1.什么是系统编程?
程序员使用系统调用或者C语言本身所携带的库函数来设计和编写具有某一特定功能的程序。
2.什么是系统调用?与C语言函数库有什么区别?
系统调用是操作系统提供给程序员所使用的接口。
C语言的函数库封装了系统调用。
3.什么是文件访问权限?
就是你可以对这个文件做什么。如:读出数据,写入数据,执行它等。。。
在linux下有fchmod和chmod 两个函数可以修改文件访问权限
-int chmod(const char *path,mode_t mode);//mode 代表访问权限
-int fchmod(int fildes ,mode_T mode);
chmod 一文件名作为第一个参数
fchmod—以文件描述符作为第一个参数
- 参数mode 数值
| 字符常量值 |
对应的八进制数值 |
含义 |
| S_IRUSR |
00400 |
所有者可读取 |
| S_IWUSR |
00200 |
所有者可写入 |
| S_IXUSR |
00100 |
所有者可执行 |
| S_IRGRP |
00040 |
用户组可读取 |
| S_IWGRP |
00020 |
用户组可写入 |
| S_IXGRP |
00010 |
用户组可执行 |
| S_IROTH |
00004 |
其他人可读取 |
| S_IWOTH |
00002 |
其他人可写入 |
| S_IXOTH |
00001 |
其他人可执行 |
记忆方法:
- USR--用户
- GRP--用户组 (group 小组)
- OTH--其他人 (other 其他人)
以下是一个简化版的chmod 命令
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
int mode ;
int mode_u ;
int mode_g ;
int mode_o ;
char *path ;
if(argc < 3)
{
printf("Your input is wrong !!
");
exit(0) ;
}
mode= atoi(argv[1]) ;
if(mode > 777 || mode < 0)
{
printf("Your input is wrong !!
") ;
exit(0) ;
}
mode_u = mode /100 ;
mode_g = mode /10 % 10 ;
mode_o = mode %10 ;
mode = mode_u*8*8 + mode_g*8 +mode_o ;
path = argv[2] ;
if( chmod(path,mode)== -1)
{
printf("chmod error !!
") ;
exit (0) ;
}
return 0;
}
4.文件的创建与打开
linux下有open和creat两个函数可创建和打开文件。
1.open 函数
-int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
-int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);//flags 代表打开文件的方式
文件打开方式:
| 常量值 |
含义 |
| O_RDONLY |
只读方式打开 |
| O_WRONLY |
只写方式打开 |
| O_RDWR |
可读写方式打开 |
三种打开方式互斥,可与下列标志进行或运算
| 常量值 |
含义 |
| O_CREAT |
文件不存在,则自动新建该文件。此时才需要用到第三个参数,说明新文件的存取权限 |
| O_EXCL |
检查文件是否存在,不存在则新建,存在导致打开文件出错 |
| O_TRUNC |
如果文件存在,且以可写的方式打开时,将文件清零 |
| O_APPEND |
写入的数据会追加到文件后面 |
成功执行返回一个文件描述符,错误执行返回-1
2.creat 函数
- int creat(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
注意事项:
1.creat 顾名思义,不管存在不存在都建立新文件,若存在则新文件覆盖旧文件
2.creat只能以只写的方式打开所创建的文件
3.无法创建设备文件
5.文件的关闭
close 函数
- int close(int fd); //fd 代表文件描述符
成功执行返回0,错误执行返回-1
6.perror函数 与 strerror 的区别
概述:perror和strerror都是C语言提供的库函数,用于获取与erno相关的错误信息
| 函数 |
不同点 |
不同点 |
| perror |
perror向stderr输出结果 |
perror(“字符”) 先输出字符,再输出错误原因 |
| strerror |
strerror向stdout输出结果 |
strerror(errno) 将错误代码转换为错误原因(即人能看的懂的) |
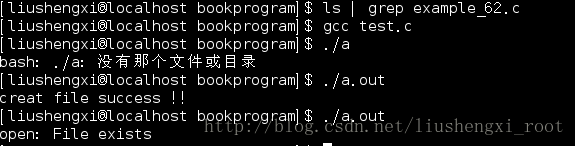
7.实例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int fd ;
if((fd=open("example_62.c" ,O_CREAT | O_EXCL ,S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR )) == -1) {
perror("open") ;
printf("open: %s with error :%d
",strerror(errno),errno);
exit(1) ;
}
else {
printf("creat file success !!
") ;
}
close(fd) ;
return 0;
}
运行结果如下: