1,上TI官网下载CDCE913的datasheet和配置软件clock Pro。如果只需要配置CDCE913成某一个固定频率,那么用clock Pro可以很方便快捷。http://www.ti.com.cn/general/cn/docs/lit/getliterature.tsp?baseLiteratureNumber=scac119&fileType=zip
TI的初衷应该就是通过I2C配置几个频率,然后写入到EEPROM中,不然没有必要设计EEPROM和频率选择PIN(S1,S2)。
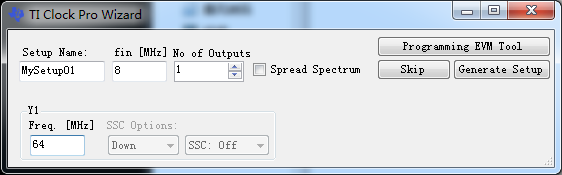
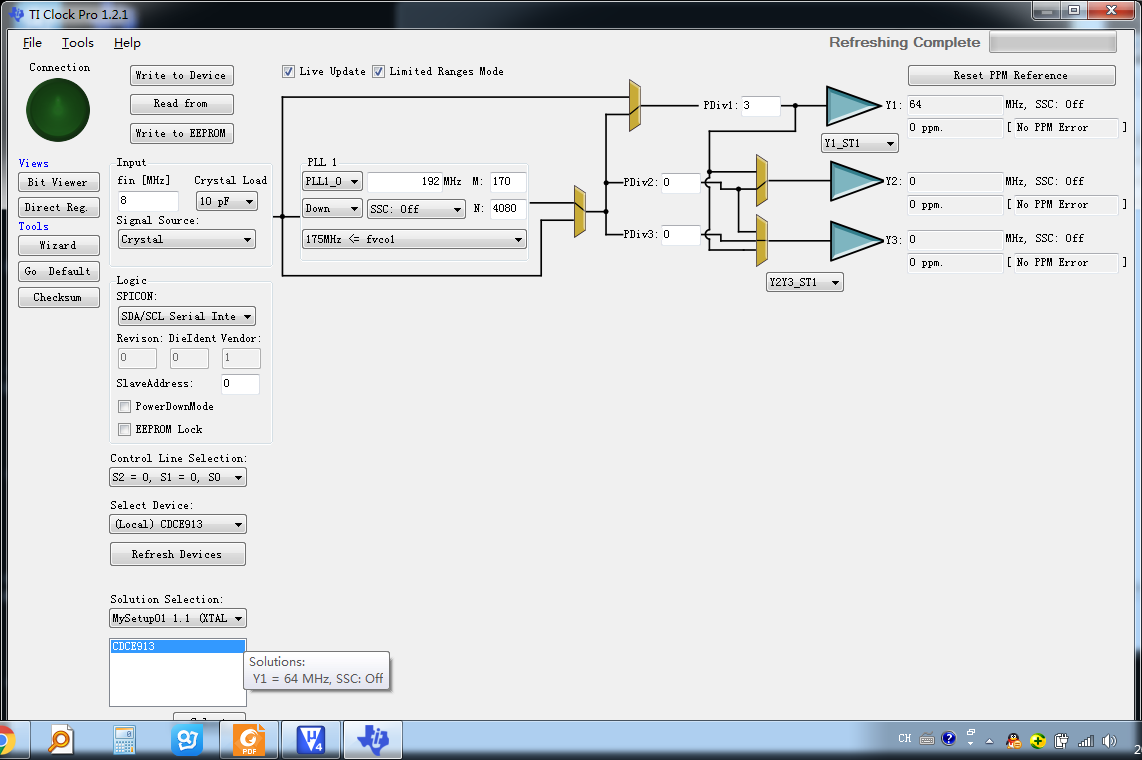
该软件产生的配置文件是二进制的csv或者txt文档,导入到Excel中处理成16进制即可。或者直接手动填写,反正也就20来个寄存器。
2,如需要在程序运行过程中动态的配置成不同的频率,那么你需要通过I2C接口配置。CDCE913的器件地址如下:
#define CDCE_ADDRESS 0x65
#define SLAVE_WRITE CDCE_ADDRESS<<1
#define SLAVE_READ ((CDCE_ADDRESS<<1) | 0x01)
3,了解一下配置原理
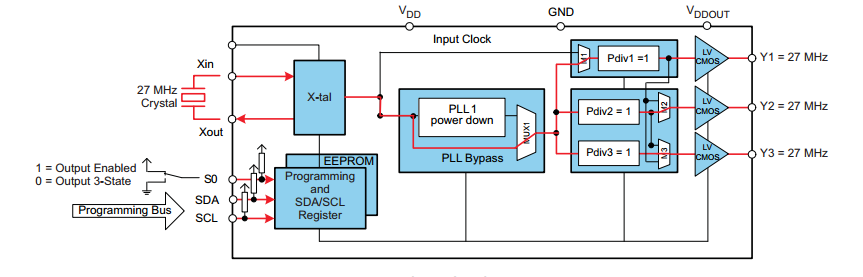
可以看到Y1,Y2,Y3都可以从PLL1配置,然后进过M(M1,M2,M3),Pdiv出来。寄存器配置完成后,需要拉高S0,才能使能输出。
4,查看datasheet,配置PLL需要配置以下参数
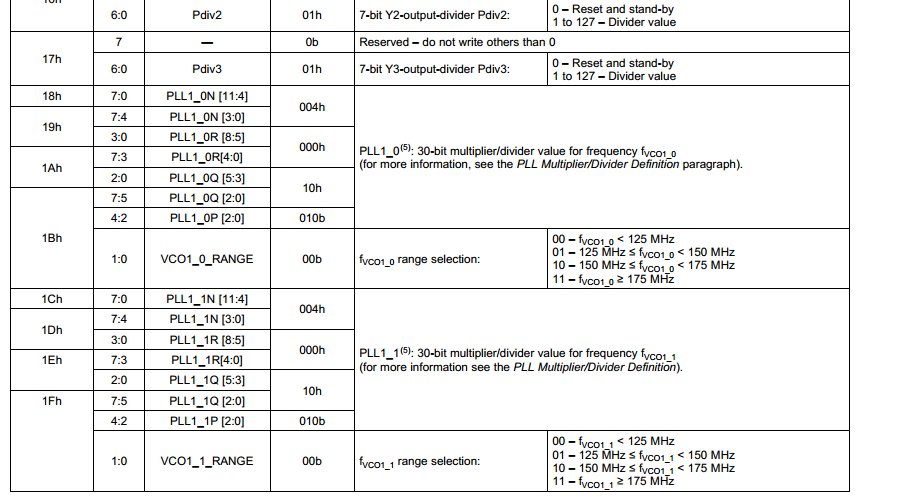
计算方法如下:

公式略微有点复杂。下面代码以配置Y1输出为例(输入晶振频率为8MHz,平台为STM32,I2C为软件模拟)。
#define CLK_IN 8
void CDCE_Init(uint16_t f_out)
{
uint8_t read_back;
uint8_t i = 1;
AckTypeDef ack;
uint32_t M, N, Pdiv, Q, R;
uint8_t reg18, reg19, reg1A, reg1B;
int P;
uint16_t f_vco = f_out;
bool result = false;
uint8_t f_range;
while (f_vco < 80)
{
i++;
f_vco = f_out * i;
}
while (f_vco < 231)
{
for (N = 4095; N > 0; N--)
{
for (M = 511; M > 0; M--)
{
if ((N * CLK_IN / M) == f_vco)
{
{
result = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (result)
{
break;
}
}
if (result)
{
break;
}
else
{
i++;
f_vco = f_out * i;
}
}
if (!result)
{
UserPrintf("Error:unsupport pclk
");
return;
}
P = 4 - (int)((log((double)N / (double)M))/log(2));
if (P < 0)
{
P = 0;
}
Q = (int)((double)N * pow(2, (double)P) / (double)M);
R = (double)N * pow(2, (double)P) - M * Q;
if (f_vco < 125)
{
f_range = 0;
}
else if ((f_vco >= 125) && (f_vco < 150))
{
f_range = 1;
}
else if ((f_vco >= 150) && (f_vco < 175))
{
f_range = 2;
}
else
{
f_range = 3;
}
S0 = 0;
ack = CDCE_Read8bit(0x00, 1, &read_back);
if (ack != I2C_ACK)
{
UserPrintf("Error:clk configuration failed , maybe no pullup res
");
return;
}
if (read_back != CDCE_ID)
{
UserPrintf("Error:clk device ID error
");
return;
}
Pdiv = f_vco / f_out;
UserPrintf("M:%d,N:%d,Pdiv:%d,f_vco:%d,P:%d,Q:%d,R:%d
", M, N, Pdiv,f_vco,P,Q, R);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x02, 0xB4);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x03, (uint8_t)Pdiv);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x04, 0x02);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x05, 0x00);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x06, 0x40);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x12, 0x00);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x13, 0x01);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x14, 0x6D);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x15, 0x02);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x16, 0);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x17, 0);
reg18 = (N >> 4) & 0xFFF;
reg19 = (N & 0xf) << 4 | (R & 0xf0) >> 5;
reg1A = (R & 0x1f) << 3 | ((Q >> 3) & 0x7);
reg1B = (Q & 0x7) << 5 | (P & 0x07) << 2 | (f_range & 0x03);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x18, reg18);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x19, reg19);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x1A, reg1A);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x1B, reg1B);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x1C, N);
CDCE_WriteByte(0x1D, ((N & 0xf) << 4) | (R & 0xf0));
CDCE_WriteByte(0x1E, (R & 0x0f) | (Q & 0xf0));
CDCE_WriteByte(0x1F, ((Q & 0x07) << 5) | ((P & 0x07) << 2) | (f_range & 0x03));
S0 = 1;
UserPrintf("Info:clk well configured
");
}