ; } public int[] getArray() { int t[] = new int[super.getArray().length] ; // 开辟一个新的数组 int count = t.length - 1 ; for(int x=0 ;x<t.length;x++){ t[count] = super.getArray()[x] ; // 数组反转 count-- ; } return t ; } }; public class ArrayDemo{ public static void main(String args[]){ // ReverseArray a = null ; // 声明反转类对象 // a = new ReverseArray(5) ; // 开辟5个空间大小 SortArray a = null ; a = new SortArray(5) ; System.out.print(a.add(23) + " ") ; System.out.print(a.add(21) + " ") ; System.out.print(a.add(2) + " ") ; System.out.print(a.add(42) + " ") ; System.out.print(a.add(5) + " ") ; System.out.print(a.add(6) + " ") ; print(a.getArray()) ; } public static void print(int i[]){ // 输出数组内容 for(int x=0;x<i.length;x++){ System.out.print(i[x] + "、") ; } } };
充分利用了继承,继承了父类的方法,利用了覆盖,利用了super关键字调用父类方法属性。