
import numpy as np def blahut_arimoto(p_y_x: np.ndarray, log_base: float = 2, thresh: float = 1e-12, max_iter: int = 1e3) -> tuple: ''' Maximize the capacity between I(X;Y) p_y_x: each row represnets probability assinmnet log_base: the base of the log when calaculating the capacity thresh: the threshold of the update, finish the calculation when gettting to it. max_iter: the maximum iterations of the calculation ''' # Input test assert np.abs(p_y_x.sum(axis=1).mean() - 1) < 1e-6 assert p_y_x.shape[0] > 1 # The number of inputs: size of |X| m = p_y_x.shape[0] # The number of outputs: size of |Y| n = p_y_x.shape[1] # Initialize the prior uniformly r = np.ones((1, m)) / m # Compute the r(x) that maximizes the capacity for iteration in range(int(max_iter)): q = r.T * p_y_x q = q / np.sum(q, axis=0) r1 = np.prod(np.power(q, p_y_x), axis=1) r1 = r1 / np.sum(r1) tolerance = np.linalg.norm(r1 - r) r = r1 if tolerance < thresh: break # Calculate the capacity r = r.flatten() c = 0 for i in range(m): if r[i] > 0: c += np.sum(r[i] * p_y_x[i, :] * np.log(q[i, :] / r[i] + 1e-16)) c = c / np.log(log_base) return c, r
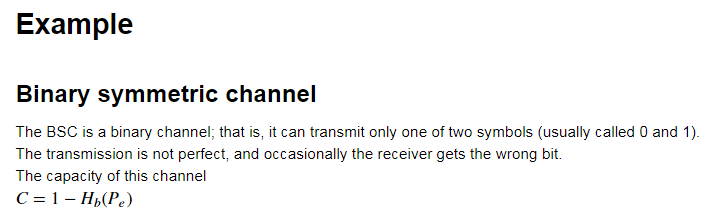
e = 0.2 p1 = [1-e, e] p2 = [e, 1-e] p_y_x = np.asarray([p1, p2]) C, r = blahut_arimoto(p_y_x) print('Capacity: ', C) print('The prior: ', r) # The analytic solution of the capaciy H_P_e = - e * np.log2(e) - (1-e) * np.log2(1-e) print('Anatliyic capacity: ', (1 - H_P_e))
输出为:
Capacity: 0.2780719051126379
The prior: [0.5 0.5]
Anatliyic capacity: 0.2780719051126377
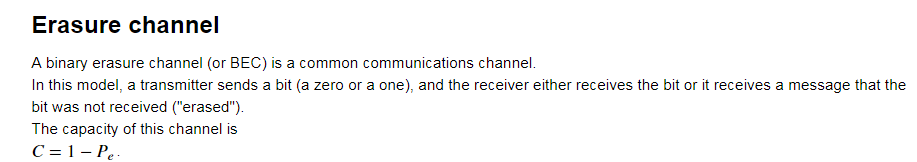
e = 0.1 p1 = [1-e, e, 0] p2 = [0, e, 1-e] p_y_x = np.asarray([p1, p2]) C, r = blahut_arimoto(p_y_x, log_base=2) print('Capacity: ', C) print('The prior: ', r) # The analytic solution of the capaciy print('Anatliyic capacity: ', (1 - e))
输出为:
Capacity: 0.9
The prior: [0.5 0.5]
Anatliyic capacity: 0.9

! jupyter nbconvert blahut_arimoto_algorithm.ipynb --to="python" --output-dir . #将jupyter notebook下的.ipynb文件另存为.py文件
完整实战代码为:

# 2019年11月9日17:01:21 import numpy as np def bluhat_arimoto(p_y_x: np.ndarray, thresh: float = 1e-12, max_iter: int = 1e3) -> tuple: ''' Maximize the capacity between I(X;Y) p_y_x: each row represnets probability assinmnet thresh: the threshold of the update, finish the calculation when gettting to it. max_iter: the maximum iterations of the calculation ''' # 检查输入是否符合要求 assert np.abs(p_y_x.sum(axis=1).mean() - 1) < 1e-6,'转移概率矩阵不符合要求' #axis=1表示矩阵每一行相加 .mean()表示矩阵所有元素的平均值 assert p_y_x.shape[0] > 1,'至少要有两个信源' # 信源信宿的个数 m = p_y_x.shape[0] #有 m 个信源 n = p_y_x.shape[1] #有 n 个信宿 # 初始化输入分布r(x)为等概分布 r = np.ones((1, m)) / m # Compute the r(x) that maximizes the capacity for iteration in range(int(max_iter)): Q = r.T * p_y_x Q = Q / np.sum(Q, axis=0) # Q的每一列相加 r1 = np.prod(np.power(Q, p_y_x), axis=1) #power(x, y),计算 x 的 y 次方; np.prod()计算数组元素乘积 r1 = r1 / np.sum(r1) tolerance = np.linalg.norm(r1 - r) #范数是一个标量,默认计算L2范数 r = r1 if tolerance < thresh: break # Calculate the capacity r = r.flatten() #将矩阵转化为一维数组 C = 0 for i in range(m): if r[i] > 0: C += np.sum(r[i] * p_y_x[i, :] * np.log2(Q[i, :] / r[i])) # 公式4.3.14 return C, r # e = 0.1 # p1 = [1-e, e, 0] # p2 = [0, e, 1-e] p1 = [0.5, 0.3, 0.2] p2 = [0.3, 0.5, 0.2] # p1 = [1/3, 1/3, 1/6, 1/6] # p2 = [1/6, 1/3, 1/6, 1/3] # p1 = [1/3, 1/3, 0, 1/3] # p2 = [0, 1/3, 1/3, 1/3] # p3 = [1/3, 0, 1/3, 1/3] # p1 = [1, 0, 0] # p2 = [0, 1/2, 1/2] # p3 = [0, 1/2, 1/2] # p1 = [1, 0, 0] # p2 = [0, 1, 0] # p3 = [0, 0, 1] # # p1 = [1/2, 1/2, 0, 0] # p2 = [0, 1/2, 1/2, 0] # p3 = [0, 0, 1/2, 1/2] # p4 = [1/2, 0, 0, 1/2] p_y_x = np.asarray([p1, p2]) print('信道转移概率矩阵P为: ') print('P = {} '.format(p_y_x)) C, r = bluhat_arimoto(p_y_x) print('信道容量为: {:.4f}bit/符号'.format(C)) print('输入分布r(x)为: ', r)
