总结:
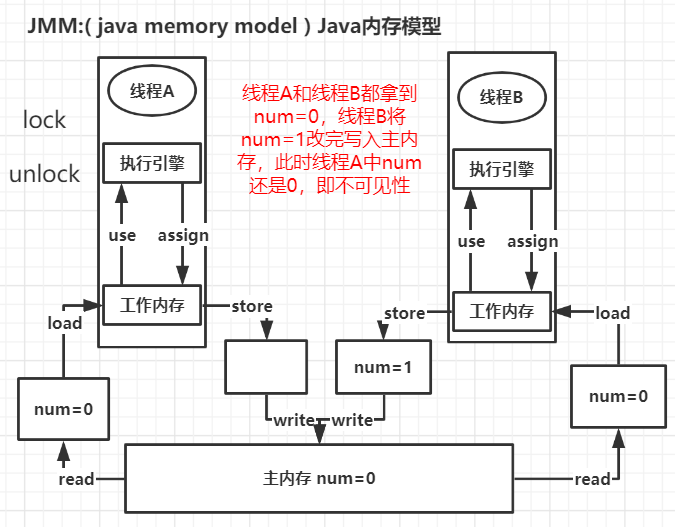
1、保证可见性(JMM)
2、不保证原子性 (核心难点:原子类)
3、禁止指令重排 (核心难点:说出单例模式。说出CAS。说出CPU原语)
1 // 验证volatile 可见性 2 public class JmmDemo { 3 private volatile static int num = 0; // 不加volatile,程序会一直运行 4 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 5 new Thread(() -> { 6 while (num==0){ 7 8 } 9 }).start(); 10 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1L); // 睡眠一秒钟,保证进入while循环 11 num = 1; 12 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+num); 13 } 14 }
1 // 验证volatile 不保证原子性 2 public class JmmDemo2 { 3 // 不用synchronized lock锁来保证原子性 4 // 使用AtomicInteger原子类 5 private static AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(); 6 7 public static void add() { 8 num.getAndIncrement(); // 相当于num++ 9 } 10 11 /* 12 // 验证volatile 不保证原子性 13 private static int num = 0; 14 // synchronized 15 public synchronized static void add() { 16 num++; 17 } 18 */ 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 // 期望 num 最终是2万 21 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 22 new Thread(() ->{ 23 for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) { 24 add(); 25 } 26 }).start(); 27 } 28 29 // 判断活着的线程 30 while (Thread.activeCount() > 2) { 31 Thread.yield(); 32 } 33 34 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ num); 35 } 36 }
1 // 指令重排理论 2 // int x = 1; // 1 3 // int y = 1; // 2 4 // x = x + 5; // 3 5 // y = x * x; // 4 6 // 可重排 1234 1324 2134 2314 3124 3214 7 // 4可能开头吗? 如4312. 8 // 不可能 因为处理器在重排的时候也会考虑指令间的依赖性 9 10 // 尝试理解多线程下的指令重排问题: 11 // int x,y,a,b = 0; 12 // 线程A 线程B 13 // x = a; y = b; 14 // b = 1; a = 2; 15 // 理想的结果下x = 0, y = 0 16 17 // 指令重排后 18 // 线程A 线程B 19 // b = 1; a = 2; 20 // x = a; y = b; 21 // 重排后的结果:x = 2,y = 1 22 23 // volatile可以禁止指令重排 24 // 内存屏障 :CPU指令 两个作用: 25 // 1、保证特定的执行顺序 26 // 2、保证某些变量的内存可见性 27 28 // 普通写 29 // 普通读 30 // ---------------------内存屏障,禁止上面普通写与volatile读指令重排 31 // volatile读 32 // ---------------------内存屏障,禁止下面普通写与volatile读指令重排 33 // 普通写 34 // 普通读 35 // 指令重排的最经典应用 DCL单例模式 DCL双重检测锁 36 // 单例的思想: 构造器私有 37 // 单例之所以安全,是因为构造器私有的!
单例模式:
1 // 单例的思想: 构造器私有 2 // 饿汉式 3 public class Hungry { 4 // 浪费空间 5 private byte[] data = new byte[10*1024*1024]; 6 7 private Hungry(){} 8 9 private final static Hungry HUNGRY = new Hungry(); 10 11 public static Hungry getInstance() { 12 return HUNGRY; 13 } 14 }
1 // 懒汉式 (基础的) 2 public class LazyMan { 3 private LazyMan(){ 4 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"__测试"); 5 } 6 7 private static LazyMan lazyMan; 8 9 public static LazyMan getInstance(){ 10 if (lazyMan == null) { 11 lazyMan = new LazyMan(); 12 } 13 return lazyMan; 14 } 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 new Thread(() -> { 18 LazyMan.getInstance(); 19 }).start(); 20 21 // 多线程下单例失效 22 /*for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 23 new Thread(() -> { 24 LazyMan.getInstance(); 25 }).start(); 26 }*/ 27 } 28 }
1 // DCL懒汉式 2 public class DclLazyMan { 3 4 // 防止反射破环单例 5 private static boolean ahsdkhaskhdkahksh = false; 6 private DclLazyMan() { 7 synchronized (DclLazyMan.class){ 8 if (ahsdkhaskhdkahksh == false) { 9 ahsdkhaskhdkahksh = true; 10 } else { 11 throw new RuntimeException("不要想破坏我的单例"); 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 private volatile static DclLazyMan dclLazyMan; 16 17 public static DclLazyMan getInstance() { 18 if (dclLazyMan == null) { 19 synchronized (DclLazyMan.class) { 20 if (dclLazyMan == null) { 21 dclLazyMan = new DclLazyMan();// 这个操作是不是原子性的? 不是 22 // java创建一个对象 23 // 1、分配内存空间 24 // 2、执行构造方法,创建对象 25 // 3、将对象指向空间 26 27 // A 先执行13,这个时候对象还没有完成初始化! 28 // B 发现对象为空,B线程拿到的对象就不是完整的 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 return dclLazyMan; 33 } 34 35 public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException { 36 /* 37 // 经过构造器 38 DclLazyMan dclLazyMan1 = DclLazyMan.getInstance(); 39 40 // 利用反射,不经过构造器破坏单例 41 Constructor<DclLazyMan> constructor = DclLazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(); 42 DclLazyMan dclLazyMan2 = constructor.newInstance(); 43 44 System.out.println(dclLazyMan1.hashCode()); 45 System.out.println(dclLazyMan2.hashCode()); 46 */ 47 48 Constructor<DclLazyMan> constructor = DclLazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(); 49 constructor.setAccessible(true); 50 DclLazyMan dclLazyMan2 = constructor.newInstance();// 创建对象 51 52 // 利用编译的.class文件拿到ahsdkhaskhdkahksh 53 // 单例再次被破坏 54 Field ahsdkhaskhdkahksh = DclLazyMan.class.getDeclaredField("ahsdkhaskhdkahksh"); 55 ahsdkhaskhdkahksh.setAccessible(true); 56 ahsdkhaskhdkahksh.set(dclLazyMan2,false); 57 58 System.out.println(dclLazyMan2.hashCode()); 59 60 } 61 }
1 // enum类型 2 public enum SingleEnum { 3 INSTANCE; 4 public SingleEnum getInstance(){ 5 return INSTANCE; 6 } 7 } 8 // 至少在做一个普通的JVM时候,jdk源码没有被修改的时候,枚举就是安全的! 9 class Demo{ 10 public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, 11 InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException { 12 13 // String.class,int.class 14 // 利用jad.exe反编译.class文件,发现反编译出的.java文件中没有无参构造器 15 Constructor<SingleEnum> declaredConstructor = SingleEnum.class.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class); 16 declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); 17 // throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot reflectively create enum objects"); 18 SingleEnum singleEnum1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); 19 SingleEnum singleEnum2 = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); 20 System.out.println(singleEnum1.hashCode()); 21 System.out.println(singleEnum2.hashCode()); 22 23 // 这里面没有无参构造! JVM 才是王道! 24 // "main" java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: com.coding.single.SingleEnum.<init>() 25 } 26 }
CAS :(Compare and swap) 比较并交换
缺点:
- 循环开销很大
- 内存操作,每次只能保证一个共享变量的原子性
- 出现ABA问题
1 // CAS :(Compare and swap) 比较并交换 2 public class CAS_Demo { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 // 默认值为0 5 AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(5); 6 7 // 期望值5,改为20 8 System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(5, 20)); 9 System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); 10 11 // 期望值为5,改为6 12 System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(5, 6)); 13 System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); 14 } 15 16 //---------------------------------------------------------------- 17 18 // private static AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(); 19 // public static void add() { 20 // num.getAndIncrement(); // 相当于num++ 21 // } 22 23 // 以getAndIncrement()分析理解 CAS 24 25 // 源码 26 // public final int getAndIncrement() { 27 // unsafe 可以直接操作内存 28 // this 调用的对象 29 // valueOffset 当前这个对象的值内存地址偏移值 30 // 1 +1 31 // return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, 1); 32 // } 33 // 34 // public final int getAndAddInt(Object var1, long var2, int var4) { 35 // int var5; //? 36 // do { // 自旋锁(就是一只判断!) 37 // var5 = 获得当前对象的内存地址中的值! 38 // var1 等于上面的this 39 // var2 等于上面的valueOffset 40 // var5 = this.getIntVolatile(var1, var2); 41 // compareAndSwapInt 比较并交换 42 // 比较当前的值var1 对象的var2 地址中的值是不是var5,如果是,则更新为var5+1(var4) 43 // 如果是期望的值,就交换,否则就不交换 44 // } while(!this.compareAndSwapInt(var1, var2, var5, var5 + var4)); 45 // 46 // return var5; 47 // } 48 }
原子引用----解决ABA问题
1 // 原子引用----解决ABA问题 2 // 通过增加一个版本号来解决,和乐观锁一模一样 3 4 // ABA问题描述: 5 // T1 将A 改为 B 再改为 A 数据已经被修改过两次 6 // T2 再来操作A 但是A不是当初的A了 因为数据被改过了两次 7 public class ABA_Demo { 8 // 设置初始版本为1 9 static AtomicStampedReference<Integer> asf = new AtomicStampedReference<>(100,1); 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // 线程T1 13 new Thread(() -> { 14 // 获得当前版本 15 int stamp = asf.getStamp(); 16 System.out.println("T1当前版本:"+stamp); 17 try { 18 // 睡眠1秒 待T2拿到stamp 19 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1L); 20 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 // 即 A 改为 B 24 asf.compareAndSet(100,101,asf.getStamp(),asf.getStamp()+1); 25 System.out.println("T1 当前版本:"+asf.getStamp()); 26 System.out.println("T1 当前获得的最新值:"+asf.getReference()); 27 // 即 B 改为 A 28 asf.compareAndSet(101,100,asf.getStamp(),asf.getStamp()+1); 29 System.out.println("T1 当前版本:"+asf.getStamp()); 30 System.out.println("T1 当前获得的最新值:"+asf.getReference()); 31 32 },"T1").start(); 33 34 // 线程T2 35 new Thread(() -> { 36 // 获得当前版本 37 int stamp = asf.getStamp(); 38 System.out.println("T2当前版本:"+stamp); 39 try { 40 // 睡眠2秒,待T1执行完 41 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2L); 42 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 // 即 A 改为 B 46 boolean result = asf.compareAndSet(100, 101, stamp, stamp + 1); 47 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"是否修改成功:"+result); 48 System.out.println("T2 当前版本:"+asf.getStamp()); 49 System.out.println("T2 当前获得的最新值:"+asf.getReference()); 50 },"T2").start(); 51 } 52 }