OpenAPI规范是描述API功能的文档,该文档的的信息基于控制器和模型中的XML属性注释。它也是OpenAPI流的核心部分,用于驱动SwaggerUI之类的工具。一般命名为openapi.json
下面是为简洁起见而缩减的 OpenAPI 规范的示例:
{ "openapi": "3.0.1", "info": { "title": "API V1", "version": "v1" }, "paths": { "/api/Todo": { "get": { "tags": [ "Todo" ], "operationId": "ApiTodoGet", "responses": { "200": { "description": "Success", "content": { "text/plain": { "schema": { "type": "array", "items": { "$ref": "#/components/schemas/ToDoItem" } } }, "application/json": { "schema": { "type": "array", "items": { "$ref": "#/components/schemas/ToDoItem" } } }, "text/json": { "schema": { "type": "array", "items": { "$ref": "#/components/schemas/ToDoItem" } } } } } } }, "post": { … } }, "/api/Todo/{id}": { "get": { … }, "put": { … }, "delete": { … } } }, "components": { "schemas": { "ToDoItem": { "type": "object", "properties": { "id": { "type": "integer", "format": "int32" }, "name": { "type": "string", "nullable": true }, "isCompleted": { "type": "boolean" } }, "additionalProperties": false } } } }
SwaggerUI 提供了基于 Web 的 UI,它使用生成的 OpenAPI 规范提供有关服务的信息。
Swashbuckle 有三个主要组成部分:
- Swagger: 将 SwaggerDocument 对象公开为 Json 终结点的Swagger对象模型和中间件。以便于我们对文档内容的设置,和中间件的调用。
- SwaggerGen:从路由、控制器和模型直接生成 SwaggerDocument 对象的 Swagger 生成器。 它通常与 Swagger 终结点中间件结合,以自动公开 Swagger JSON。 这样我们在编写API时,Swagger便会自动识别我们的API并加入SwaggerDocument。公开到UI。
- SwaggerUI:Swagger UI 工具的嵌入式版本。它解释了Swagger Json文档来生成具有我们描述性的Web API,还具有对公共方法的内置测试工具。
我们引入NuGet工具包时,选择最新的“Swashbuckle.AspNetCore”包。然后配置Swagger中间件和服务:
中间件:
我们需要添加Swagger中间件将SwaggerDocument文档暴露出,然后使用SwaggerUI中间件解释 SwaggerDocument 来生成具有描述性的Web API,并指定我们要暴露的 Swagger Json endpoint。
注意UseSwaggerUI方法调用启用了UseStaticFile中间件。在一些 UseStaticFile 会影响的中间件出现时,需要考虑中间件的引用顺序。
所以大概是这个样子:
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseStatciFile(); //useSwaggerUI自动引入 app.UseSwaggerUI(options => { //暴露Json文档终结点 options.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/v1/swagger.json", "Api V1");
}); app.UseRouting(); app.UseAuthorization(); app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => { endpoints.MapControllers(); });
可在 http://localhost:<port>/swagger 找到 Swagger UI。 通过 Swagger UI 浏览 API。要在应用的根 (http://localhost:<port>/) 处提供 Swagger UI,请将 RoutePrefix 属性设置为空字符串:
app.UseSwaggerUI(c => { c.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/v1/swagger.json", "My API V1"); c.RoutePrefix = string.Empty; });
服务:
将SwaggerGen注册在服务中,便可以将控制器的公共方法和模型的信息生成到SwaggerDocument中以便于暴露至Web UI,另外我们可以额外的指定信息:
传递给 AddSwaggerGen 方法的配置操作会添加诸如作者、许可证和说明的信息:使用 OpenApiInfo 类修改 UI 中显示的信息:
services.AddSwaggerGen(c => { c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new OpenApiInfo() { Version = "v1", Title = "Xieyi API", Description = "xieyi's simple example ASP.NET Core Web API", TermsOfService = new Uri("https://www.baidu.com"), Contact = new OpenApiContact { Name = "Zhou Xieyi", Email = "zhouxieyi@qq.com", Url = new Uri("https://www.sina.com.cn") }, License = new OpenApiLicense { Name = "Go to Learn Swashbuckle", Url = new Uri("https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/tutorials/getting-started-with-swashbuckle?view=aspnetcore-5.0&tabs=visual-studio") } });
});
效果展示:

启用XML注释,反射用于生成与 Web API 项目相匹配的 XML 文件名。 AppContext.BaseDirectory属性用于构造 XML 文件的路径。 一些 Swagger 功能(例如,输入参数的架构,或各自属性中的 HTTP 方法和响应代码)无需使用 XML 文档文件即可起作用。
var xmlFile = $"{Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Name}.xml"; var xmlPath = Path.Combine(AppContext.BaseDirectory, xmlFile); c.IncludeXmlComments(xmlPath);
Tips:若启动时,出现不能发现XML文档,则是没有生成,检查此处。项目属性中。
对于大多数功能(即方法摘要以及参数说明和响应代码说明),必须使用 XML 文件。

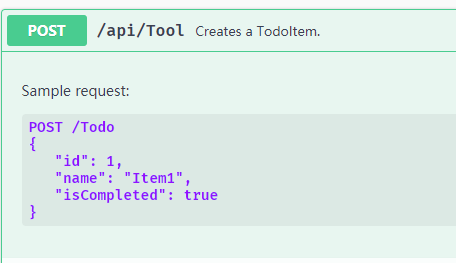
<remarks> 元素可提供我们自定义的指定信息,提供更加可靠的Swagger UI,比如我们认为POST方法中ExameValue不够具体,我们可以自定义我们的备注提供给SwaggerUI:
/// <summary> /// Creates a TodoItem. /// </summary> /// <remarks> /// Sample request: /// /// POST /Todo /// { /// "id": 1, /// "name": "Item1", /// "isCompleted": true /// } /// </remarks> /// <param name="item">model to add</param> /// <returns></returns>
效果图:
我们可以对模型进行必填特性来改变Json中的架构,并可以自定义规定响应内容类型:
[Produces("application/json")] [Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class TodoController : ControllerBase { private readonly TodoContext _context;
描述响应类型:
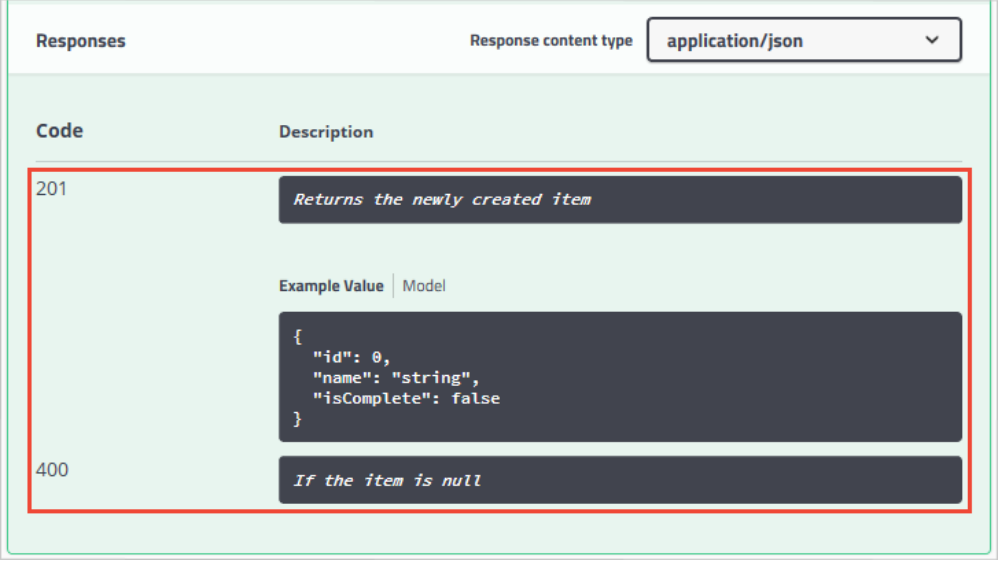
在我们进行POST操作时,通常会判断模型是否为null,若为null则返回400,但文档描述中可能只有我们返回的200状态码,那么就会使使用者对我们的API描述不够全面。我们可以自己规定响应类型和错误代码。
/// <summary> /// Creates a TodoItem. /// </summary> /// <remarks> /// Sample request: /// /// POST /Todo /// { /// "id": 1, /// "name": "Item1", /// "isComplete": true /// } /// /// </remarks> /// <param name="item"></param> /// <returns>A newly created TodoItem</returns> /// <response code="201">Returns the newly created item</response> /// <response code="400">If the item is null</response> [HttpPost] [ProducesResponseType(StatusCodes.Status201Created)] [ProducesResponseType(StatusCodes.Status400BadRequest)] public ActionResult<TodoItem> Create(TodoItem item) { _context.TodoItems.Add(item); _context.SaveChanges(); return CreatedAtRoute("GetTodo", new { id = item.Id }, item); }
Swagger UI 现在清楚地记录预期的 HTTP 响应代码: