广度优先搜索算法(Breadth-First-Search,BFS),又称作宽度优先搜索。BFS算法是从根节点开始,沿着树的宽度遍历树的节点。如果所有节点均被访问,则算法中止。
算法思想
1、首先将根节点放入队列中。
2、从队列中取出第一个节点,并检验它是否为目标。
- 如果找到目标,则结束搜索并回传结果。
- 否则将它所有尚未检验过的直接子节点加入队列中。
3、若队列为空,表示整张图都检查过了——亦即图中没有欲搜索的目标。结束搜索并回传“找不到目标”。
4、重复步骤2。
搜索过程演示
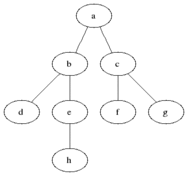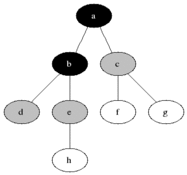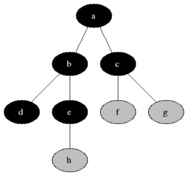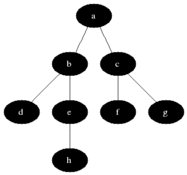
说明
-
灰色的是加入队列中的活动节点,黑色是从活动节点队列中选取的扩展节点。
-
每次将一个活动节点标记为扩展节点后,进行判断,并将该点从活动节点队列中移除,再将该节点所有未检测的子节点加入活动节点队列中去。
-
接下来再从队列中选取新的活动节点作为扩展节点,如此循环下去,直至队列为空为止,说明已经遍历过所有的节点。
复杂度
-
因为所有节点都必须被存储,因此BFS的空间复杂度为 O(|V|+|E|),其中 |V| 是节点的数目,而 |E| 是图中边的数目。
-
最差情形下,BFS必须查找所有到可能节点的所有路径,因此其时间复杂度为 O(|V|+|E|)。
C++实现
//Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
//The minimum depth is the number of nodes along
//the shortest path from the root node down to
//the nearest leaf node.
// 递归方法
class Solution
{
public:
int run(TreeNode *root)
{
if (!root)
{
return 0;
}
// 若左子树为空,返回右子树深度 + 1
if (root->left == nullptr)
{
return (run(root->right) + 1);
}
// 若右子树为空,返回左子树深度 + 1
if (root->right == nullptr)
{
return (run(root->left) + 1);
}
// 左右子树都不为空,返回较小值
int leftDepth = run(root->left);
int rightDepth = run(root->right);
return ((leftDepth < rightDepth) ? (leftDepth + 1) : (rightDepth + 1));
}
};
// BFS方法
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int run(TreeNode *root)
{
if (!root)
{
return 0;
}
vector <TreeNode *> que;
TreeNode *now = root; // 当前访问的节点
TreeNode *last = root; // 每层最后的一个节点
que.push_back(root);
int depth = 1; // 初始深度
while (que.size())
{
// 取出队列中的第一个节点作为当前节点
now = que.front();
que.erase(que.begin());
// 如果当前节点没有子节点了,直接终止循环,说明是叶子节点,返回最小深度
if ((now->left == nullptr) && (now->right == nullptr))
{
break;
}
// 将子节点加入队列中
if (now->left != nullptr)
{
que.push_back(now->left);
}
if (now->right != nullptr)
{
que.push_back(now->right);
}
// 当访问到每层的最后一个节点时,深度+1
if (now == last)
{
depth++;
last = que.back(); // 将下一层最后一个节点赋给last
}
}
return depth;
}
};