1.MultiType简单介绍
1.1.MultiType用于比较复杂的页面。
如下图,今日头条用到了MultiType处理各种复杂的页面。
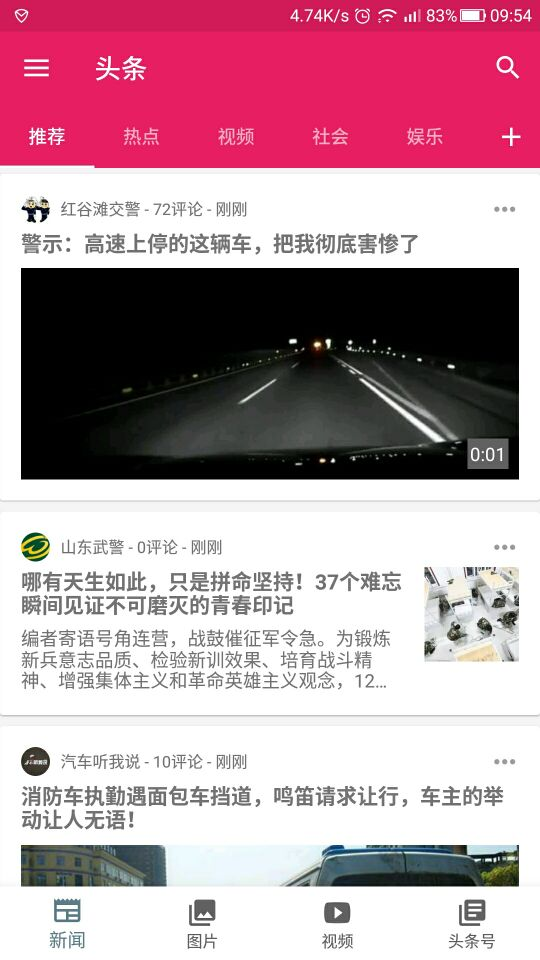

这种还是比较简单的类型。因为一个页面也就这种类型。
下面看看这个页面。

这个就比较复杂了,所以这时候MultiType的作用就体现出来了。
一个页面用一个单独的RecyclerView就可以实现。
再比如微博列表页面:
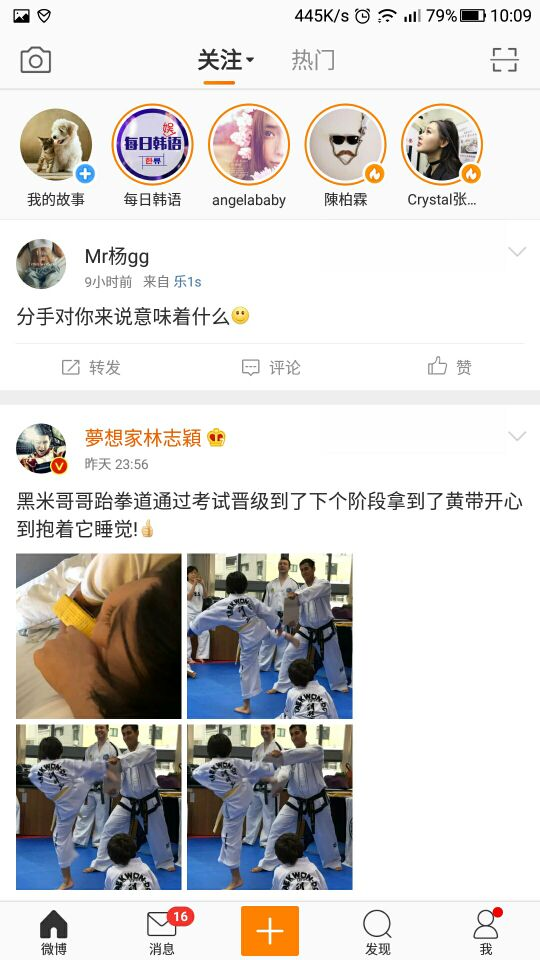

有纯文本的、代转发原文的,带图片的、带视频的、带文章的等等,甚至穿插一条可以横向滑动的好友推荐条目。
不同的item类型众多,而且随着业务发展,还会更多。
如果我们使用传统的开发方式,经常要做一些繁琐的工作,代码可能都堆积在一个Adapter中,我们需要复写
RecyclerView.Adapter的getItemViewType方法,罗列一些type整型常量,并且ViewHolder转型、绑定数据
也比较麻烦。
一旦产品需求有变,或者产品设计需要增加一种新的item类型,我们需要去代码堆里找到我们原来的逻辑去修改,
或者找到正确的位置去增加代码。非常繁琐。
1.2.现在有了MultiType,简单来说,MultiType就是一个多类型列表视图的中间分发框架,它能帮助你快速并且清晰
地开发一些复杂的列表页面。它本是为聊天页面开发的,聊天页面的消息类型也是有大量不同种类,并且新增频繁
而MultiType能够轻松胜任,代码模块化,随时可扩展新的类型进入列表当中。它内建了类型-View的复用池系统,
支持RecyclerView,使用简单灵活,令代码清晰,适应需求变化。
1.3.MultiType也能轻松实现如下页面。
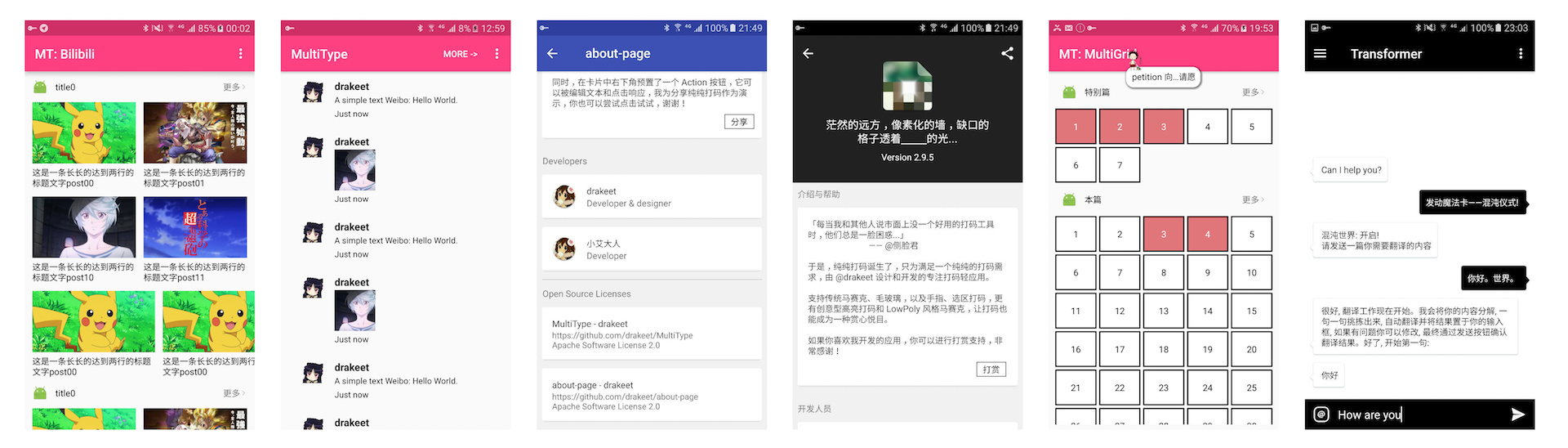
在github中有相关页面介绍。
2.基本使用方法
2.1.引入MultiType==>在build.gradle中加入:
dependencies { compile 'me.drakeet.multitype:multitype:3.3.0' }
注意:MultiType不支持低于23.0.0的RecyclerView,不过现在基本都没有用那么低版本的RecyclerView了吧。
2.2.小贴士:
MultiType这个框架使用RecyclerView,但是不需要写adapter,需要些ItemViewBinder,这是框架里面定义
的一个类。在多Type的情况下,每一种item对应一个数据模型(一个bean类)+一个ItemViewBinder。
2.3.新建一个数据模型bean
public class Title { public String title; public String url; }
2.4.新建一个类==>继承ItemViewBinder的一个绑定类。
public class TitleViewBinder extends ItemViewBinder<Title, TitleViewBinder.TitleHolder> { @NonNull @Override protected TitleHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater,
@NonNull ViewGroup parent) { View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.layout_title, parent, false); return new TitleHolder(view); } @Override protected void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull TitleHolder holder, @NonNull Title item) { //填充数据渲染页面,比如setText setImage等工作 } static class TitleHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder { ImageView imageView; TextView textView; TitleHolder(View itemView) { super(itemView); imageView = (ImageView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.iv_title); textView = (TextView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.tv_title); } } }
这里R.layout.layout_title,就是定义布局资源,要加载这个布局。
这个布局中有R.id_iv_title+R.id_tv_title。
返回的是一个自定义的视图持有者==>TitleHolder
这个视图持有者是定义在这个视图绑定类里面的类部类。
2.5.最后一步==>注册绑定。
在Activity中将类和ItemViewBinder注册绑定。
其余的工作就和普通的RecyclerView一样。
因为MultiType使用了自己的adapter==>MultiTypeAdapter,在里面填充的数据列表应该是List<Object>
这里就根据自己的需求来设置这个Object类(就是自己定义Bean类)。
public class MainActivtiy extends AppCompatActivity { RecyclerView rv_design; List<Object> list; private MultiTypeAdapter adapter; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_new_design); rv_design = (RecyclerView) findViewById(R.id.rv_design); rv_design.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this)); adapter = new MultiTypeAdapter(); adapter.register(Title.class, new TitleViewBinder()); rv_design.setAdapter(adapter); list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new Title());//模拟的初始化数据,伪代码 adapter.setItems(list); adapter.notifyDataSetChanged(); }
活动的布局为==>R.layout.activity_new_design
活动里面的RecyclerView==>R.id.rv_design
RecyclerView设置布局管理器
新建一个MultiTypeAdapter()适配器
将MultiTypeAdapter注册Bean+绑定类(Object+继承ItemViewBinder类)
RecyclerView设置这个MultiTypeAdapter适配器。
新建一个ArrayList<>()
这个ArrayList用自定义的Bean类填充。
将MultiTypeAdapter适配器来设置数据,adapter.setItems(list)
最后调用MultiTypeAdapter的刷新方法。
3.以一个复杂页面为例
3.1.例子来源于简书:MultiType的基本使用和复杂页面的写法实例。
3.2.需要实现的页面:
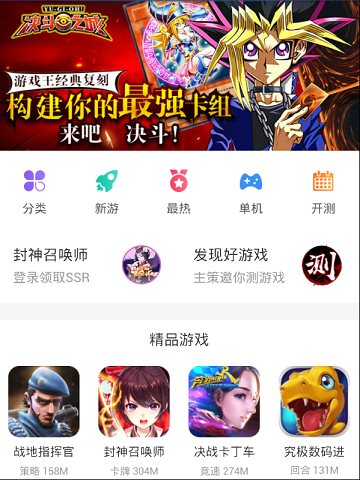
3.3.布局分析:
第一行是一个横屏大图。
第二行是5个分类的入口。
第三块是2个入口。
.................
怎么写这个布局呢?
第一行作为一个Item
第二行5个入口作为5个Item
第三行2个入口作为2个Item
如何将第一行的一个Item的排列转接到第二行的5个item转接到第三行的2个Item呢?
3.4.关键实现技术
这里使用了GridLayoutManager。
其实GridLayoutManager和LinearLayoutManager是差不多的,最大的区别就是其中的getSpanSize方法。
GridLayoutManager的构造方法是:
GridLayoutManager layoutManager = new GridLayoutManager(this, total);
其中total是一行的网格个数。
所以可以利用getSpanSize方法动态改变total的大小。如下面的代码:
/**每一行占的个数不固定的例子 * 比如有一行1个,5个,2个 同时存在 * 全部相乘是10 * 第一种 SpanSize=10/1 * 第二种 SpanSize=10/5 * 第三种 SpanSize=10/2 * 为什么呢?因为要保证10/1 10/5 10/2 都是整数。 */ GridLayoutManager layoutManager = new GridLayoutManager(this, 10);//10=1*5*2 layoutManager.setSpanSizeLookup(new GridLayoutManager.SpanSizeLookup() { @Override public int getSpanSize(int position) { if (list.get(position) instanceof Title) { return 10/1;//一行占1个 } if (list.get(position) instanceof Ad) { return 10/5;//一行占5个 } if (list.get(position) instanceof EmptyValue) { return 10/2;//一行占2个 } return 10;//默认一行占1个 } });
如果拿到了list数据,然后判断当前的list中的当前项的类型是什么(这个类型就是我们之前定义的Bean类)。
所以这里可以将所有的Bean冗杂在一起,然后这里判断是哪个类型,再选择不同入口就行了。
3.5.如果要求一对多,就是如果就是第一行有时候要标题或者分割线怎么办?
这里假设我们的需求不确定,就是第一行有时候要标题,有时候要分割线。
处理方式==>参考这篇文章:一个类型对应多个ItemViewBinder。
在注册Bean类的时候就只用一个空类,我们暂且叫做EmptyValue。它可以对应我们需要的多种类型。
从某个角度,有点像泛型了。
写法如下:
adapter.register(EmptyValue.class) .to(new GoodTitleViewBinder(), new LineViewBinder()) .withClassLinker(new ClassLinker<EmptyValue>() { @NonNull @Override public Class<? extends ItemViewBinder<EmptyValue, ?>>
index(@NonNull EmptyValue emptyValue) { if (emptyValue.type == EmptyValue.TYPE_GOODTITLE) { return GoodTitleViewBinder.class; } if (emptyValue.type == EmptyValue.TYPE_LINE) { return LineViewBinder.class; } return LineViewBinder.class; } });
这里使用emptyVaule.type来应对不同的类型。
我们在一对多的时候需要区分这个Item是标题还是分割线。
/** * EmptyValue * 占一整行而无数据的类型,适用于分割线、写死的标题等等。 */ public class EmptyValue { public static final int TYPE_GOODTITLE = 1; public static final int TYPE_LINE = 2; public int type; public EmptyValue(int type) { this.type = type; } }
3.6.效果预览

3.7.分析代码

加入的测试数据:
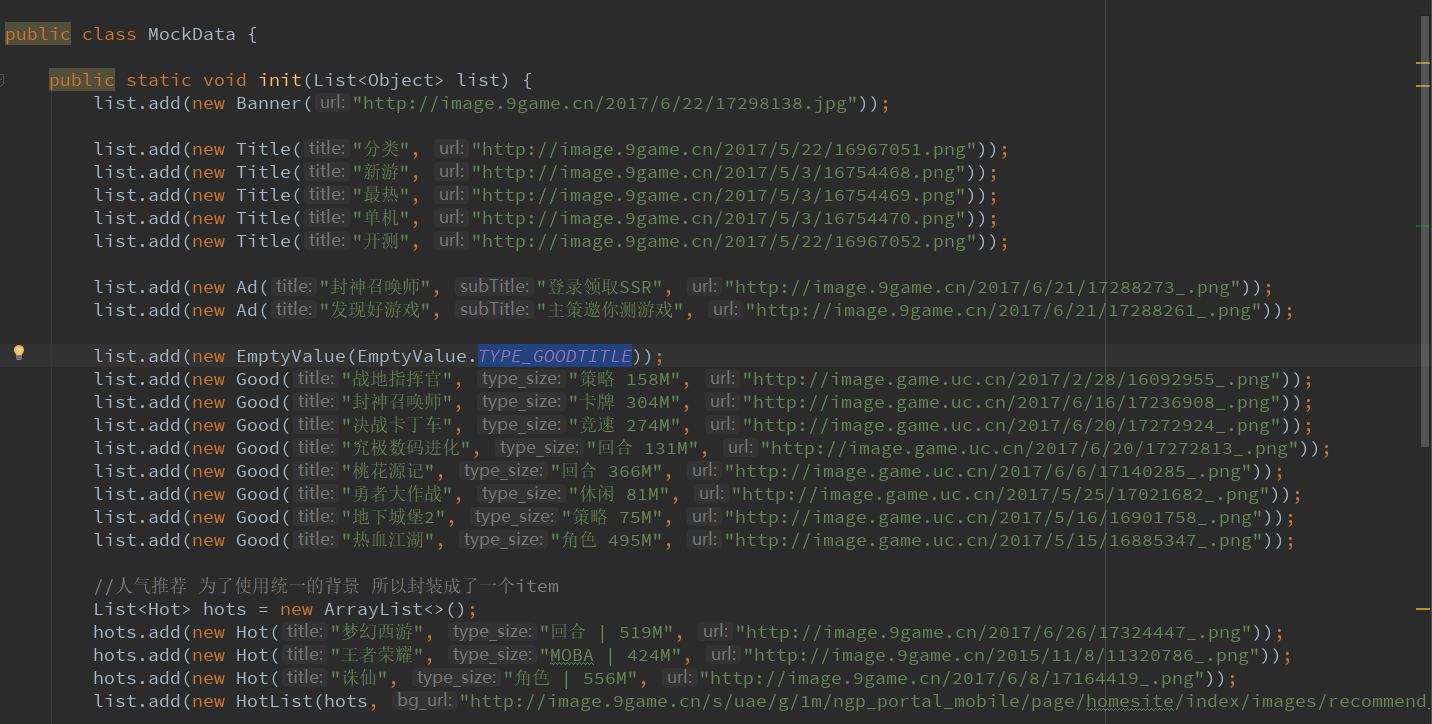
关键主活动代码:

public class NewDesignActivity extends AppCompatActivity { RecyclerView rv_design; List<Object> list; private MultiTypeAdapter adapter; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_new_design); rv_design = (RecyclerView) findViewById(R.id.rv_design); final int num_banner = 1; final int num_title = 5; final int num_ad = 2; final int num_good_title = 1; final int num_good = 4; final int num_hot = 1; final int num_main_game = 1; final int num_new_title = 1; final int num_new_game = 2; int[] types = new int[]{num_banner, num_title, num_ad, num_good_title, num_good, num_hot}; final int total = MockData.getTotal(types); /**每一行占的个数不固定的例子 * 比如有一行1个,5个,2个 同时存在 * 全部相乘是10 * 第一种 SpanSize=10/1 * 第二种 SpanSize=10/5 * 第三种 SpanSize=10/2 * 为什么呢?因为要保证10/1 10/5 10/2 都是整数。 */ GridLayoutManager layoutManager = new GridLayoutManager(this, total); layoutManager.setSpanSizeLookup(new GridLayoutManager.SpanSizeLookup() { @Override public int getSpanSize(int position) { if (list.get(position) instanceof Title) { return total / num_title; } if (list.get(position) instanceof Ad) { return total / num_ad; } if (list.get(position) instanceof EmptyValue) { return total / num_good_title; } if (list.get(position) instanceof Good) { return total / num_good; } if (list.get(position) instanceof HotList) { return total / num_hot; } if (list.get(position) instanceof MainGame) { return total / num_main_game; } return total; } }); rv_design.setLayoutManager(layoutManager); adapter = new MultiTypeAdapter(); adapter.register(Banner.class, new BannerViewBinder()); adapter.register(Title.class, new TitleViewBinder()); adapter.register(Ad.class, new ADViewBinder()); adapter.register(EmptyValue.class) .to(new GoodTitleViewBinder(), new LineViewBinder()) .withClassLinker(new ClassLinker<EmptyValue>() { @NonNull @Override public Class<? extends ItemViewBinder<EmptyValue, ?>> index(@NonNull EmptyValue emptyValue) { if (emptyValue.type == EmptyValue.TYPE_GOODTITLE) { return GoodTitleViewBinder.class; } if (emptyValue.type == EmptyValue.TYPE_LINE) { return LineViewBinder.class; } return LineViewBinder.class; } }); adapter.register(Good.class, new GoodViewBinder()); adapter.register(HotList.class, new HotViewBinder()); adapter.register(MainGame.class, new MainGameViewBinder()); rv_design.setAdapter(adapter); list = new ArrayList<>(); MockData.init(list); adapter.setItems(list); adapter.notifyDataSetChanged(); } }
图解:

4.今日头条真实案例
4.1.今日头条的段子页面布局为:R.item_joke_content.

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <android.support.v7.widget.CardView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginBottom="4dp" android:layout_marginTop="4dp" android:background="@color/viewBackground" app:cardElevation="1dp"> <RelativeLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="?attr/selectableItemBackground" android:foreground="?attr/selectableItemBackground" android:orientation="vertical" android:padding="16dp"> <LinearLayout android:id="@+id/header" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal"> <com.jasonjan.headnews.widget.CircleImageView android:id="@+id/iv_avatar" android:layout_width="22dp" android:layout_height="22dp" android:layout_gravity="center"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_username" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:layout_marginLeft="8dp" android:layout_marginStart="8dp" android:ellipsize="end" android:maxLength="30" android:maxLines="1" android:textAppearance="@style/TextAppearance.AppCompat.Caption" tools:text="小恢恢的帽子"/> <RelativeLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_dots" android:layout_width="22dp" android:layout_height="22dp" android:layout_alignParentEnd="true" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:padding="4dp" android:scaleType="center" app:srcCompat="@drawable/ic_dots_horizontal_grey500_24dp" tools:ignore="ContentDescription"/> </RelativeLayout> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/header" android:layout_marginTop="4dp" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_text" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" tools:text="昨天和闺蜜出去逛街,闺密问她老公要钱,她老公坐在沙发上,翘着二郎腿抽着烟问:“20行吗?”闺密想了想,温柔的点点头,我正惊讶她老公能把她管制的服服贴贴,只见她老公从钱包里掏出20,然后把钱包递给了媳妇……"/> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="20dp" android:layout_gravity="bottom" android:layout_marginTop="6dp" android:gravity="bottom" android:orientation="horizontal"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_digg_count" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" tools:text="53"/> <ImageView android:layout_width="16dp" android:layout_height="16dp" android:layout_marginLeft="4dp" android:layout_marginStart="4dp" app:srcCompat="@drawable/ic_like_gray_24dp" tools:ignore="ContentDescription"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_bury_count" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginLeft="16dp" android:layout_marginStart="16dp" tools:text="11"/> <ImageView android:layout_width="16dp" android:layout_height="16dp" android:layout_marginLeft="4dp" android:layout_marginStart="4dp" app:srcCompat="@drawable/ic_dislike_gray_24dp" tools:ignore="ContentDescription"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_comment_count" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:gravity="end" tools:text="48评论"/> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout> </RelativeLayout> </android.support.v7.widget.CardView>
预览图+实际预览图


4.2.段子视图绑定==>JokeContentViewBinder
逻辑处理都在这里面进行。
包括什么点击事件啊,设置真实数据的显示情况啊。
这里就有可能用到很多图片加载的第三方库等,圆形图片等,不过都是一些显示问题了。
4.3.加载完毕所有视图绑定==>LoadingEndViewBinder
这里的布局很简单。也可以很复杂,有些做的花里胡哨的,都是这里做一些手脚的。
R.item_loading_end.xml==>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="48dp" android:layout_marginBottom="1dp" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:orientation="horizontal"> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:text="@string/no_more_content" android:textSize="16sp"/> </LinearLayout>
实图预览:

4.4.正在加载视图绑定==>LoadingViewBinder
这里正在加载的话,应该有一个进度条加载框(andorid自带的是PregressBar)
这里的布局文件为:R.layout.item_loading==>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="48dp" android:layout_marginBottom="1dp" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:orientation="horizontal"> <ProgressBar android:id="@+id/progress_footer" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:visibility="visible"/> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_marginLeft="16dp" android:layout_marginStart="8dp" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:text="@string/loading"/> </LinearLayout>
预览图片为:

4.5.在段子页面==>JokeContentView执行如下代码:
@Override protected void initView(View view) { super.initView(view); adapter = new MultiTypeAdapter(oldItems); Register.registerJokeContentItem(adapter); recyclerView.setAdapter(adapter); recyclerView.addOnScrollListener(new OnLoadMoreListener() { @Override public void onLoadMore() { if(NetWorkUtil.isNetworkConnected(InitApp.AppContext)){ if (canLoadMore) { canLoadMore = false; presenter.doLoadMoreData(); } }else{ presenter.doShowNetError(); } } }); }
这里监听了recyclerView是否滑动最低端了,用处理器的doLoadMoreData方法来加载下一页。
这里注册的类型,自己封装了一个类Register。
public class Register { public static void registerJokeContentItem(@NonNull MultiTypeAdapter adapter) { adapter.register(JokeContentBean.DataBean.GroupBean.class, new JokeContentViewBinder()); adapter.register(LoadingBean.class, new LoadingViewBinder()); adapter.register(LoadingEndBean.class, new LoadingEndViewBinder()); } }
如果当前页面可见的话,将会执行fetchData方法,这个是懒加载碎片中定义的一个抽象方法。
执行了onLoadData()方法来
@Override public void onLoadData() { onShowLoading(); presenter.doLoadData(); }
先展示加载框。
然后用处理器的一个doLoadData()方法来加载数据。
所以这个处理器中一定有一个适配器,而且就是这里面定义的适配器。
所以进入JokeContentPresenter处理器中,发现这里面并没有前面定义adapter啊!
但是这里数据在处理器中加载完毕,相当于执行了一个回调,到JokeContentView中的onSetAdapter中添加。
@Override public void doLoadData(){ if(NetWorkUtil.isNetworkConnected(InitApp.AppContext)) { //这里需要更改!!! Map<String, String> map = ToutiaoUtil.getAsCp(); RetrofitFactory.getRetrofit().create(IJokeApi.class).getJokeContent(time, map.get(Constant.AS), map.get(Constant.CP)) .subscribeOn(Schedulers.io()) .map(new Function<JokeContentBean, List<JokeContentBean.DataBean.GroupBean>>() { @Override public List<JokeContentBean.DataBean.GroupBean> apply(@NonNull JokeContentBean jokeContentBean) throws Exception { List<JokeContentBean.DataBean> data = jokeContentBean.getData(); for (JokeContentBean.DataBean dataBean : data) { groupList.add(dataBean.getGroup()); } time = jokeContentBean.getNext().getMax_behot_tim() + ""; return groupList; } }) .compose(view.<List<JokeContentBean.DataBean.GroupBean>>bindToLife()) .observeOn(AndroidSchedulers.mainThread()) .subscribe(new Consumer<List<JokeContentBean.DataBean.GroupBean>>() { @Override public void accept(@NonNull List<JokeContentBean.DataBean.GroupBean> groupBeen) throws Exception { if (groupBeen.size() > 0) { doSetAdapter(); } else { doShowNoMore(); } } }, ErrorAction.error()); }else{ doShowNetError(); } }
这是主要加载数据的方法。将所有数据放到一个groupList中。
然后执行doSetAdapter回调方法。
@Override public void doSetAdapter(){ view.onSetAdapter(groupList); view.onHideLoading(); }
这里调用了一个接口的方法,所以必然要在JokeContentView中实现这个接口,才有这个回调。
@Override public void onSetAdapter(List<?> list) { Items newItems = new Items(list); newItems.add(new LoadingBean()); DiffCallback.notifyDataSetChanged(oldItems, newItems, DiffCallback.JOKE, adapter); oldItems.clear(); oldItems.addAll(newItems); canLoadMore = true; }
这里先将 list保存到一个newItems,就是从API请求到的数据。
这里将新增的Items动态添加在oldItems中,执行了一个DiffCallback自定义类来添加。
最后将oldItems重写。
设置canLoadMore为true。
这个oldItems定义在BaseListFragment中。
protected Items oldItems = new Items();
@Override public void onShowNoMore() { getActivity().runOnUiThread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { if (oldItems.size() > 0) { Items newItems = new Items(oldItems); newItems.remove(newItems.size() - 1); newItems.add(new LoadingEndBean()); adapter.setItems(newItems); adapter.notifyDataSetChanged(); } else if (oldItems.size() == 0) { oldItems.add(new LoadingEndBean()); adapter.setItems(oldItems); adapter.notifyDataSetChanged(); } canLoadMore = false; } }); }
如果没有更多了,要先判断一下。
如果之前没有数据,直接在尾巴加一个LoadingEndBean。
如果之前有数据,先移除最后一个数据,将一个LoadingEndBean加到尾巴。
最后将canLoadMore为false。
其实这里是处理没有更多的情况。
5.自定义DiffUtil简单用法
5.1..如何利用DiffCallback将adapter填充了Items数据的?
参考文章:Android详解7.0带来的新工具类DiffUtil。
用处:在RecyclerView刷新时,不再无脑adapter.notifyDataSetChanged()。
RecyclerVIew刷新不会触发RecyclerView的动画(删除、新增、位移、change动画)
性能较低,毕竟是无脑的刷新了一遍整个RecyclerView,极端情况下,新老数据集一样,效率最低。
它会自动计算新老数据集的差异,并根据差异情况,自动调用以下四个方法。
adapter.notifyItemRangeInserted(position, count);
adapter.notifyItemRangeRemoved(position, count);
adapter.notifyItemMoved(fromPosition, toPosition);
adapter.notifyItemRangeChanged(position, count, payload);
实现增量更新效果。
5.2.仅仅需要额外编写一个Callback回调类。
它的意义是:定义了一些用来比较新老Item是否相等的契约(Contract)、规则(Rule)的类。
DiffUtil.Callback抽象类如下:
public abstract static class Callback { public abstract int getOldListSize();//老数据集size public abstract int getNewListSize();//新数据集size //新老数据集在同一个postion的Item是否是一个对象?(可能内容不同,如果这里返回true,会调用下面的方法) public abstract boolean areItemsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition); //这个方法仅仅是上面方法返回ture才会调用,我的理解是只有notifyItemRangeChanged()才会调用,判断item的内容是否有变化 public abstract boolean areContentsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition); //该方法在DiffUtil高级用法中用到 ,暂且不提 @Nullable public Object getChangePayload(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) { return null; } }
5.3.以某个项目的DiffCallback为例。

public class DiffCallback extends DiffUtil.Callback { public static final int JOKE = 1; private List oldList, newList; private int type; public DiffCallback(List oldList, List newList, int type) { this.oldList = oldList; this.newList = newList; this.type = type; } public static void notifyDataSetChanged(List oldList, List newList, int type, RecyclerView.Adapter adapter) { DiffCallback diffCallback = new DiffCallback(oldList, newList, type); DiffUtil.DiffResult result = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(diffCallback, true); result.dispatchUpdatesTo(adapter); } @Override public int getOldListSize() { return oldList != null ? oldList.size() : 0; } @Override public int getNewListSize() { return newList != null ? newList.size() : 0; } @Override public boolean areItemsTheSame(int oldItemPosition,int newItemPosition){ try{ switch(type){ case JOKE: return ((JokeContentBean.DataBean.GroupBean) oldList.get(oldItemPosition)).getContent().equals( ((JokeContentBean.DataBean.GroupBean) newList.get(newItemPosition)).getContent()); } }catch(Exception e){ } return false; } @Override public boolean areContentsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) { try { switch (type) { case JOKE: return ((JokeContentBean.DataBean.GroupBean) oldList.get(oldItemPosition)).getShare_url().equals( ((JokeContentBean.DataBean.GroupBean) newList.get(newItemPosition)).getShare_url()); } } catch (Exception e) { } return false; } }
具体分析:
构造函数不用多说,一个老的List,一个新的List,一个类型。
public DiffCallback(List oldList, List newList, int type) { this.oldList = oldList; this.newList = newList; this.type = type; }
为什么要传入一个类型呢?==>因为这里可能数据很多,类型也很多,所以先设置type铺垫一下。
然后是一个静态函数,供外部调用。
public static void notifyDataSetChanged(List oldList, List newList, int type,
RecyclerView.Adapter adapter) { DiffCallback diffCallback = new DiffCallback(oldList, newList, type); DiffUtil.DiffResult result = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(diffCallback, true); result.dispatchUpdatesTo(adapter); }
耦合度非常低,外部只需要传入两个List,一个自己自愿加的type,一个关键的adapter。
所以外部调用这个方法后,会执行这个抽象函数DiffCallback(oldList,newList,type)。
DiffUtil.DiffResult result=DiffUtil.calculateDiff(diffCallback,true)怎么理解呢?==>
在将newDatas 设置给Adapter之前,先调用DiffUtil.calculateDiff()方法,
计算出新老数据集转化的最小更新集,就是DiffUtil.DiffResult对象。
DiffUtil.calculateDiff()方法定义如下:
第一个参数是DiffUtil.Callback对象,
第二个参数代表是否检测Item的移动,改为false算法效率更高,按需设置,我们这里是true。
result.dispatchUpdatesTo(adapter)怎么理解呢?
利用DiffUtil.DiffResult对象的dispatchUpdatesTo()方法,传入RecyclerView的Adapter,
替代普通青年才用的mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged()方法。
查看源码可知,该方法内部,就是根据情况调用了adapter的下面的四大定向刷新方法。
public void dispatchUpdatesTo(final RecyclerView.Adapter adapter) { dispatchUpdatesTo(new ListUpdateCallback() { @Override public void onInserted(int position, int count) { adapter.notifyItemRangeInserted(position, count); } @Override public void onRemoved(int position, int count) { adapter.notifyItemRangeRemoved(position, count); } @Override public void onMoved(int fromPosition, int toPosition) { adapter.notifyItemMoved(fromPosition, toPosition); } @Override public void onChanged(int position, int count, Object payload) { adapter.notifyItemRangeChanged(position, count, payload); } }); }
关于重写的areItemsTheSame(int oldItemPosition,int newItemPosition)方法的理解。
/** * 被DiffUtil调用,用来判断 两个对象是否是相同的Item。 * 例如,如果你的Item有唯一的id字段,这个方法就 判断id是否相等。 * 本例判断name字段是否一致,不一定全部是这样!!!! */ @Override public boolean areItemsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) { return mOldDatas.get(oldItemPosition).getName().equals
(mNewDatas.get(newItemPosition).getName()); }
关于重写的areContentsTheSame(int oldItemPositon,int newItemPosition)方法的理解。
/** * 被DiffUtil调用,用来检查 两个item是否含有相同的数据 * DiffUtil用返回的信息(true false)来检测当前item的内容是否发生了变化 * DiffUtil 用这个方法替代equals方法去检查是否相等。 * 所以你可以根据你的UI去改变它的返回值 * 例如,如果你用RecyclerView.Adapter 配合DiffUtil使用,你需要返回Item的视觉表现是否相同。 * 这个方法仅仅在areItemsTheSame()返回true时,才调用。 */ @Override public boolean areContentsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) { TestBean beanOld = mOldDatas.get(oldItemPosition); TestBean beanNew = mNewDatas.get(newItemPosition); if (!beanOld.getDesc().equals(beanNew.getDesc())) { return false;//如果有内容不同,就返回false } if (beanOld.getPic() != beanNew.getPic()) { return false;//如果有内容不同,就返回false } return true; //默认两个data内容是相同的 }
小贴士:
我一开始想找adapter在哪里设置数据的,因为DiffCallback只是比较差异,并没有自己将数据加载进去。
所以我找了半天都不知道这个方法在哪里。
后来,我发现,根本不用setDatas。
因为我用了MultiType第三方库,所以它自己有一个方法,率先将数据绑定到适配器了。
adapter = new MultiTypeAdapter(oldItems);
就是这个方法,oldItems变化的时候,adapter也随之添加了这个数据。
