大小堆是笔者接触过的关于操作系统的算法,现在再添加一个LRU,也是在任务调度方面常常遇到的。最近也在 InnoDB 的缓冲池中遇到了优化的 LRU,当然 redis 中淘汰机制也有
1. LUR
LRU(Least Recently Used)基于一种假设——最近最少使用,也就是说最近使用得少的数据,在未来使用到的几率也不大,那么当资源不够用时,就可以选择移除那些最近最少使用的数据
1.1 数据组织形式
我们将 Task(任务)使用双向链表连接起来,这样就明确了任务的时序关系(显示哪些最近使用与未使用)。而且当内存不够时就要将暂时不需要的数据移出,这就涉及到增删,增删使用双向链表的效率较高 O(1)。那么我们就可以创建一个 Node 节点来组成双向链表。其中key 为该任务的唯一标识,value 为具体的任务
class Node {
K key;
V value;
Node pre;
Node next;
}
1.2 数据查找效率
删除具体任务时需要将其查找出来然后才进行删除,双向链表的查找效率并不高O(N),说到查找我们可以利用哈希表,其查找效率为O(1)。结合哈希表和双向链表的形式其查找和增删的效率都为O(1)了,哈希表中的 key 就是任务的唯一标识,而 value 则为双向链表的 Node 节点
1.3 数据结构图
图里简化了 HashMap 的指向(有红黑树和拉链法的形式)
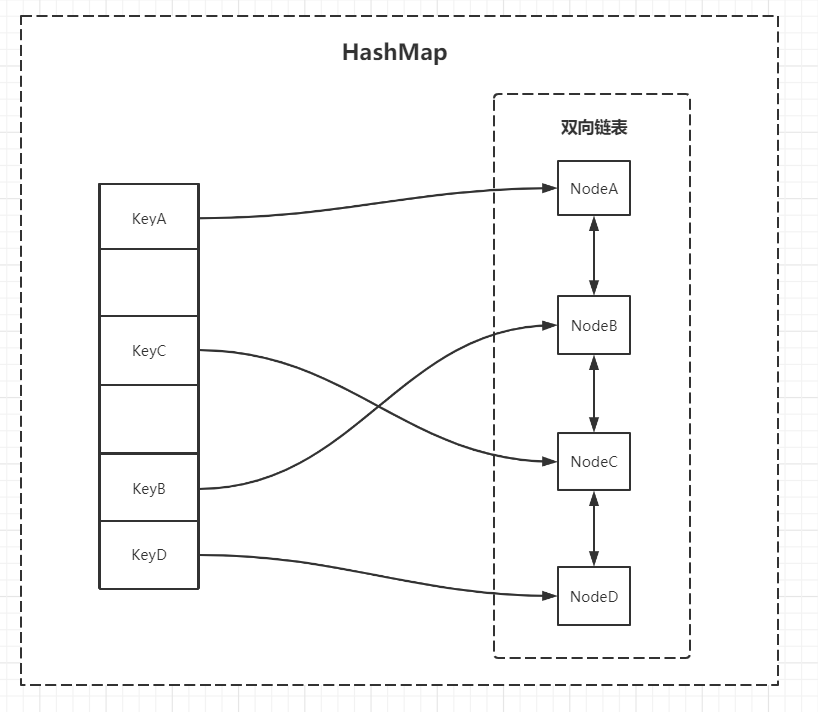
1.4 具体操作
新任务:任务不在 HashMap 中,直接加入到链表尾部
旧任务:任务在 HashMap中,通过哈希表找到该任务,并其在链表中删除,然后插入到链表头部
淘汰:判断限制资源条件(长度或内存),移除 HashMap 中的 key,再移除链表末尾的节点
2. 代码
public class LRUCache<K, V> {
private Long cacheSize; // 这里使用任务长度来限制资源
private Long currentSize;
private HashMap<K, Node> hashMap;
private Node first; // 链表头
private Node last; // 链表尾
/**
* 双向链表的节点,存放具体内容
* key为唯一标志
*/
class Node {
K key;
V value;
Node pre;
Node next;
}
/**
* 限制任务长度
*
* @param cacheSize
*/
public LRUCache(Long cacheSize) {
this.currentSize = 0L;
this.cacheSize = cacheSize;
hashMap = new HashMap<K, Node>();
}
/**
* 放入hashmap方便快速查找、放入双向链表记录时序
*
* @param key
* @param value
*/
public void put(K key, V value) {
Node node = hashMap.get(key);
if (node == null) {
if (size() >= cacheSize) {
hashMap.remove(last.key);
removeLast();
}
node = new Node();
node.key = key;
}
node.value = value;
moveToFirst(node);
hashMap.put(key, node);
if (size() < cacheSize) {
currentSize++;
}
// 下面是顺手打印
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Node pnode = first;
while (pnode != null) {
sb.append(String.format("%s:%s ", pnode.key, pnode.value));
pnode = pnode.next;
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
// 上面是顺手打印
}
/**
* 舍弃最近最久未使用,即链尾
*/
private void removeLast() {
if (last != null) {
last = last.pre;
if (last == null) {
first = null;
} else {
last.next = null;
}
}
}
/**
* 最近使用,移动到表头
*
* @param node
*/
private void moveToFirst(Node node) {
if (first == node) {
return;
}
if (node.next != null) {
node.next.pre = node.pre;
}
if (node.pre != null) {
node.pre.next = node.next;
}
if (node == last) {
last = last.pre;
}
if (first == null || last == null) {
first = last = node;
return;
}
node.next = first;
first.pre = node;
first = node;
first.pre = null;
}
/**
* 获取某个任务,任务调度
*
* @param key
* @returnV
*/
public V get(K key) {
Node node = hashMap.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
moveToFirst(node);
return node.value;
}
/**
* 移除
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public V remove(K key) {
Node node = hashMap.get(key);
if (node != null) {
if (node.pre != null) {
node.pre.next = node.next;
}
if (node.next != null) {
node.next.pre = node.pre;
}
if (node == first) {
first = node.next;
}
if (node == last) {
last = node.pre;
}
}
currentSize--;
return hashMap.remove(key).value;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return currentSize == 0;
}
public Long size() {
return this.currentSize;
}
/**
* 清空缓存
*/
public void clear() {
first = null;
last = null;
hashMap.clear();
currentSize = 0L;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
LRUCache lruCache = new LRUCache<>(3L);
lruCache.put(1, 1);
lruCache.put(2, 2);
lruCache.put(3, 3);
lruCache.put(4, 4);
lruCache.put(2, 2);
}
}
// 1:1
// 2:2 1:1
// 3:3 2:2 1:1
// 4:4 3:3 2:2
// 2:2 4:4 3:3
3. 基于内存限制
笔者还在想着基于内存怎么限制,刚好学着 Elasticsearch ,所以了解到 lucene
3.0 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.lucene</groupId>
<artifactId>lucene-core</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
3.1 初始化内存大小
public LRUCache(Long cacheSize) {
Long JMVCache = 0L;
if ((JMVCache = JVMUsebaleSize()) < cacheSize) {
System.out.println("JVM可用大小为:" + JMVCache);
System.out.println("当前设置为:" + cacheSize + ",但任然可用,超过内存即报错 OOM");
}
this.cacheSize = cacheSize;
hashMap = new HashMap<K, Node>();
}
/**
* 获取JVM可用内存大小,用于提示初始化 Cache 时可用内存不足
*
* @return 字节
*/
public Long JVMUsebaleSize() {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
long max = runtime.maxMemory();
long total = runtime.totalMemory();
long free = runtime.freeMemory();
return max - total + free;
}
3.2 获取实际占用大小
// getSizeof 获取的是对象本身内存大小,不包括内部属性指向的对象大小
// RamUsageEstimator.sizeOf() 包含内部属性指向,lucene-core4.0.0之前才有这个方法
public Long size() {
return RamUsageEstimator.sizeOf(this);
}
3.3 使用百分比
public String userPercent() {
new DecimalFormat("0.00");
return (size() / 1.0 / this.cacheSize) * 100 + "%";
}
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/wangxilong1991/article/details/70172302