1.运行时异常 是指编译器不要求强制处置的异常。一般是指编程时的逻辑错误,是程序 员应该积极避免其出现的异常。java.lang.RuntimeException类及它的子 类都是运行时异常。 对于这类异常,可以不作处理,因为这类异常很普遍,若全处理可能会对 程序的可读性和运行效率产生影响。 2.编译时异常 是指编译器要求必须处置的异常。即程序在运行时由于外界因素造成的一 般性异常。编译器要求Java程序必须捕获或声明所有编译时异常。 对于这类异常,如果程序不处理,可能会带来意想不到的结果。
常见异常
java.lang.RuntimeException
ClassCastException
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
NullPointerException
ArithmeticException
NumberFormatException
InputMismatchException
。。。
java.io.IOExeption
FileNotFoundException
EOFException
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
java.lang.InterruptedException
java.io.FileNotFoundException
java.sql.SQLException
package com.atguigu.java; /* * Error: * Java虚拟机无法解决的严重问题。如:JVM系统内部错误、资源耗尽等严重情况。比如:StackOverflowError和OOM。 * * 一般不编写针对性的代码进行处理。 * * */ public class ErrorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.栈溢出:java.lang.StackOverflowError // main(args); //2.堆溢出:java.lang.OutOfMemoryError Integer[] arr = new Integer[1024*1024*1024]; } }
package com.atguigu.java1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Scanner; import org.junit.Test; /* * 一、异常体系结构 * * java.lang.Throwable * |-----java.lang.Error:一般不编写针对性的代码进行处理。 * |-----java.lang.Exception:可以进行异常的处理 * |------编译时异常(checked) * |-----IOException * |-----FileNotFoundException * |-----ClassNotFoundException * |------运行时异常(unchecked,RuntimeException) * |-----NullPointerException * |-----ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException * |-----ClassCastException * |-----NumberFormatException * |-----InputMismatchException * |-----ArithmeticException * * * * 面试题:常见的异常都有哪些?举例说明 */ public class ExceptionTest { //******************以下是编译时异常*************************** @Test public void test7(){ // File file = new File("hello.txt"); // FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); // // int data = fis.read(); // while(data != -1){ // System.out.print((char)data); // data = fis.read(); // } // // fis.close(); } //******************以下是运行时异常*************************** //ArithmeticException @Test public void test6(){ int a = 10; int b = 0; System.out.println(a / b); } //InputMismatchException @Test public void test5(){ Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); int score = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.println(score); scanner.close(); } //NumberFormatException @Test public void test4(){ String str = "123"; str = "abc"; int num = Integer.parseInt(str); } //ClassCastException @Test public void test3(){ Object obj = new Date(); String str = (String)obj; } //IndexOutOfBoundsException @Test public void test2(){ //ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException // int[] arr = new int[10]; // System.out.println(arr[10]); //StringIndexOutOfBoundsException String str = "abc"; System.out.println(str.charAt(3)); } //NullPointerException @Test public void test1(){ // int[] arr = null; // System.out.println(arr[3]); String str = "abc"; str = null; System.out.println(str.charAt(0)); } }
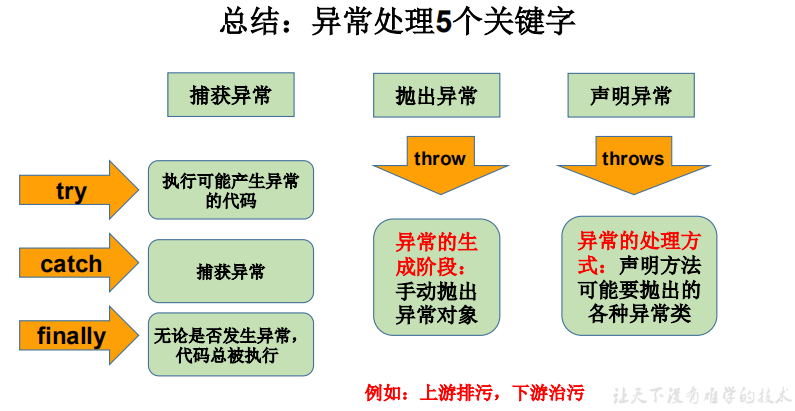
Java异常处理的方式:
方式一:try-catch-finally
方式二:throws + 异常类型
package com.atguigu.java1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import org.junit.Test; /* * 一、异常的处理:抓抛模型 * * 过程一:"抛":程序在正常执行的过程中,一旦出现异常,就会在异常代码处生成一个对应异常类的对象。 * 并将此对象抛出。 * 一旦抛出对象以后,其后的代码就不再执行。 * * 关于异常对象的产生:① 系统自动生成的异常对象 * ② 手动的生成一个异常对象,并抛出(throw) * * 过程二:"抓":可以理解为异常的处理方式:① try-catch-finally ② throws * * * 二、try-catch-finally的使用 * * try{ * //可能出现异常的代码 * * }catch(异常类型1 变量名1){ * //处理异常的方式1 * }catch(异常类型2 变量名2){ * //处理异常的方式2 * }catch(异常类型3 变量名3){ * //处理异常的方式3 * } * .... * finally{ * //一定会执行的代码 * } * * 说明: * 1. finally是可选的。 * 2. 使用try将可能出现异常代码包装起来,在执行过程中,一旦出现异常,就会生成一个对应异常类的对象,根据此对象 * 的类型,去catch中进行匹配 * 3. 一旦try中的异常对象匹配到某一个catch时,就进入catch中进行异常的处理。一旦处理完成,就跳出当前的 * try-catch结构(在没有写finally的情况)。继续执行其后的代码 * 4. catch中的异常类型如果没有子父类关系,则谁声明在上,谁声明在下无所谓。 * catch中的异常类型如果满足子父类关系,则要求子类一定声明在父类的上面。否则,报错 * 5. 常用的异常对象处理的方式: ① String getMessage() ② printStackTrace() * 6. 在try结构中声明的变量,再出了try结构以后,就不能再被调用 * 7. try-catch-finally结构可以嵌套 * * 体会1:使用try-catch-finally处理编译时异常,是得程序在编译时就不再报错,但是运行时仍可能报错。 * 相当于我们使用try-catch-finally将一个编译时可能出现的异常,延迟到运行时出现。 * * 体会2:开发中,由于运行时异常比较常见,所以我们通常就不针对运行时异常编写try-catch-finally了。 * 针对于编译时异常,我们说一定要考虑异常的处理。 */ public class ExceptionTest1 { @Test public void test2(){ try{ File file = new File("hello.txt"); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); int data = fis.read(); while(data != -1){ System.out.print((char)data); data = fis.read(); } fis.close(); }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void test1(){ String str = "123"; str = "abc"; int num = 0; try{ num = Integer.parseInt(str); System.out.println("hello-----1"); }catch(NumberFormatException e){ // System.out.println("出现数值转换异常了,不要着急...."); //String getMessage(): // System.out.println(e.getMessage()); //printStackTrace(): e.printStackTrace(); }catch(NullPointerException e){ System.out.println("出现空指针异常了,不要着急...."); }catch(Exception e){ System.out.println("出现异常了,不要着急...."); } System.out.println(num); System.out.println("hello-----2"); } }
package com.atguigu.java1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import org.junit.Test; /* * try-catch-finally中finally的使用: * * * 1.finally是可选的 * * 2.finally中声明的是一定会被执行的代码。即使catch中又出现异常了,try中有return语句,catch中有 * return语句等情况。 * * 3.像数据库连接、输入输出流、网络编程Socket等资源,JVM是不能自动的回收的,我们需要自己手动的进行资源的 * 释放。此时的资源释放,就需要声明在finally中。 * * * */ public class FinallyTest { @Test public void test2(){ FileInputStream fis = null; try { File file = new File("hello1.txt"); fis = new FileInputStream(file); int data = fis.read(); while(data != -1){ System.out.print((char)data); data = fis.read(); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { if(fis != null) fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } @Test public void testMethod(){ int num = method(); System.out.println(num); } public int method(){ try{ int[] arr = new int[10]; System.out.println(arr[10]); return 1; }catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ e.printStackTrace(); return 2; }finally{ System.out.println("我一定会被执行"); return 3; } } @Test public void test1(){ try{ int a = 10; int b = 0; System.out.println(a / b); }catch(ArithmeticException e){ e.printStackTrace(); // int[] arr = new int[10]; // System.out.println(arr[10]); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } // System.out.println("我好帅啊!!!~~"); finally{ System.out.println("我好帅啊~~"); } } }
package com.atguigu.java1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; /* * 异常处理的方式二:throws + 异常类型 * * 1. "throws + 异常类型"写在方法的声明处。指明此方法执行时,可能会抛出的异常类型。 * 一旦当方法体执行时,出现异常,仍会在异常代码处生成一个异常类的对象,此对象满足throws后异常 * 类型时,就会被抛出。异常代码后续的代码,就不再执行! * * 2. 体会:try-catch-finally:真正的将异常给处理掉了。 * throws的方式只是将异常抛给了方法的调用者。 并没有真正将异常处理掉。 * * 3. 开发中如何选择使用try-catch-finally 还是使用throws? * 3.1 如果父类中被重写的方法没有throws方式处理异常,则子类重写的方法也不能使用throws,意味着如果 * 子类重写的方法中有异常,必须使用try-catch-finally方式处理。 * 3.2 执行的方法a中,先后又调用了另外的几个方法,这几个方法是递进关系执行的。我们建议这几个方法使用throws * 的方式进行处理。而执行的方法a可以考虑使用try-catch-finally方式进行处理。 * */ public class ExceptionTest2 { public static void main(String[] args){ try{ method2(); }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } // method3(); } public static void method3(){ try { method2(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void method2() throws IOException{ method1(); } public static void method1() throws FileNotFoundException,IOException{ File file = new File("hello1.txt"); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); int data = fis.read(); while(data != -1){ System.out.print((char)data); data = fis.read(); } fis.close(); System.out.println("hahaha!"); } }
package com.atguigu.java2; public class StudentTest { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Student s = new Student(); s.regist(-1001); System.out.println(s); } catch (Exception e) { // e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } } class Student{ private int id; public void regist(int id) throws Exception { if(id > 0){ this.id = id; }else{ // System.out.println("您输入的数据非法!"); //手动抛出异常对象 // throw new RuntimeException("您输入的数据非法!"); // throw new Exception("您输入的数据非法!"); throw new MyException("不能输入负数"); //错误的 // throw new String("不能输入负数"); } } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [id=" + id + "]"; } }
package com.atguigu.java2; /* * 如何自定义异常类? * 1. 继承于现有的异常结构:RuntimeException 、Exception * 2. 提供全局常量:serialVersionUID * 3. 提供重载的构造器 * */ public class MyException extends Exception{ static final long serialVersionUID = -7034897193246939L; public MyException(){ } public MyException(String msg){ super(msg); } }
package com.atguigu.java2; public class ReturnExceptionDemo { static void methodA() { try { System.out.println("进入方法A"); throw new RuntimeException("制造异常"); } finally { System.out.println("用A方法的finally"); } } static void methodB() { try { System.out.println("进入方法B"); return; } finally { System.out.println("调用B方法的finally"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { try { methodA(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } methodB(); } }
/*
进入方法A
用A方法的finally
制造异常
进入方法B
调用B方法的finally
*/
package com.atguigu.exer; /* * 编写应用程序EcmDef.java,接收命令行的两个参数,要求不能输入负数,计算两数相除。 对数据类型不一致(NumberFormatException)、缺少命令行参数(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException、 除0(ArithmeticException)及输入负数(EcDef 自定义的异常)进行异常处理。 提示: (1)在主类(EcmDef)中定义异常方法(ecm)完成两数相除功能。 (2)在main()方法中使用异常处理语句进行异常处理。 (3)在程序中,自定义对应输入负数的异常类(EcDef)。 (4)运行时接受参数 java EcmDef 20 10 //args[0]=“20” args[1]=“10” (5)Interger类的static方法parseInt(String s)将s转换成对应的int值。 如:int a=Interger.parseInt(“314”); //a=314; */ public class EcmDef { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ int i = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); int j = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); int result = ecm(i,j); System.out.println(result); }catch(NumberFormatException e){ System.out.println("数据类型不一致"); }catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ System.out.println("缺少命令行参数"); }catch(ArithmeticException e){ System.out.println("除0"); }catch(EcDef e){ System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } public static int ecm(int i,int j) throws EcDef{ if(i < 0 || j < 0){ throw new EcDef("分子或分母为负数了!"); } return i / j; } }
package com.atguigu.exer; //自定义异常类 public class EcDef extends Exception { static final long serialVersionUID = -33875164229948L; public EcDef() { } public EcDef(String msg) { super(msg); } }