两者思路对比:
直接操作:因为传入的是两个有序的链表,所以说我就直接以其中一个链表为基准,与另外一个链表比较,只将比返回值链表的最后一个记录的值大的插入,不将等值的插入,理论时间复杂度为O(n)
Set操作:将所有的节点取出放入TreeSet有序集合中,最后生成一个链表返回,理论时间复杂度为O(2n)
直接操作步骤示意图:
以{1,3,5}{1,2,4,5,5,6}为例
- 先取个返回值链表的表头,并将该链表作为基准链表,比较第一个值小的为基准链表,相同就取第一个
返回值链表:1->null
基准链表:3->5->null
非基准链表:1->2->4->5->5->6->null - 继续下一步后的链表,这一步中,取两个链表中的小值尝试插入,但是发现与返回值链表末端值相同就丢弃
返回值链表:1->null
基准链表:3->5->null
非基准链表:2->4->5->5->6->null - 继续下一步后的链表,这一步中,取两个链表中的小值尝试插入,但是发现与返回值链表末端值不同就插入
返回值链表:1->2->null
基准链表:3->5->null
非基准链表:4->5->5->6->null - 继续下一步后的链表,这一步中,取两个链表中的小值尝试插入,但是发现与返回值链表末端值不同就插入
返回值链表:1->2->3->null
基准链表:5->null
非基准链表:4->5->5->6->null - 继续下一步后的链表,这一步中,取两个链表中的小值尝试插入,但是发现与返回值链表末端值不同就插入
返回值链表:1->2->3->4->null
基准链表:5->null
非基准链表:5->5->6->null - 继续下一步后的链表,这一步中,取两个链表中的小值尝试插入,但是发现与返回值链表末端值不同就插入
返回值链表:1->2->3->4->5->null
基准链表:null
非基准链表:5->5->6->null - 其中一个链表为null之后直接只遍历另外一个链,因为要去重,所以要遍历完,取非基准链表中的一个值尝试插入,但是发现与返回值链表末端值相同就丢弃
返回值链表:1->2->3->4->5->null
基准链表:null
非基准链表:5->6->null - 取非基准链表中的一个值尝试插入,但是发现与返回值链表末端值相同就丢弃
返回值链表:1->2->3->4->5->null
基准链表:null
非基准链表:6->null - 取非基准链表中的一个值尝试插入,但是发现与返回值链表末端值不同就保留,此时两个链表都为null则结束
返回值链表:1->2->3->4->5->6null
基准链表:null
非基准链表:null
对于Set操作的算法则不展开
自己写的比较的算法:

import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Node headOne = new Node(-1); Node headTwo = new Node(-1); Node p1 = headOne; Node p2 = headTwo; int[] one = new int[10000]; int[] two = new int[15000]; Random rm = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++){ one[i] = rm.nextInt(500); } for (int i = 0; i < 15000; i++){ two[i] = rm.nextInt(500); } Arrays.sort(one); Arrays.sort(two); for (int i = 0; i < one.length; i++){ Node node = new Node(one[i]); p1.next = node; p1 = p1.next; } for (int i = 0; i < two.length; i++){ Node node = new Node(two[i]); p2.next = node; p2 = p2.next; } long start = System.nanoTime(); Node re = change(headOne.next, headTwo.next); long end = System.nanoTime(); System.out.println("直接操作:" + (end - start) + "ns"); start = System.nanoTime(); Node reSet = changeSet(headOne.next, headTwo.next); end = System.nanoTime(); System.out.println("Set时间: " + (end - start) + "ns"); } private static Node change(Node headOne, Node headTwo){ //空值判断 if (headTwo == null){ return headOne; } if (headOne == null){ return headTwo; } //返回首元素较小的头结点, 先取一个节点为基准 Node reHead = headOne.data <= headTwo.data? headOne: headTwo; Node p2 = headOne.data >= headTwo.data? headTwo: headOne; //另一条链 Node pre = reHead; //上一个节点 Node p1 = reHead.next; //当前链 while(p1 != null && p2 != null){ if(p1.data <= p2.data){ if (p1.data == p2.data){ p2 = p2.next; } if (p1.data != pre.data){ pre = pre.next; p1 = p1.next; }else{ pre.next = p1.next; //跳过该相同节点 p1 = p1.next; } }else{ if (p2.data != pre.data){ pre.next = p2; p2 = p2.next; pre = pre.next; pre.next = p1; }else { p2 = p2.next; } } } Node now = p1 != null? p1: p2; pre.next = now; while(now!= null){ if (pre.data == now.data){ now = now.next; pre.next = now; }else{ pre = pre.next; now = now.next; } } return reHead; } private static Node changeSet(Node headOne, Node headTwo){ Node re = new Node(-1); Node head = re; TreeSet<Node> s = new TreeSet<>(); while(headOne != null){ s.add(headOne); headOne = headOne.next; } while(headTwo != null){ s.add(headTwo); headTwo = headTwo.next; } Iterator iterator = s.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ Node p = (Node) iterator.next(); Node tmp = new Node(p.data); head.next = tmp; head = head.next; } return re.next; } } class Node implements Comparable{ int data; Node next; public Node(int data){ this.data = data; } @Override public int compareTo(Object o) { Node t = (Node)o; if (this.data > t.data){ return 1; }else if (this.data == t.data){ return 0; }else { return -1; } } }
然后运行的时间截图:
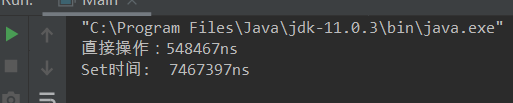
如有错误和不足,望指正
千里之行,始于足下
