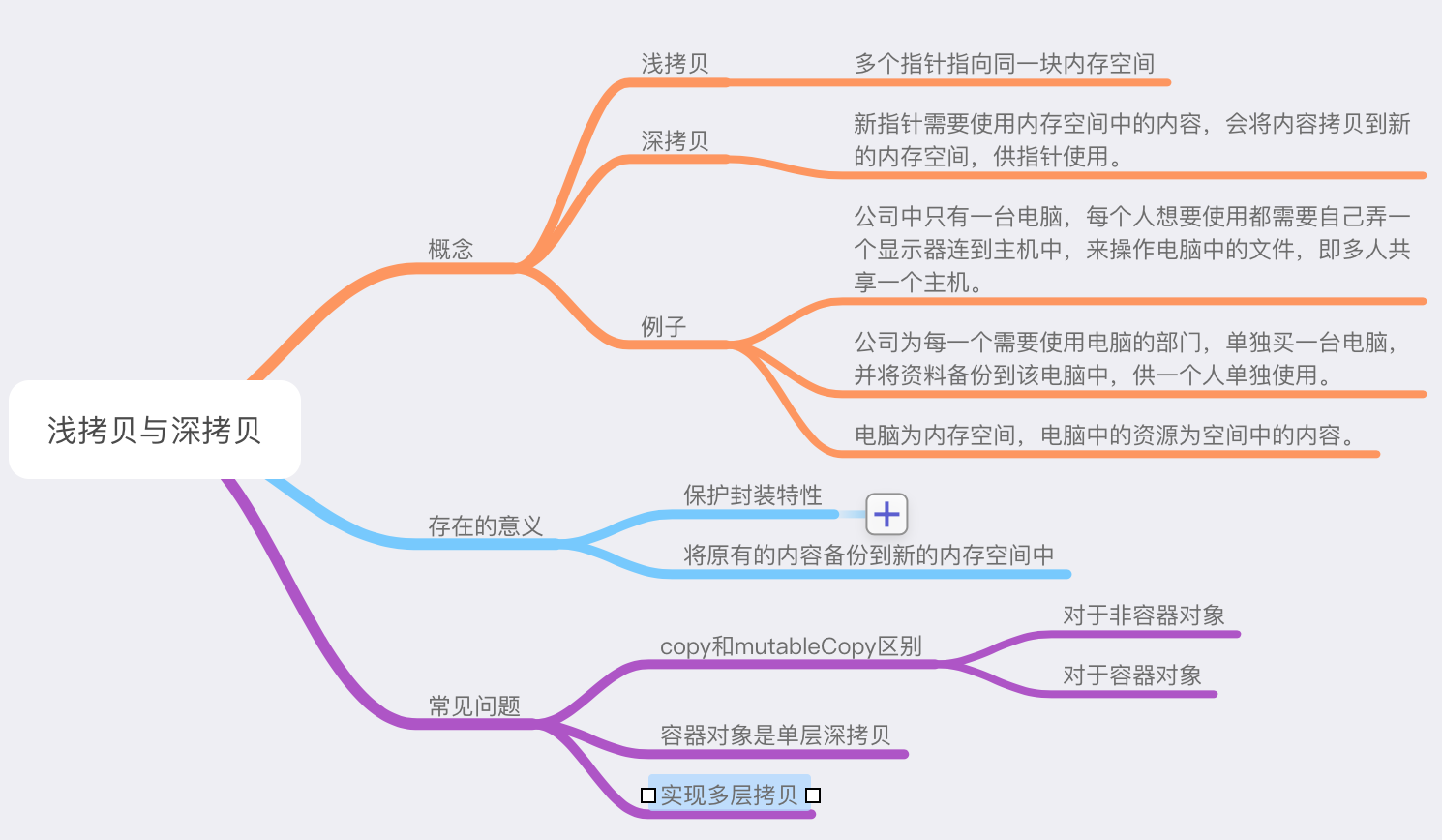
1、保护封装性:
// Person对象中的name属性使用copy修饰 @interface Person : NSObject @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *name; @end // Man对象中的name属性使用strong修饰 @interface Man : NSObject @property (strong, nonatomic) NSString *name; @end int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { Person *p = [[Person allow] init]; Man *m = [[Man allow] init]; NSMutableString *str = [NSMutableString stringWithFormat:@"%@", @"hello"]; p.name = str; m.name = str; [str appendFormat:@"%@", @" world"]; NSLog(@"%p === %@ === %@", p.name, p.name, str); NSLog(@"%p === %@ === %@", m.name, m.name, str);
}
打印结果:
0x6f6c6c656855 === hello === hello world
0x100442af0 === hello world === hello world
总结:上面的实例中,Man实例对象中的name属性,没有通过setter方法,就完成了name属性的修改,破坏了封装性。
2、备份内容:
// 拷贝一个内存空间的内容,只需要一行代码就搞定,不需要再进行繁琐操作了(申请内存空间,将原内存空间的内容赋值到新内存空间中) int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { NSString *str1 = nil; NSMutableString *str = [NSMutableString stringWithFormat:@"%@", @"hello"]; // 复制str中的内容到str1中。 str1 = [str copy]; }
3、copy和mutableCopy使用区别:

总结:
- 使用copy创建的对象,永远是不可变对象
- 使用mutableCopy创建的对象,永远是可变对象,并且一定是深拷贝。
- 不可变对象使用copy,永远是浅拷贝,可变对象使用copy,永远是深拷贝。
3、容器对象的单层深拷贝
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { NSMutableArray *arrM = [NSMutableArray arrayWithObject:@"aaa"]; // 对arrM进行深拷贝 NSArray *arr = [arrM copy]; // 打印两个数组的首地址,是否是深拷贝 NSLog(@"arrM = %p", arrM); NSLog(@"arr = %p", arr); // 打印两个数组第0个元素的地址,是否也是深拷贝 NSLog(@"arrM[0] = %p", arrM[0]); NSLog(@"arr[0] = %p", arr[0]); } 打印结果: arrM = 0x10200ad00 arr = 0x102004d30 arrM[0] = 0x1000021e0 arr[0] = 0x1000021e0
总结:
对于容器对象的深拷贝,是单层拷贝,虽然两个数组不共享同一块内存空间,但是数组中的元素,却是共享一块内存空间。

4、实现数组的元素的深拷贝:
/* * 1、创建数组类的分类 * 2、重新copy和mutableCopy方法 * 3、在方法中实现数组元素的深拷贝 * 4、不要实现copyWithZone:和mutableCopyWithZone:方法,不会调用的。 */ @interface NSMutableArray (Copy) @end @implementation NSMutableArray (Copy) // 重写copy方法 - (id)copy { NSMutableArray *arrM = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:self.count]; // 对数组中的元素进行深拷贝,并保存到新数组中。 for (NSObject *obj in self) { // 判断数组中的元素是否实现NSCopying协议 if([obj conformsToProtocol:@protocol(NSCopying)]){ NSObject *temp = [obj copy]; [arrM addObject:temp]; } [arrM addObject:obj]; } // 将数组转成不可变对象 return [NSArray arrayWithArray:arrM]; } // 重写mutableCopy方法 - (id)mutableCopy { NSMutableArray *arrM = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:self.count]; // 对数组中的元素进行深拷贝,并保存到新数组中。 for (NSObject *obj in self) { // 判断数组中的元素是否实现NSCopying协议 if([obj conformsToProtocol:@protocol(NSCopying)]){ NSObject *temp = [obj copy]; [arrM addObject:temp]; } [arrM addObject:obj]; } return arrM; } @end ----------main.m---------------------------------- #import "NSMutableArray+Copy.h" int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { NSMutableString *s5 = [[NSMutableString alloc] initWithString:@"aaa"]; NSMutableArray *arrM = [NSMutableArray arrayWithObject:s5]; // 调用数组分类中的copy方法。 NSArray *arr = [arrM copy]; NSLog(@"arrM = %p", arrM); NSLog(@"arr = %p", arr); NSLog(@"arrM[0] = %p", arrM[0]); NSLog(@" arr[0] = %p", arr[0]); return 0; } 打印结果: arrM = 0x10300eea0 arr = 0x10064e5d0 arrM[0] = 0x10300ecd0 arr[0] = 0x61616135
5、自定义对象的深拷贝:
- 自定义类的实例对象调用copy方法时,会调用copyWithZone:方法,但是系统的字符串、数组、字典对象调用copy方法时,不会调用copyWithZone:方法。
- 要实现自定义对象的拷贝功能,需要遵循NSCopying协议,并实现copyWithZone:和mutableCopyWithZone:方法。
- 自定义类中的实例对象的属性存在另外的自定义对象(Person类中有Man类属性),如果需要保证Person的封装性,可以使用copy修饰属性对象,如果想要共享内存空间,可以使用strong修饰属性对象。
---------------Man.h---------------- @interface Man : NSObject<NSCopying> @property (strong, nonatomic) NSString *name; @end @implementation Man // 自定义对象不分可变和不可变,一般需要深拷贝时,在copyWithZone:中写深拷贝代码,不需要就写浅拷贝代码。 - (id)copyWithZone:(NSZone *)zone { Man *m = [[Man alloc] init]; m.name = self.name; return m; } - (id)mutableCopyWithZone:(NSZone *)zone { Man *m = [[Man alloc] init]; m.name = self.name; return m; } @end --------------------Person.h--------------- #import "Man.h" @interface Person : NSObject<NSCopying> @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *name; @property (copy, nonatomic) Man *m1; @property (strong, nonatomic) Man *m2; @end @implementation Person - (id)copyWithZone:(NSZone *)zone { return self; } - (id)mutableCopyWithZone:(NSZone *)zone { Person *p = [[Person alloc] init]; // Person的name属性是浅拷贝 p.name = [self.name copy]; p.m1 = self.m1; p.m2 = self.m2; return p; } @end --------------main.h------------------- #import "Person.h" int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { Person *p1 = [[Person alloc] init]; Person *p2 = [p1 copy]; // p1指向的内存空间的引用计数器为2,原因copyWithZone:方法中写的是浅拷贝代码。 Person *p3 = [p1 mutableCopy]; // p3指向了一块新的内存空间,原因mutableCopyWithZone:方法中写的是深拷贝代码 NSLog(@"p1"); } -----------------main.h------------------- int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { Person *p1 = [[Person alloc] init]; Man *m = [[Man alloc] init]; m.name = @"man"; p1.m1 = m; p1.m2 = m; m.name = @"Man"; Person *p2 = [p1 mutableCopy]; NSLog(@"Man === %p", m); NSLog(@"P1.m1 copy=== %p", p1.m1); NSLog(@"P1.m2 strong=== %p", p1.m2); NSLog(@"P3.m1 copy=== %p", p3.m1); NSLog(@"P3.m1 strong === %p", p3.m2); } --------------打印------------------------ Man === 0x100432150 P1.m1 copy=== 0x100432eb0 P1.m2 strong=== 0x100432150 P3.m1 copy=== 0x10041de00 P3.m1 strong === 0x100432150
6、stringWithFormat:方法:
NSString *str1 = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"hello"]; NSString *str2 = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"hello"]; NSMutableString *str3 = [NSMutableString stringWithFormat:@"hello"]; NSMutableString *str4 = [NSMutableString stringWithFormat:@"hello"]; NSLog(@"str1 == %p", str1); NSLog(@"str2 == %p", str2); NSLog(@"str3 == %p", str3); NSLog(@"str4 == %p", str4); -------------打印结果------------------------- str1 == 0x6f6c6c656855 str2 == 0x6f6c6c656855 str3 == 0x1007112a0 str4 == 0x100711180
总结:
- 对于NSString对象,不管调用多少次stringWithFormat:方法,只要内容一样,它们的地址都一样。
- 对于NSMutableString对象,尽管内容一样,每次调用stringWithFormat:方法都会创建新的内存空间来保持。