1. 使用Ping做什么
ping用于确定本地主机是否能与另一台主机成功交换(发送与接收)数据包,再根据返回的信息,就可以推断TCP/IP参数是否设置正确,以及运行是否正常、网络是否通畅等。
2. 效果
CMD命令:
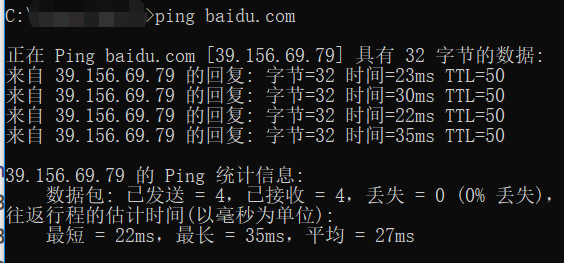
Python程序:

3. 在验证两台主机是否能正常联通时做了什么
验证的过程就像打电话一样,我们如果要知道自己能否给另一个人交流就给他打一个电话,如果你听到了对方的声音那就是打通了,否则就是失败。但是无论成功与否我们都有一个这样的过程:
通过电话线(或是无线,即手机)给对方发送一个请求通话的消息,无论对方是否接通都会返回一条应答的消息。
这里我们发送或接收的消息就是报文(IP报文),其中,发送的请求通话消息我们称为“请求回显”(Ping请求),而接收到的应答消息称为“回显应答”(Ping应答)。
我们通过“回显应答”类型报文中的内容来判断是否能够正常连接(交换数据包)。
而在Ping过程中需要进行四次(并不固定,一般默认四次)请求,这个可以看做是连续打四次电话。
4. IP报文中有什么
由于IP协议并不是一个可靠的协议,它不保证数据被成功送达,那么,如何才能保证数据的可靠送达呢? 这里就需要使用到一个重要的协议模块ICMP(网络控制报文)协议。它传递差错报文以及其他需要注意的信息,经常供IP层或更高层协议(TCP或UDP)使用。所以它经常被认为是IP层的一个组成部分。它在IP数据报文中的封装如下:
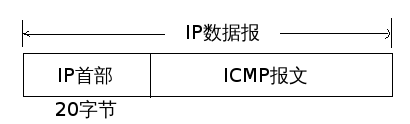
在这里我们不关心IP首部内容(只需要记住它有20bytes即可),而ICMP报文的类型正如上述所说有好多种,我们根据报文的type和code来判断ICMP报文的类型(当然这里我们也只关系回显请求和回显应答):
ICMP报文 = ICMP报头+Data(这个消息可以自定义,当然每个不同类型的报文的data都会有所不同)
(ICMP_Packet = ICMPHeader + Data)
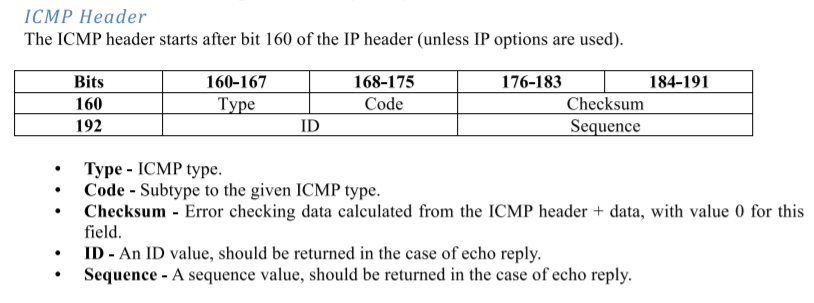
5. ICMP报文中的各个数据是什么,有什么用
(1)type和code
type和code决定了ICMP报文是什么类型(当然这里我们也只关系回显请求和回显应答)。
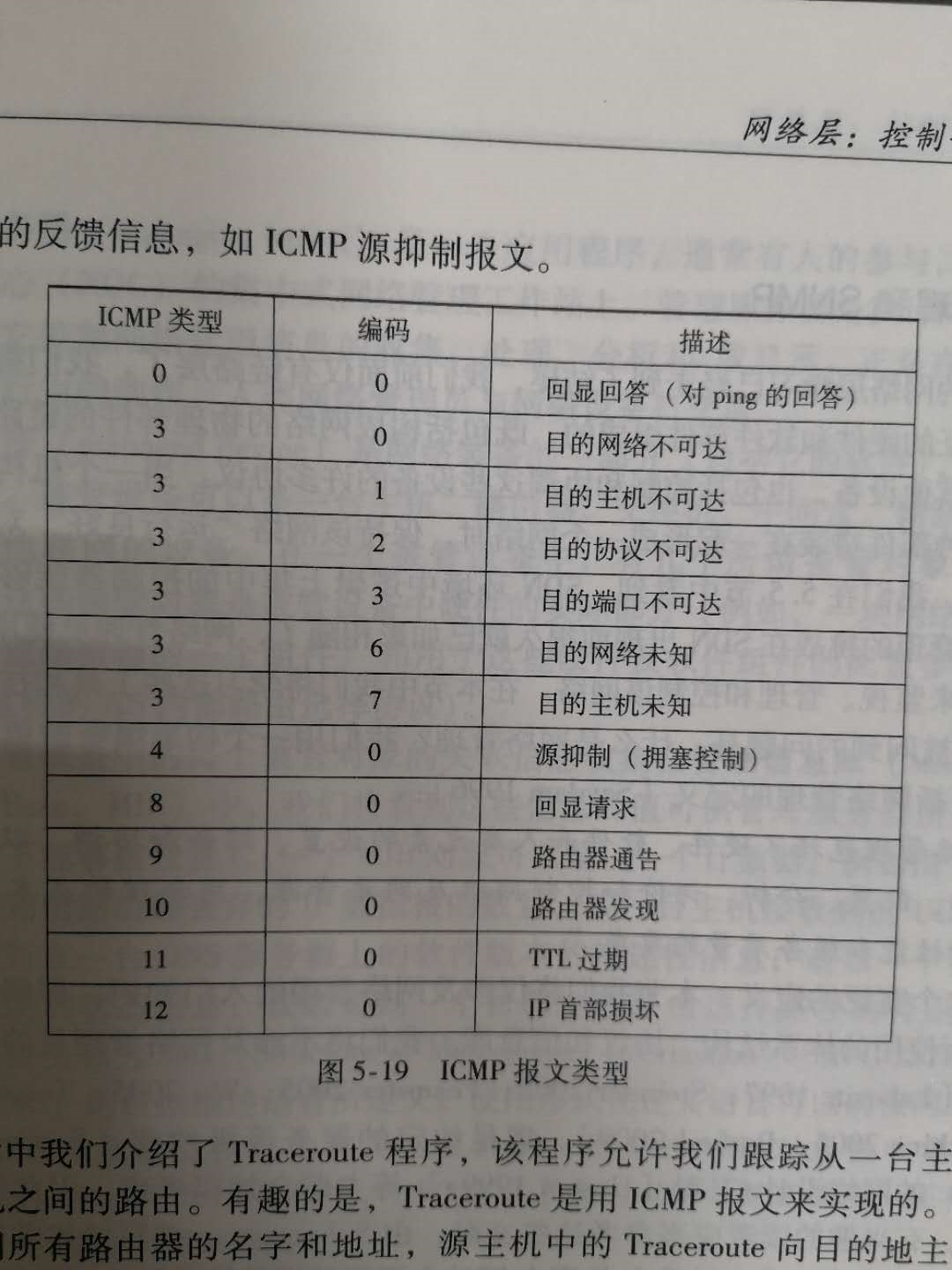
以下是不同type(ICMP类型)和code(编码)对应的不同ICMP报文类型,不用全部记住,在这里我们只要知道:
type = 8, code = 0 表示 回显请求
type = 0, code = 0 表示 回显应答
(2)Checksum(校验和)
用于检验数据包是否正确。
(3)ID(标识符)
每一个不同的进程都有一个ID作为标识,即每次运行这个Ping程序都会获得一个进程ID,我们通过这个比较发送进程ID和回显应答中的ID,如果一样则说明是同一个Ping程序
(4)sequence(序列号)
每发送一次消息,就有一个序列号,第一个就是1,第二次就是2等等(也可以从“0”开始,可以自己定义),按照收发四次来讲就是0、1、2、3
(5)Data(数据)
你可以将你自己想要的其他信息放到这里,比如发送消息的时间,这样就可以计算延迟了
6. 程序框架及具体代码
首先,我们知道要做到两台host通信需要借助socket,以下内容也是在此基础上展开的
(1)全局变量
设置了几个全局变量,包括:回显请求(8),回显应答(0),Ping标识符(ID),Ping序列号(sequence)
ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST = 8 # ICMP type code for echo request messages ICMP_ECHO_REPLY = 0 # ICMP type code for echo reply messages ID = 0 # ID of icmp_header SEQUENCE = 0 # sequence of ping_request_msg
(2)main()
首先我们要有这个程序的入口,俗称“主函数”
在这里我们调用Ping(host, timeout = 1)【自定义】函数正式开始这个过程
ping("baidu.com")
(3)Ping(host, timeout = 1)
有两个参数(host,timeout):
host是要尝试连接的主机的域名或者直接写IP地址也没问题
timeout是设置的超时时间,当等待时间超过1s时我们认为连接超时,即连接失败(表示无法正常交流)
内容简介:
定义变量---在Ping函数中我们设置了几个变量用于表示发送、成功接收、丢失包的数量 和 最长时延、最短时延、总时延
调用doOnePing【自定义】函数---这个函数包括对发送和接收报文消息的函数,返回值就是时延
此外---当然,我们对doOnePing函数调用了四次
def ping(host, timeout=1): send = 0 lost = 0 receive = 0 maxTime = 0 minTime = 1000 sumTime = 0 # 1. Look up hostname, resolving it to an IP address desIp = socket.gethostbyname(host) global ID ID = os.getpid() for i in range(0, 4): global SEQUENCE SEQUENCE = i # 2. Call doOnePing function, approximately every second delay = doOnePing(desIp, timeout) * 1000 send += 1 if delay > 0: receive += 1 if maxTime < delay: maxTime = delay if minTime > delay: minTime = delay sumTime += delay # 3. Print out the returned delay print("Receive from: " + str(desIp) + ", delay = " + str(int(delay)) + "ms") else: lost += 1 print("Fail to connect.") time.sleep(1) # 4. Continue this process until stopped avgTime = sumTime / receive recvRate = receive / send * 100.0 print(" Send: " + str(send) + ", success: " + str(receive) + ", lost: " + str(lost) + ", rate of success: " + str(recvRate) + "%.") print( "MaxTime = " + str(int(maxTime)) + "ms, MinTime = " + str(int(minTime)) + "ms, AvgTime = " + str(int(avgTime)))
(4) doOnePing(destination, timeout)
有两个参数(destination,timeout):
destination就是获得的目标主机的IP地址
timeout就是超时时间(自定义的)
def doOnePing(destinationAddress, timeout): # 1. Create ICMP socket icmpName = socket.getprotobyname('icmp') icmp_Socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_RAW, icmpName) # 2. Call sendOnePing function sendOnePing(icmp_Socket, destinationAddress, ID) # 3. Call receiveOnePing function totalDelay = receiveOnePing(icmp_Socket, destinationAddress, ID, timeout) # 4. Close ICMP socket icmp_Socket.close() # 5. Return total network delay return totalDelay
内容简介:
创建socket---正如上述所说,我们通过socket来做这个通信,由于是使用ICMP协议,我们需要提前获取这个协议(根据协议名)
调用sendOnePing---发送一条回显请求给目标主机
调用receiveOnePing---接收回显应答函数,返回值为时延
关闭socket
返回在调用receiveOnePing函数后获得的时延
(5)sendOnePing(icmpSocket, destination, ID)
参数有三个,用于做什么很显然了,这里不再赘述
def sendOnePing(icmpSocket, destinationAddress, ID): icmp_checksum = 0 # 1. Build ICMP header icmp_header = struct.pack('!bbHHh', ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST, 0, icmp_checksum, ID, SEQUENCE) time_send = struct.pack('!d', time.time()) # 2. Checksum ICMP packet using given function icmp_checksum = checksum(icmp_header + time_send) # 3. Insert checksum into packet icmp_header = struct.pack('!bbHHh', ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST, 0, icmp_checksum, ID, SEQUENCE) # 4. Send packet using socket icmp_packet = icmp_header + time_send icmpSocket.sendto(icmp_packet, (destinationAddress, 80)) # 5. Record time of sending
内容简介:
这个函数的目的就在于向目标主机发送一条回显请求报文,而这个报文中应该包括:ICMP_Header+Data(这里是发送的时间,用于计算时延)
其中用到的struct.pack函数请自行百度,如果不想知道细节的话只需要记住pack的第一个参数规定了其编码格式(有各种字母符号的映射,可以自己编排),而之后的参数都是根据这个编码格式进行打包的数据
在这个函数中调用了校验和程序,这个原理也自行百度(很容易找到),不做深究的话也可以直接拿来用
函数编写步骤:
* 将ICMP_Header的那几个打包成为数据包(其中的校验和只是为了Header的完整性而随意设置的,占位用)
* 用校验和程序检测数据包的完整性
* 加入真正的校验和(这里“真正”似乎不太正确,但暂时想不出有什么其他的词汇形容了)重新打包
* 将发送的时间(time.time())编码打包,作为ICMP的Data
* ICMP_Packet = ICMP-Header + Data
* 借助socket发送报文
* 此外,sendto(msg, (IP, Port))中的Port为80是因为Web默认使用端口号80(还有许多网络应用有特定的端口号——方便访问,一般靠前的port都是分配好的,如果是自己构建的程序则可以申请使用空闲的port)
(6)receiveOnePing(icmpSocket, destination, ID, timeout)
这里参数不再介绍
def receiveOnePing(icmpSocket, destinationAddress, ID, timeout): # 1. Wait for the socket to receive a reply timeBeginReceive = time.time() whatReady = select.select([icmpSocket], [], [], timeout) timeInRecev = time.time() - timeBeginReceive if not whatReady[0]: print("none") return -1 # 2. Once received, record time of receipt, otherwise, handle a timeout recPacket, addr = icmpSocket.recvfrom(1024) timeReceived = time.time() # 3. Compare the time of receipt to time of sending, producing the total network delay byte_in_double = struct.calcsize("!d") timeSent = struct.unpack("!d", recPacket[28: 28 + byte_in_double])[0] totalDelay = timeReceived - timeSent # 4. Unpack the packet header for useful information, including the ID rec_header = recPacket[20:28] replyType, replyCode, replyCkecksum, replyId, replySequence = struct.unpack('!bbHHh', rec_header) # 5. Check that the ID matches between the request and reply if ID == replyId and replyType == ICMP_ECHO_REPLY: # 6. Return total network delay return totalDelay if timeInRecev > timeout: print('overtime') return -1
内容简介:
在这里我们统一规定如果成功接收了就返回delay(时延),如果没有就返回-1(也可以是其他的自定义数值,只要能区分就可以)
select.select函数自行了解:whatReady[0] 用于判断是否接收到回显应答,返回true/false,应答不为空就是成功(继续计算时延),否则就是失败(直接返回-1跳出)
其中的timeInRecev用于判断超时
我们在一开始就说了,IPHeader为20bytes,所以ICMPHeader应该从20开始截取(str[20:28]为ICMP_Header部分)
获取发送时间的那一部分中涉及到了struct.calcsize()函数,可以看这个链接中的内容做基本了解:https://blog.51cto.com/firefish/112690:因为unpack函数解码的内容至少要是8bytes,这个函数可以考虑为占位用的
7. 完整代码
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import os import struct import time import select import socket ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST = 8 # ICMP type code for echo request messages ICMP_ECHO_REPLY = 0 # ICMP type code for echo reply messages ICMP_Type_Unreachable = 11 # unacceptable host ICMP_Type_Overtime = 3 # request overtime ID = 0 # ID of icmp_header SEQUENCE = 0 # sequence of ping_request_msg def checksum(strings): csum = 0 countTo = (len(strings) / 2) * 2 count = 0 while count < countTo: thisVal = strings[count + 1] * 256 + strings[count] csum = csum + thisVal csum = csum & 0xffffffff count = count + 2 if countTo < len(strings): csum = csum + strings[len(strings) - 1] csum = csum & 0xffffffff csum = (csum >> 16) + (csum & 0xffff) csum = csum + (csum >> 16) answer = ~csum answer = answer & 0xffff answer = answer >> 8 | (answer << 8 & 0xff00) return answer def receiveOnePing(icmpSocket, ID, timeout): # 1. Wait for the socket to receive a reply timeBeginReceive = time.time() whatReady = select.select([icmpSocket], [], [], timeout) timeInRecev = time.time() - timeBeginReceive if not whatReady[0]: return -1 timeReceived = time.time() # 2. Once received, record time of receipt, otherwise, handle a timeout recPacket, addr = icmpSocket.recvfrom(1024) # 3. Compare the time of receipt to time of sending, producing the total network delay byte_in_double = struct.calcsize("!d") timeSent = struct.unpack("!d", recPacket[28: 28 + byte_in_double])[0] totalDelay = timeReceived - timeSent # 4. Unpack the packet header for useful information, including the ID rec_header = recPacket[20:28] replyType, replyCode, replyCkecksum, replyId, replySequence = struct.unpack('!bbHHh', rec_header) # 5. Check that the ID matches between the request and reply if ID == replyId and replyType == ICMP_ECHO_REPLY: # 6. Return total network delay return totalDelay elif timeInRecev > timeout or replyType == ICMP_Type_Overtime: return -3 # ttl overtime/timeout elif replyType == ICMP_Type_Unreachable: return -11 # unreachable else: print("request over time") return -1 def sendOnePing(icmpSocket, destinationAddress, ID): icmp_checksum = 0 # 1. Build ICMP header icmp_header = struct.pack('!bbHHh', ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST, 0, icmp_checksum, ID, SEQUENCE) time_send = struct.pack('!d', time.time()) # 2. Checksum ICMP packet using given function icmp_checksum = checksum(icmp_header + time_send) # 3. Insert checksum into packet icmp_header = struct.pack('!bbHHh', ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST, 0, icmp_checksum, ID, SEQUENCE) # 4. Send packet using socket icmp_packet = icmp_header + time_send icmpSocket.sendto(icmp_packet, (destinationAddress, 80)) def doOnePing(destinationAddress, timeout): # 1. Create ICMP socket icmpName = socket.getprotobyname('icmp') icmp_Socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_RAW, icmpName) # 2. Call sendOnePing function sendOnePing(icmp_Socket, destinationAddress, ID) # 3. Call receiveOnePing function totalDelay = receiveOnePing(icmp_Socket, ID, timeout) # 4. Close ICMP socket icmp_Socket.close() # 5. Return total network delay return totalDelay def ping(host, count, timeout): send = 0 lost = 0 receive = 0 maxTime = 0 minTime = 1000 sumTime = 0 # 1. Look up hostname, resolving it to an IP address desIp = socket.gethostbyname(host) global ID ID = os.getpid() for i in range(0, count): global SEQUENCE SEQUENCE = i # 2. Call doOnePing function, approximately every second delay = doOnePing(desIp, timeout) * 1000 send += 1 if delay > 0: receive += 1 if maxTime < delay: maxTime = delay if minTime > delay: minTime = delay sumTime += delay # 3. Print out the returned delay print("Receive from: " + str(desIp) + ", delay = " + str(int(delay)) + "ms") else: lost += 1 print("Fail to connect. ", end="") if delay == -11: # type = 11, target unreachable print("Target net/host/port/protocol is unreachable.") elif delay == -3: # type = 3, ttl overtime print("Request overtime.") else: # otherwise, overtime print("Request overtime.") time.sleep(1) # 4. Continue this process until stopped if receive != 0: avgTime = sumTime / receive recvRate = receive / send * 100.0 print( " Send: {0}, success: {1}, lost: {2}, rate of success: {3}%.".format(send, receive, lost, recvRate)) print( "MaxTime = {0}ms, MinTime = {1}ms, AvgTime = {2}ms".format(int(maxTime), int(minTime), int(avgTime))) else: print(" Send: {0}, success: {1}, lost: {2}, rate of success: 0.0%".format(send, receive, lost)) if __name__ == '__main__': while True: try: hostName = input("Input ip/name of the host you want: ") count = int(input("How many times you want to detect: ")) timeout = int(input("Input timeout: ")) ping(hostName, count, timeout) break except Exception as e: print(e) continue
8. 写在最后
写的时候翻了不少文章,但是都找不到了,只有这个离写这篇文章的时间最近,就贴上来